
International Atomic Energy Agency
Wagramer Strasse 5, P.O.Box 100, A-1400 Vienna, Austria
Tel:(+43 1) 2600-21714; Fax:(+43 1) 26007
NGATLAS
Atlas of neutron capture cross sections
Prepared by
J.Kopecky
Contributions by
J.-Ch.Sublet, J.A.Simpson, R.A.Forrest and D.Nierop
Web Design and Plots by
V.Zerkin
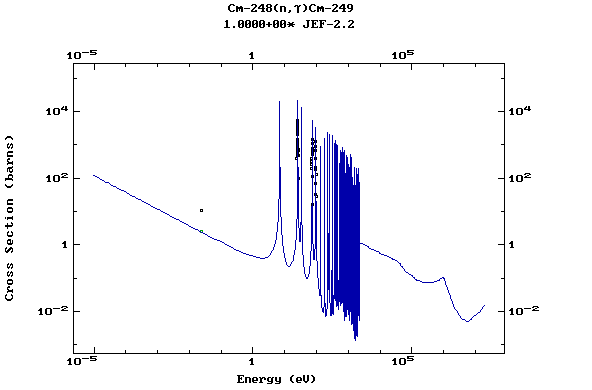
The NGATLAS contains neutron capture cross sections in the range
10-5eV - 20MeV as evaluated and compiled in recent activation
libraries. Numerical values of (n,g) cross sections are
available for a total of 739 targets for the elements
H (Z=1, A=1) to Cm (Z=96, A=248) totaling 972 reactions.
Plots of the pointwise data and comparisons
with the available experimental values at thermal energy, 30 keV
and 14.5 MeV can be found in the Report INDC(NDS)-362 (IAEA,
Vienna 1997) available upon request from the IAEA Nuclear Data
Section.
Z=1, H
(Hydrogen)

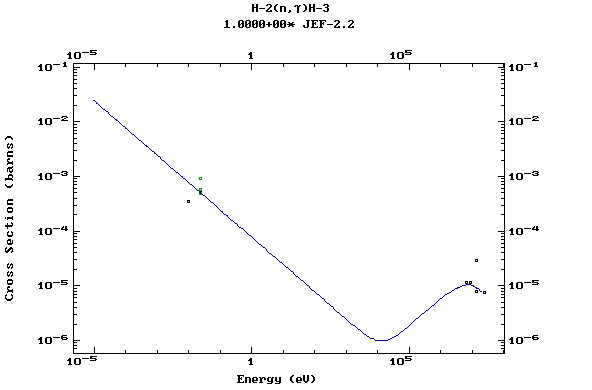
Z=2, He
(Helium)
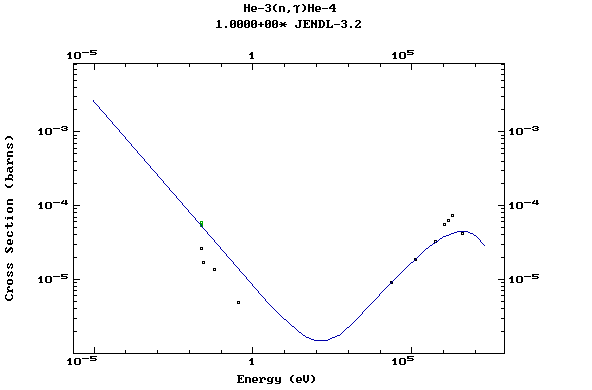
Z=3, Li
(Lithium)
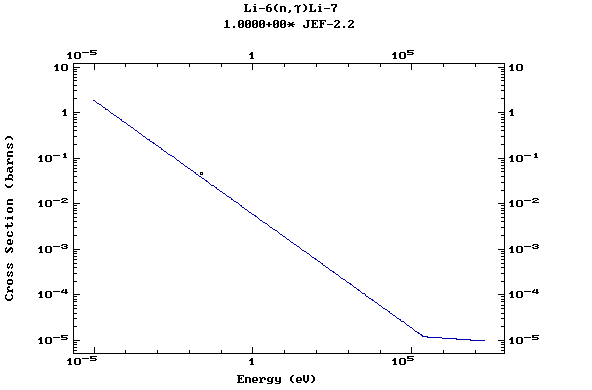
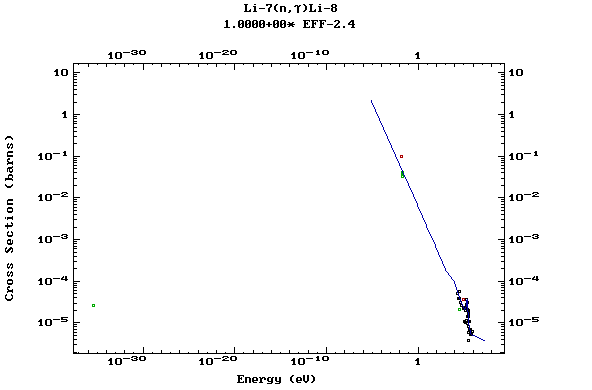
Z=4, Be
(Berylium)
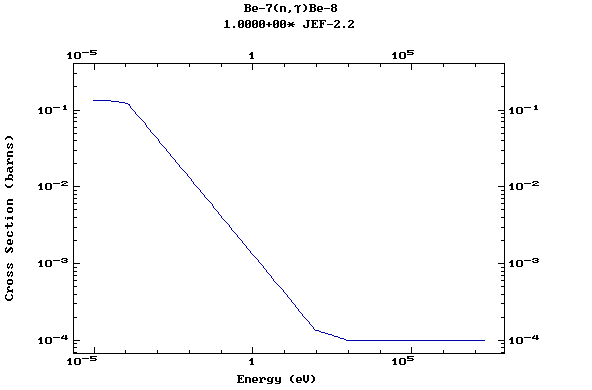
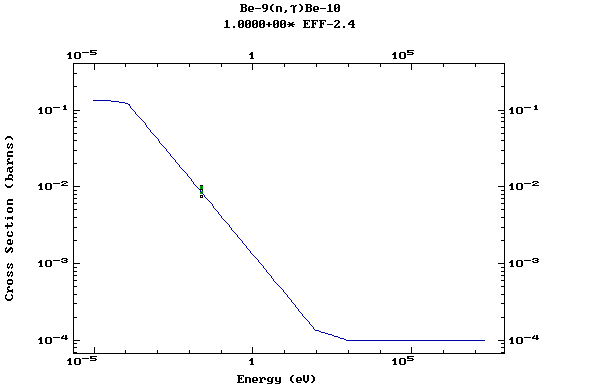
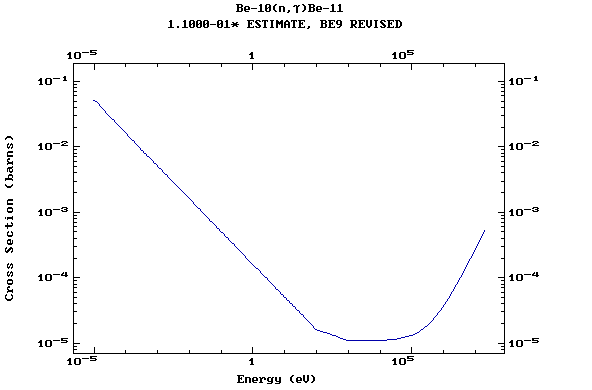
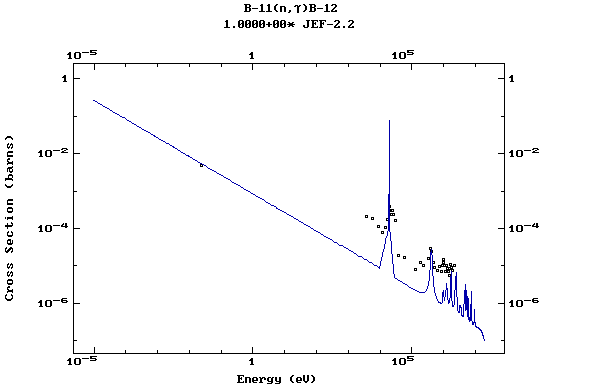
Z=5, B
(Boron)
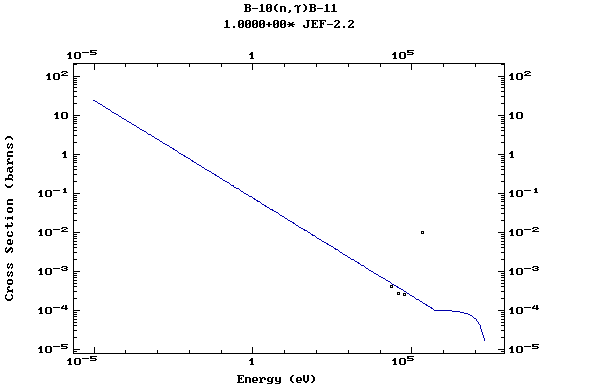
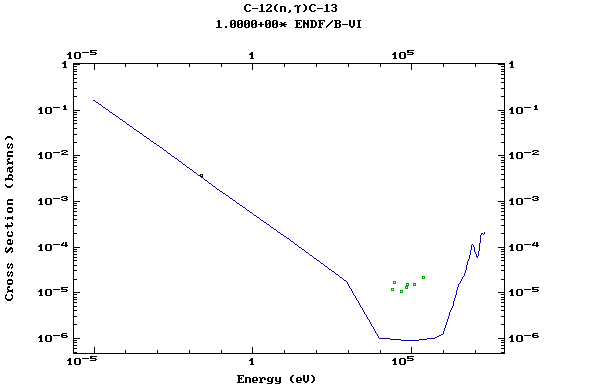
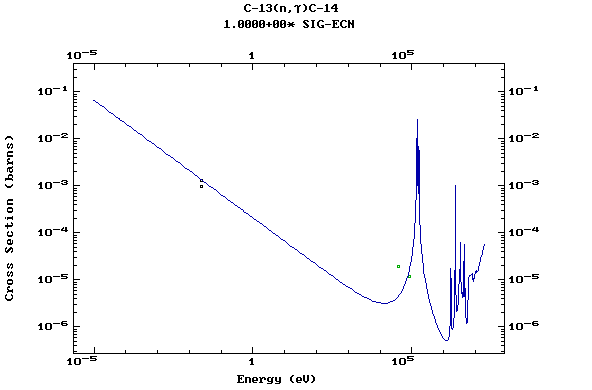
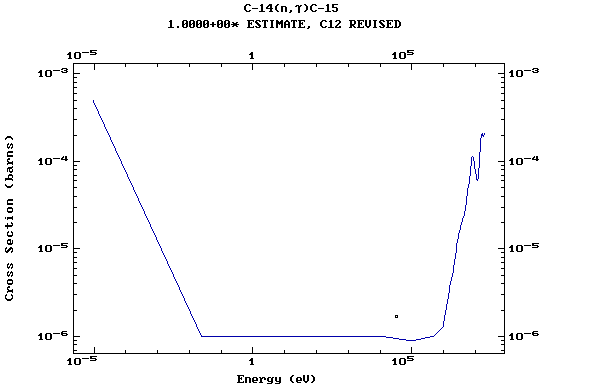
Z=6, C
(Carbon)
Z=7, N
(Nitrogen)
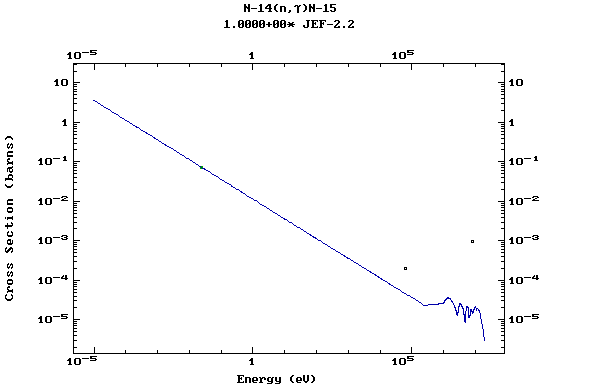
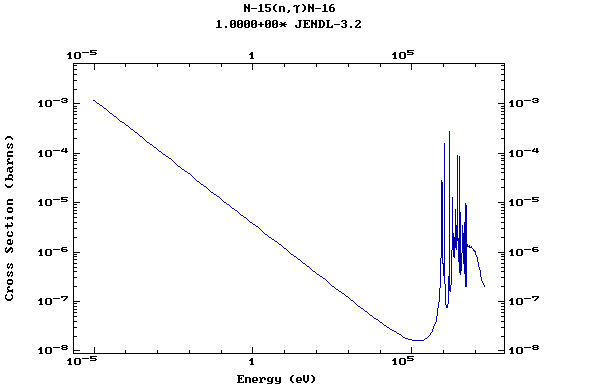
Z=8, O
(Oxygen)
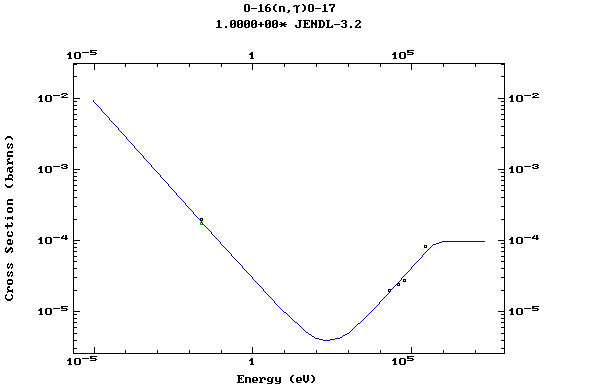
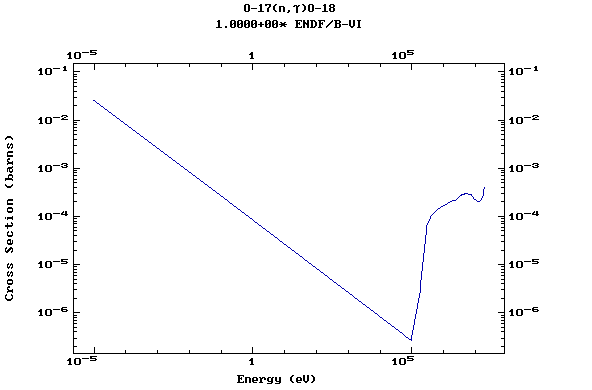
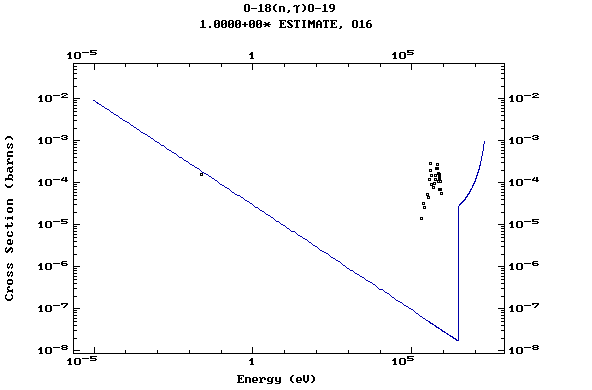
Z=9, F
(Fluorine)
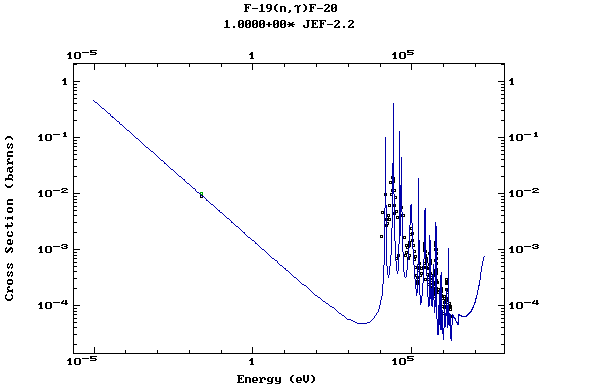
Z=10, Ne
(Neon)
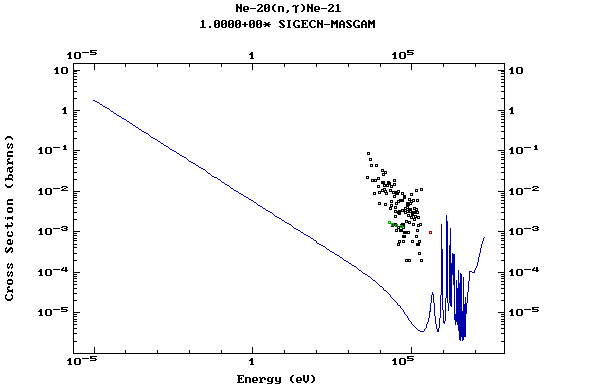
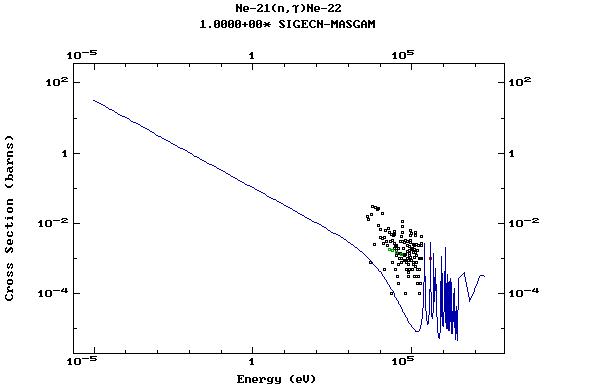
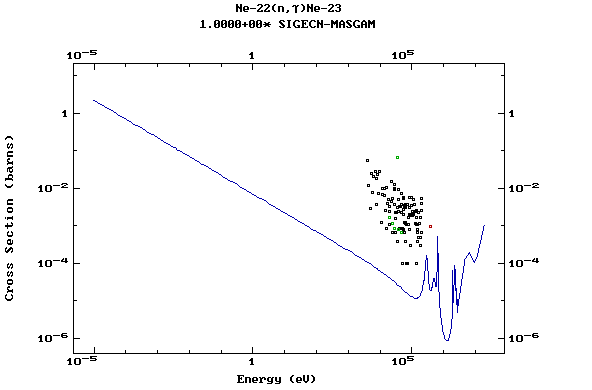
Z=11, Na
(Sodium)
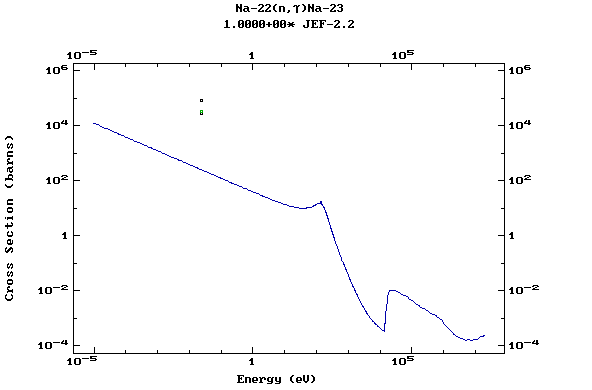
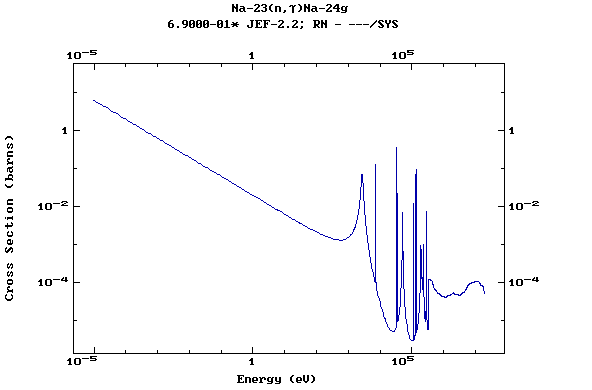
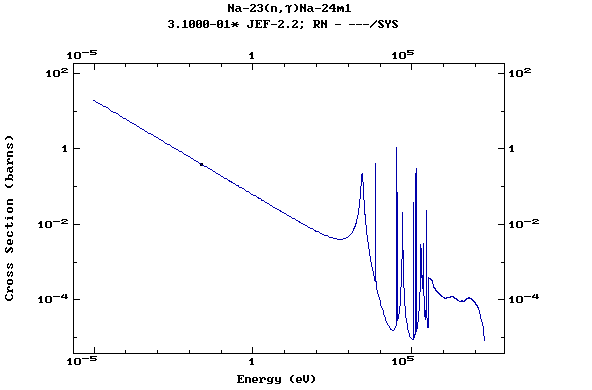
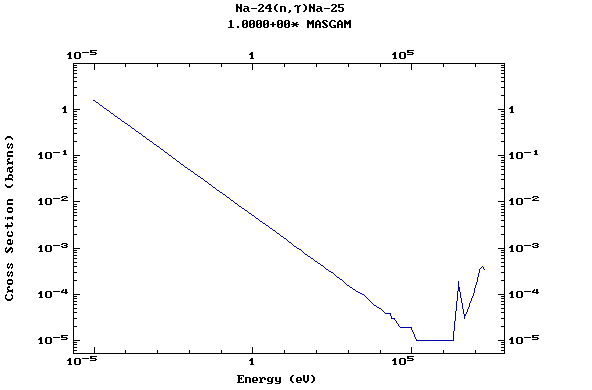
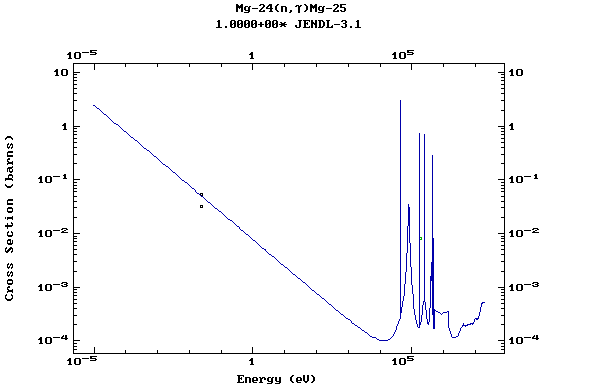
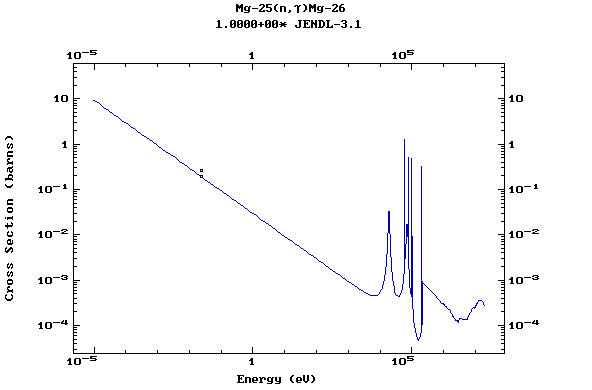
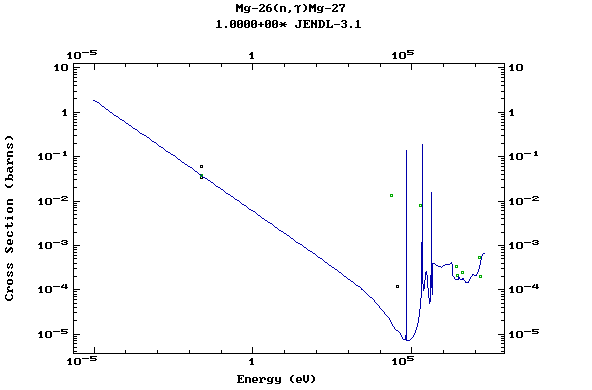
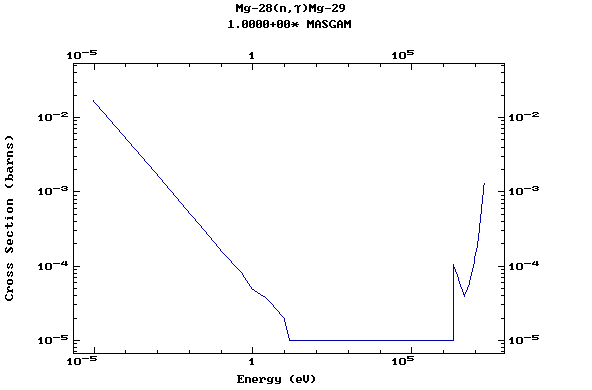
Z=12, Mg
(Magnesium)
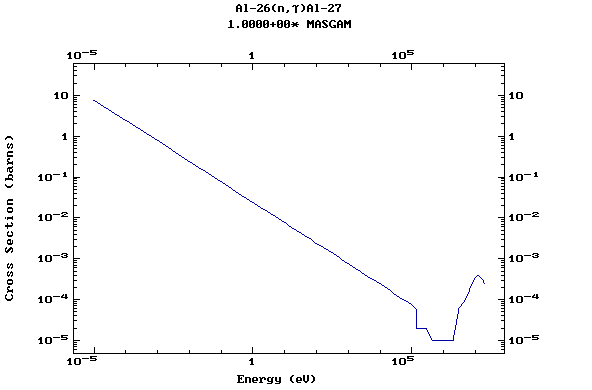
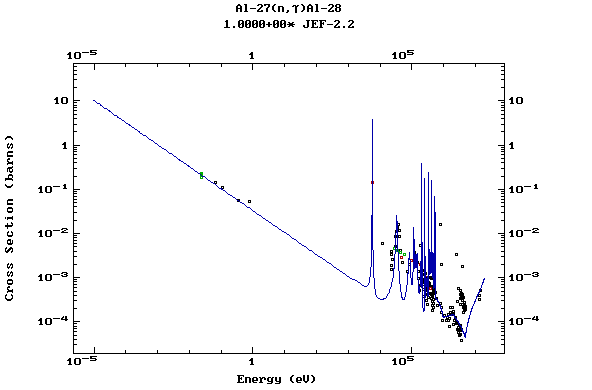
Z=13, Al
(Aluminium)
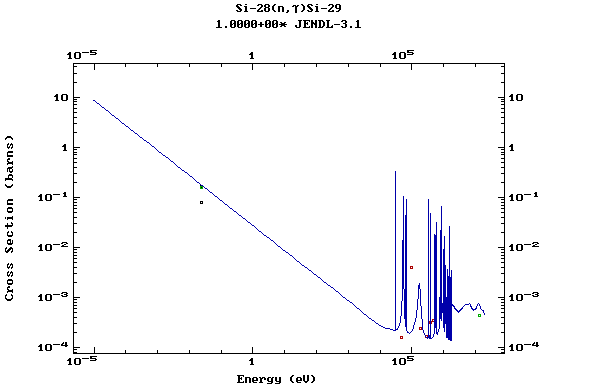
Z=14, Si
(Silicon)
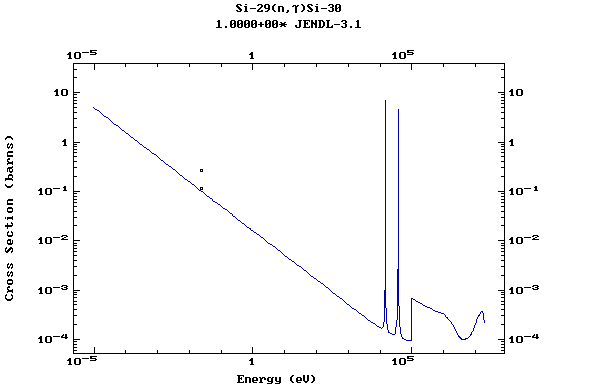
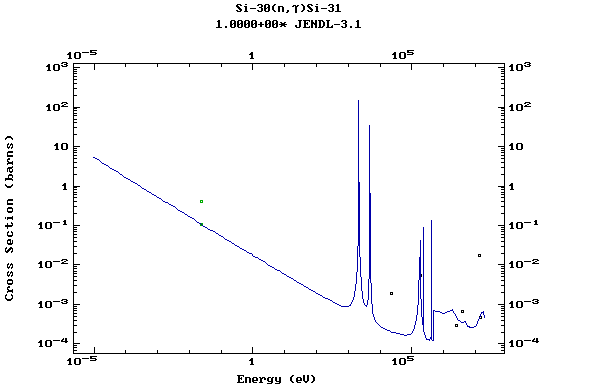
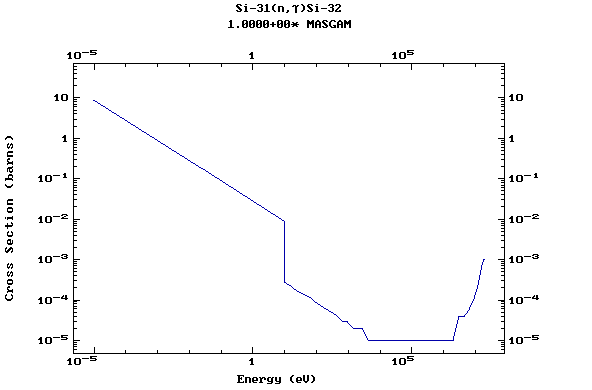
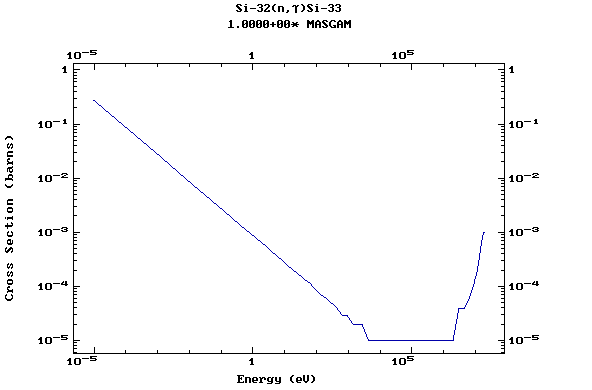
Z=15, P
(Phosphorus)
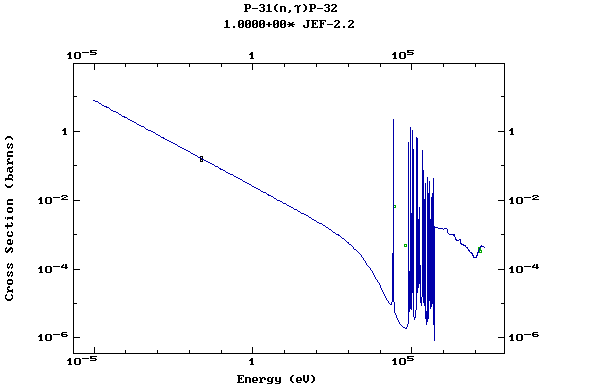
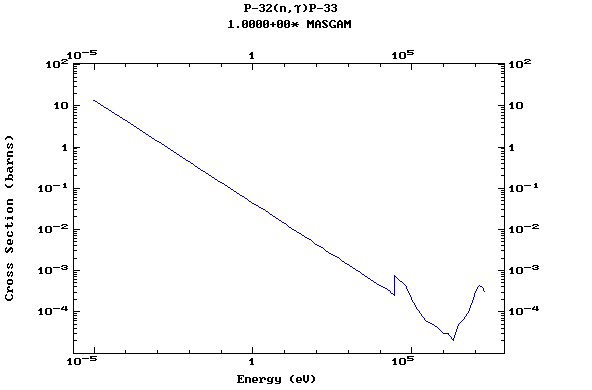
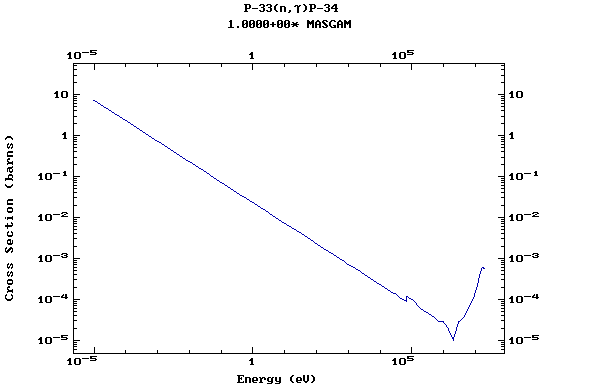
Z=16, S
(Sulphur)
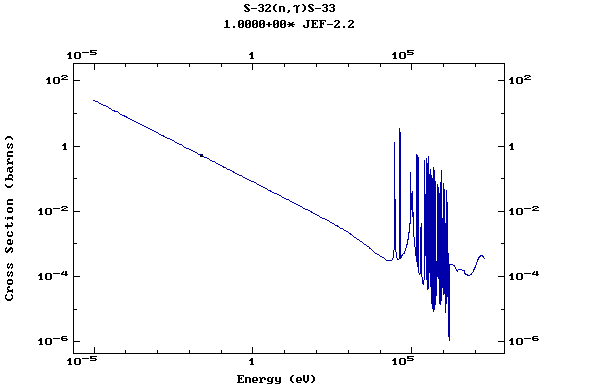
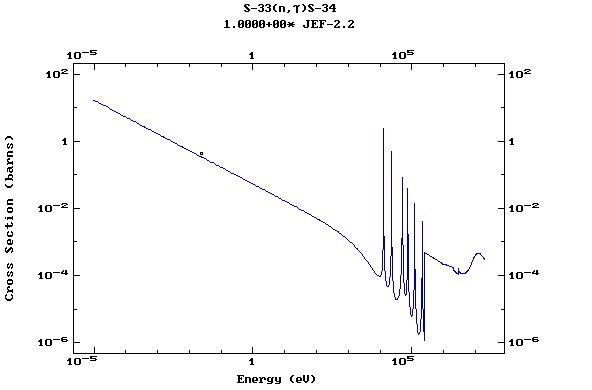
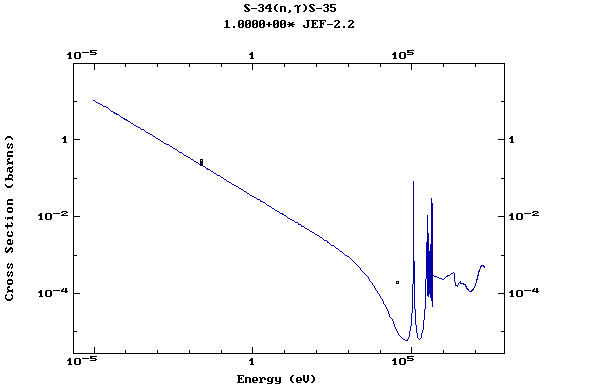
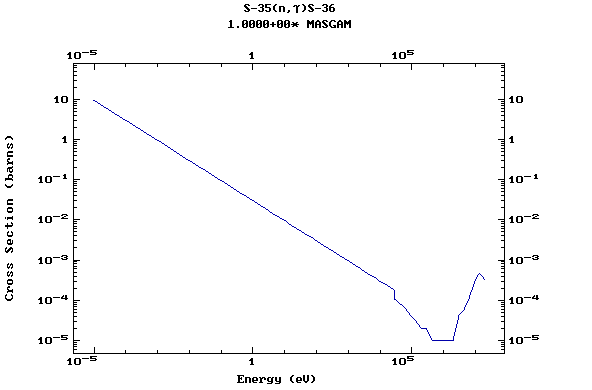
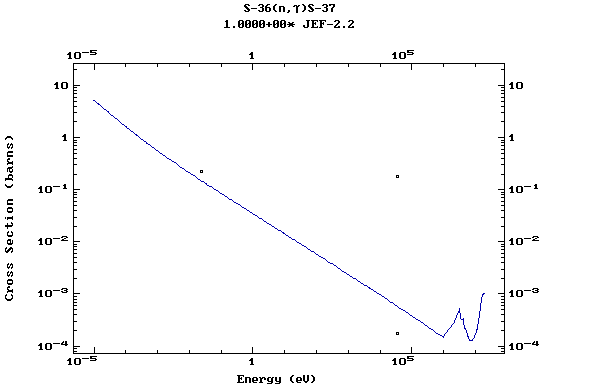
Z=17, Cl
(Chlorine)
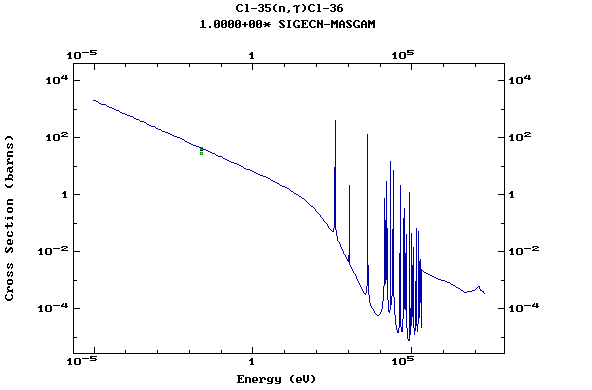
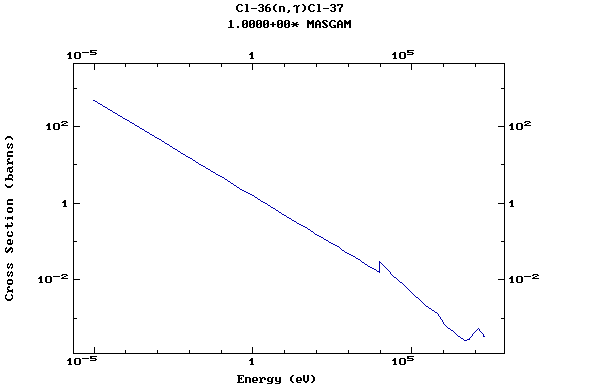
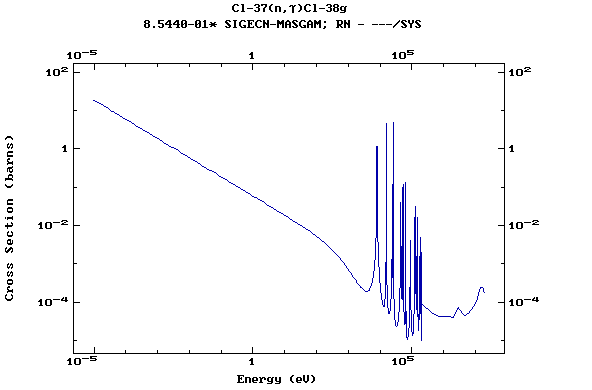
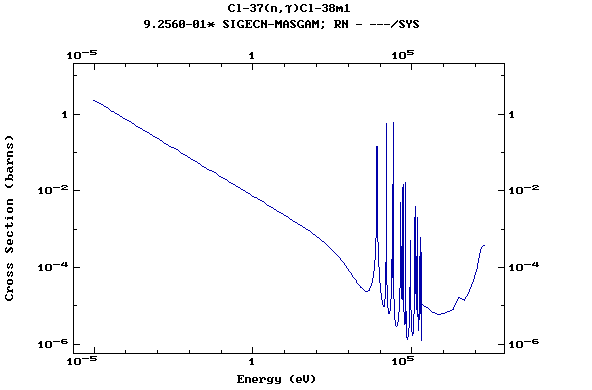
Z=18, Ar
(Argon)
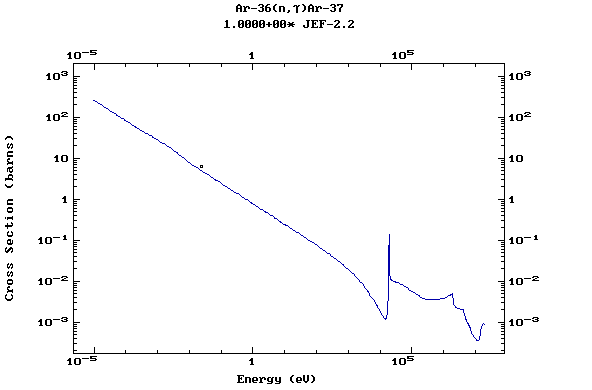
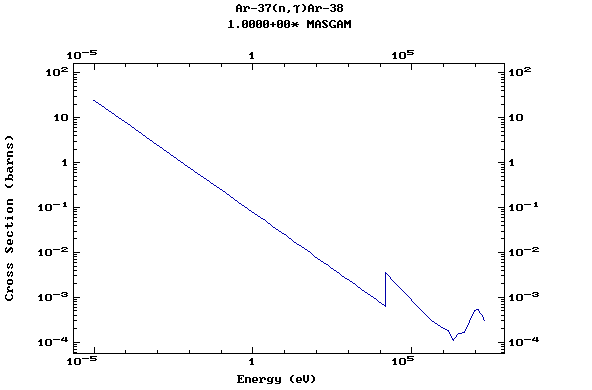
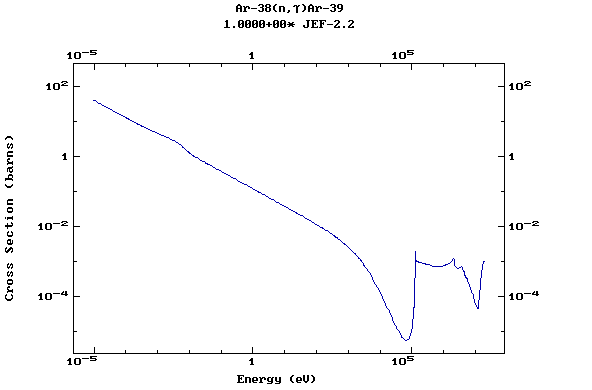
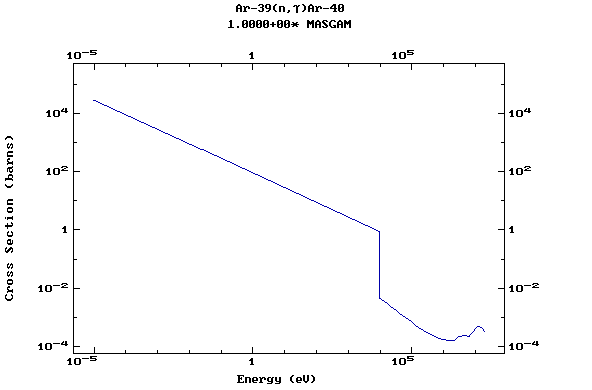
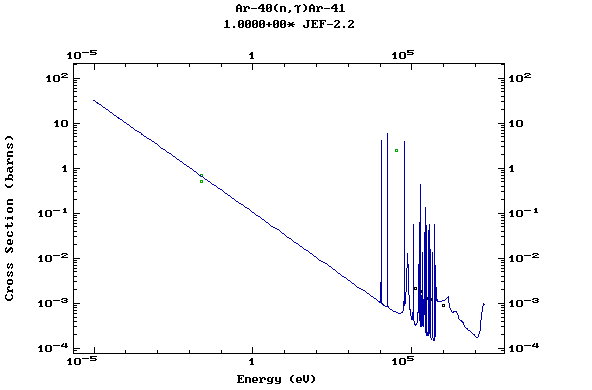
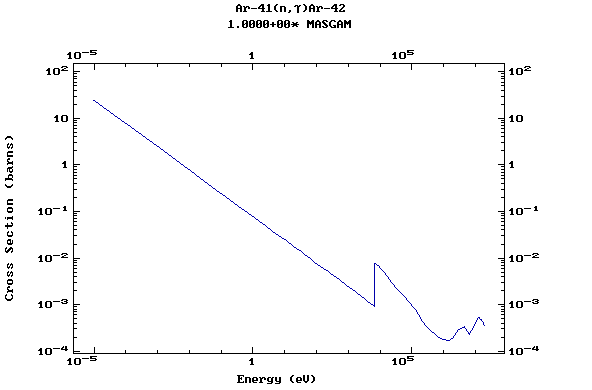
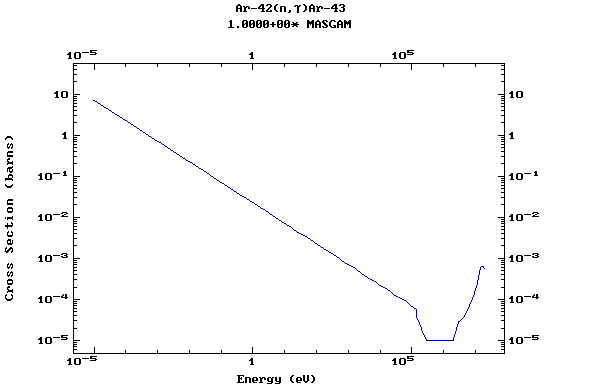
Z=19, K
(Potassium)
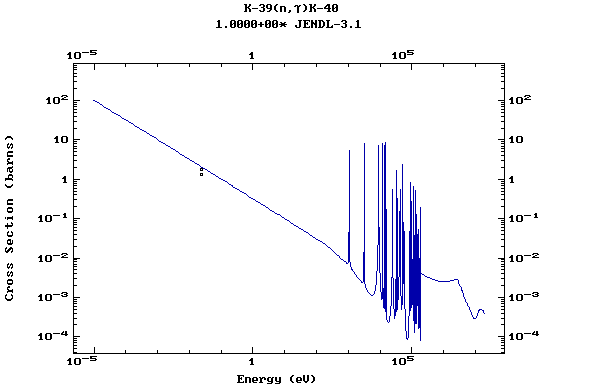
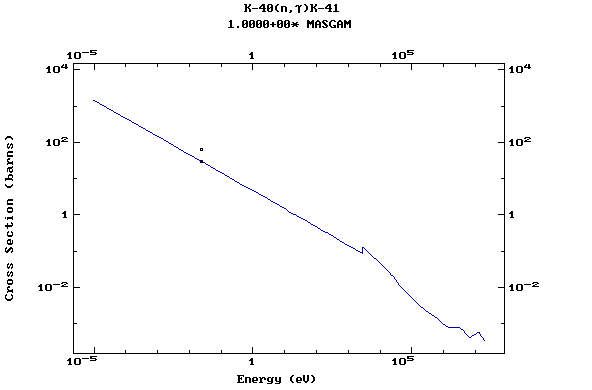
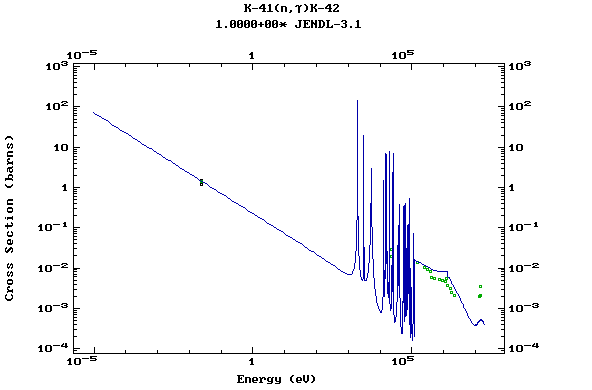
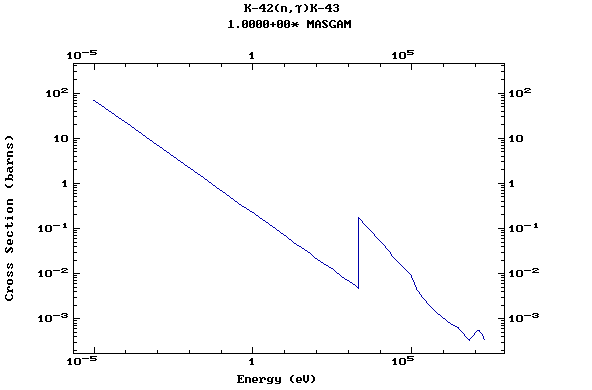
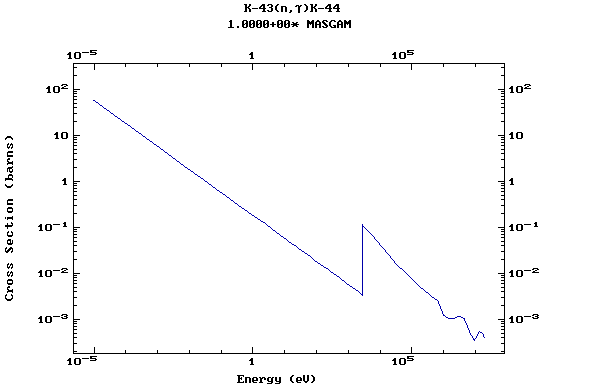
Z=20, Ca
(Calcium)
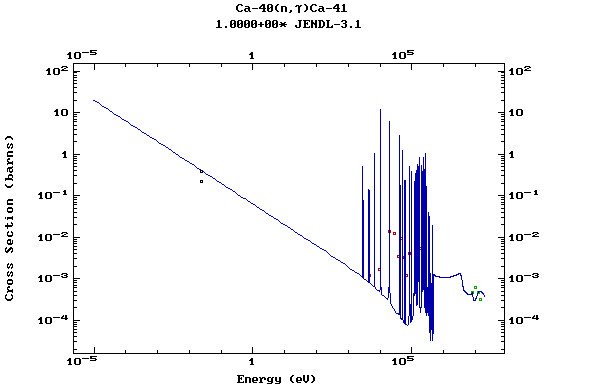
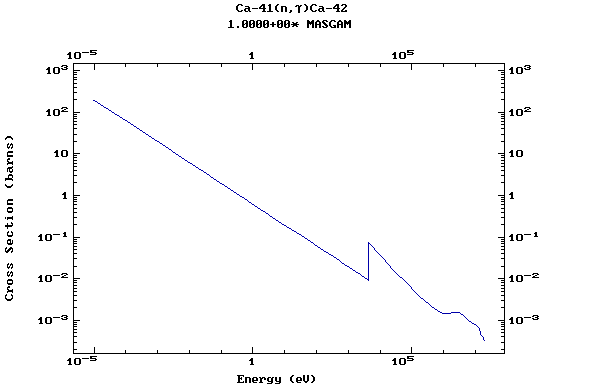
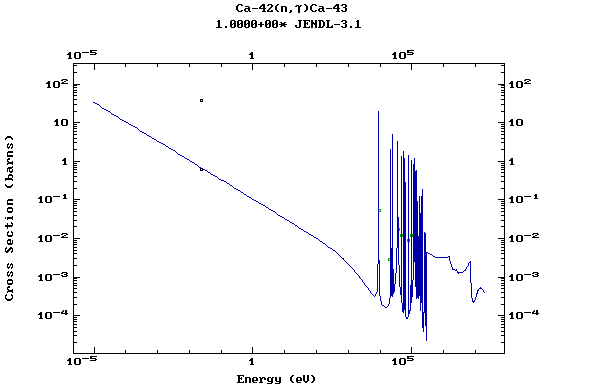
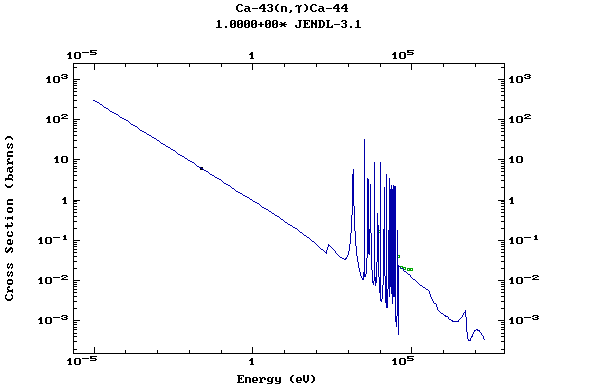
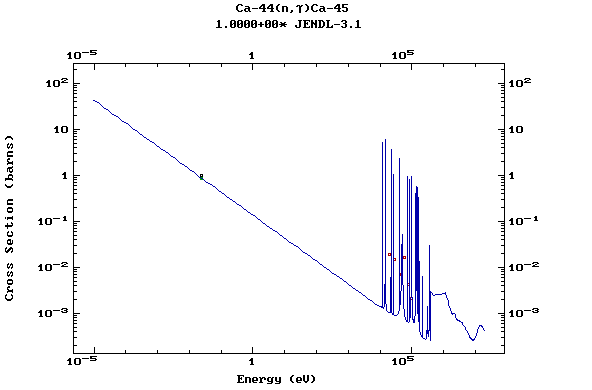
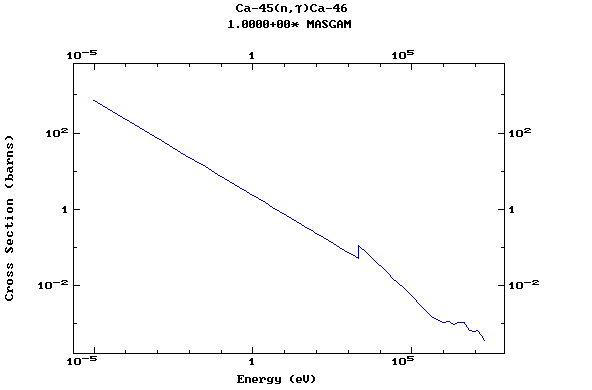
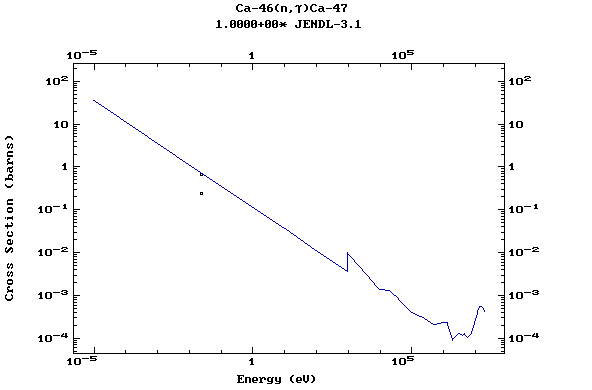
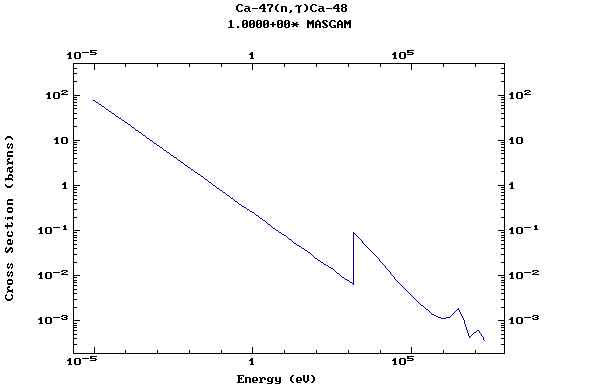
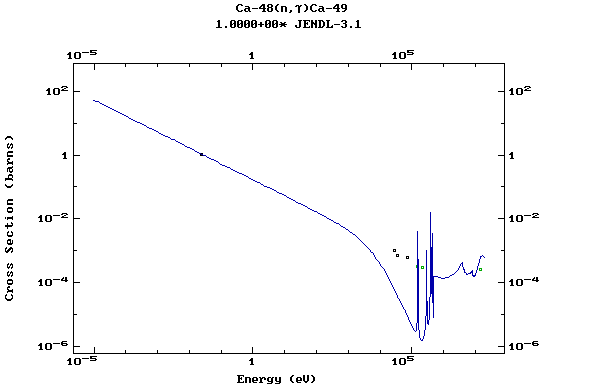
Z=21, Sc
(Scandium)
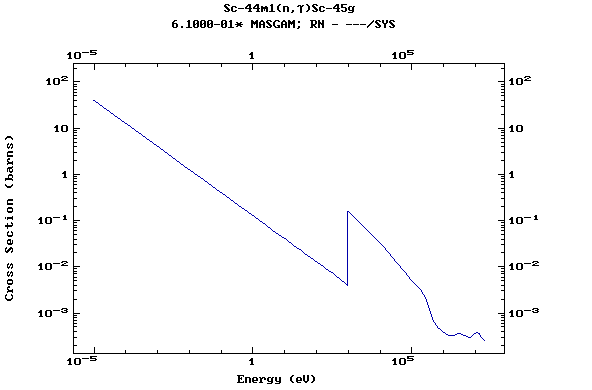
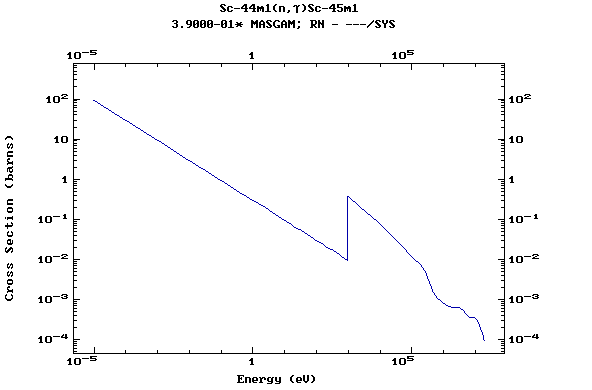
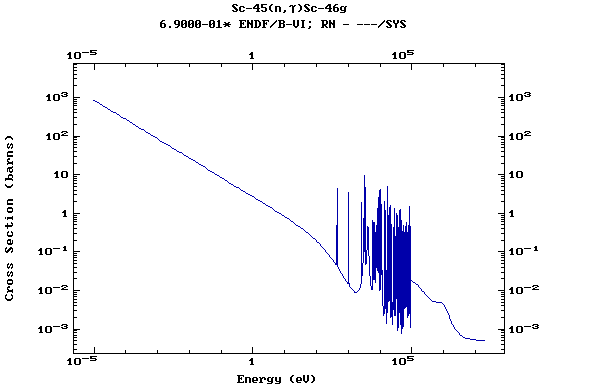
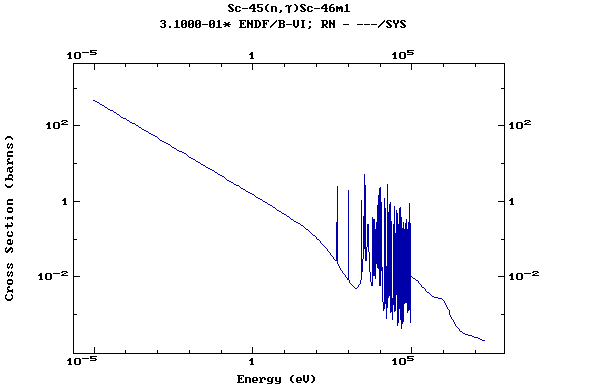
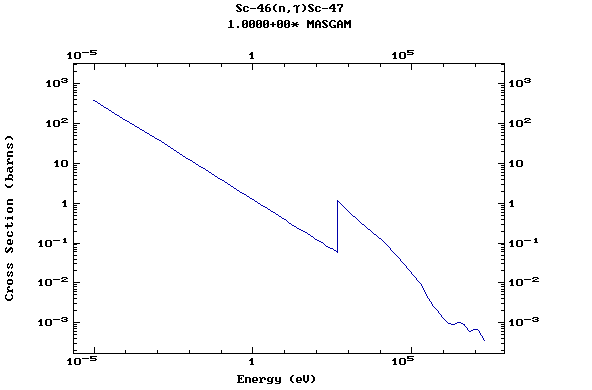
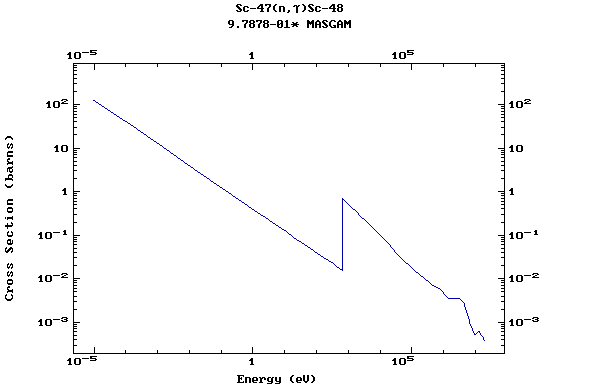
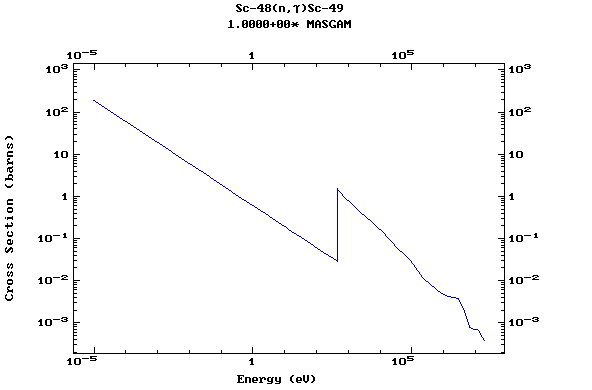
Z=22, Ti
(Titanium)
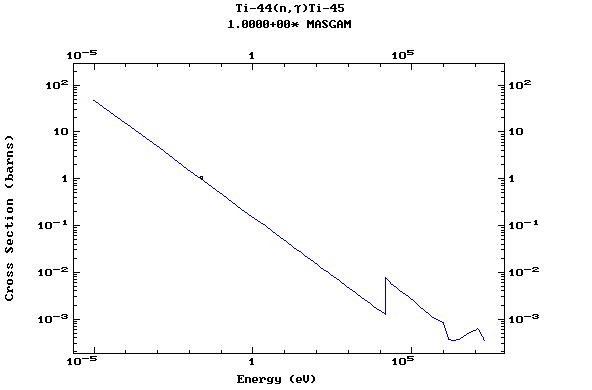
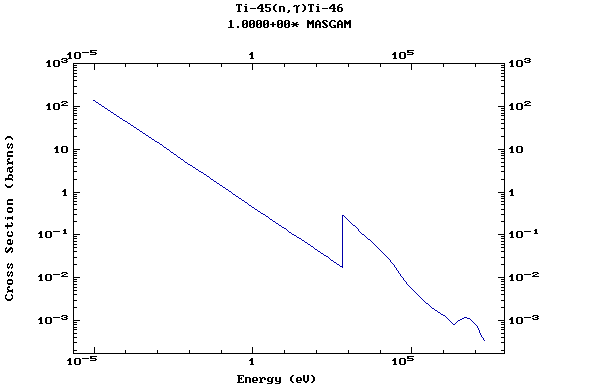
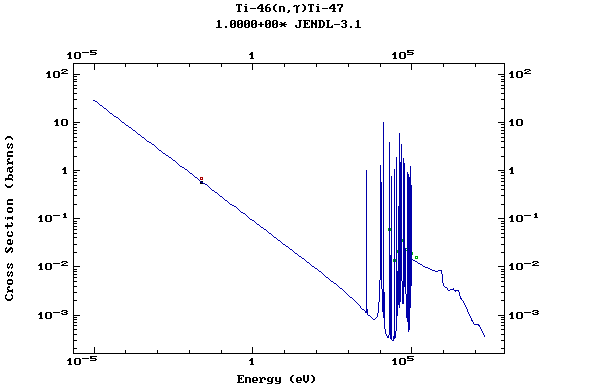
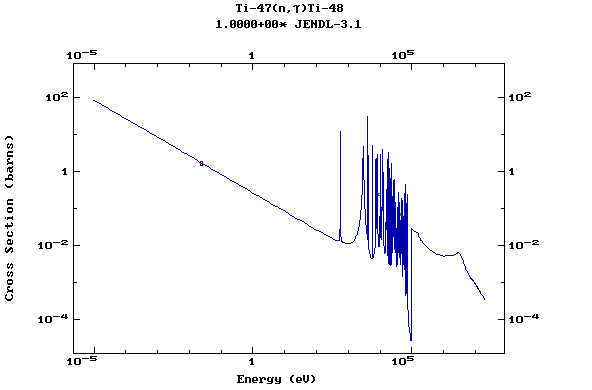
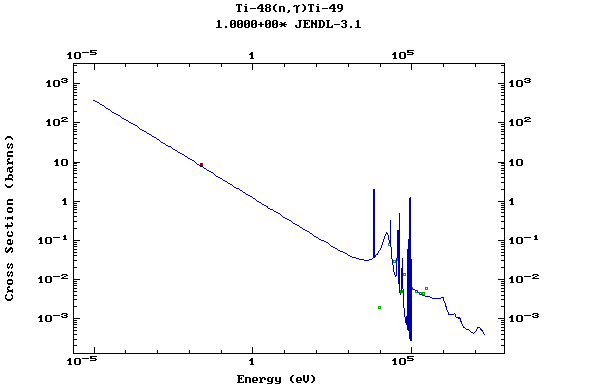
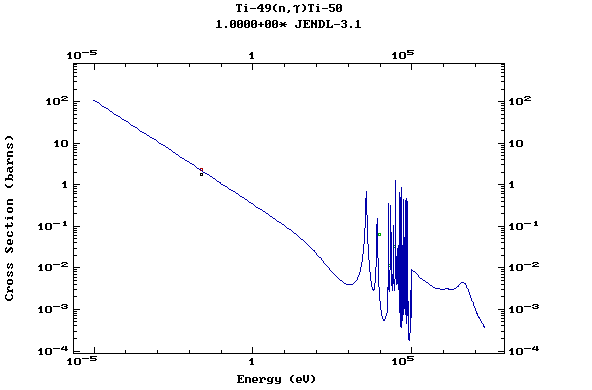
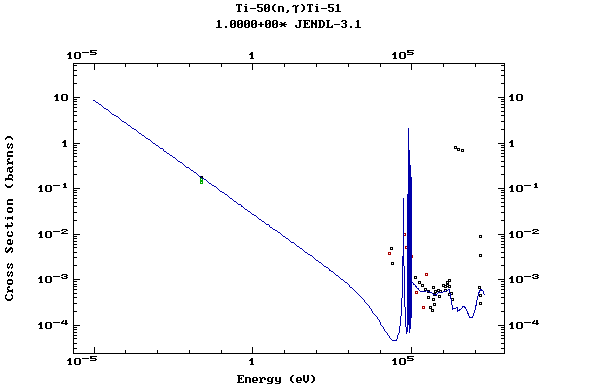
Z=23, V
(Vanadium)
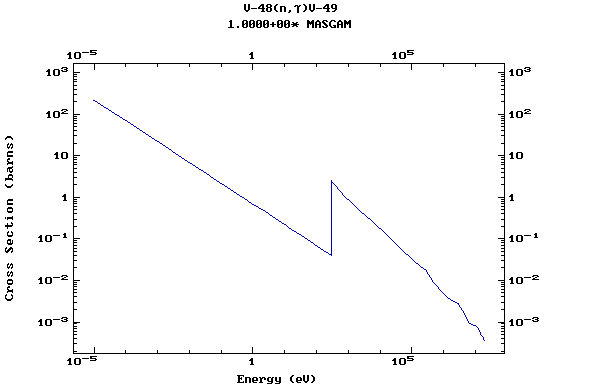
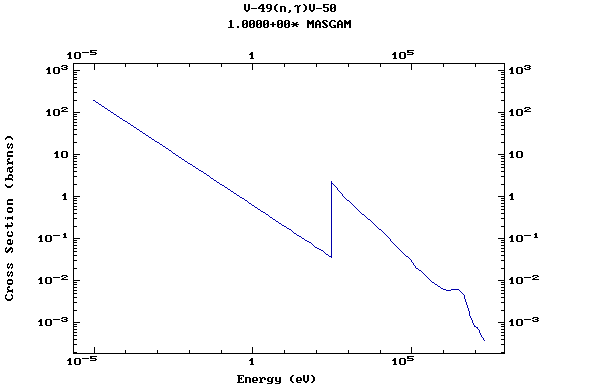
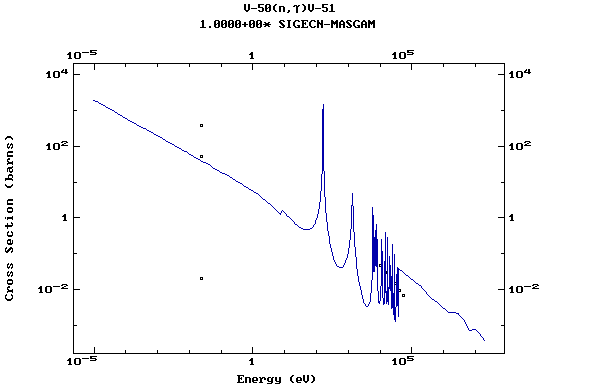
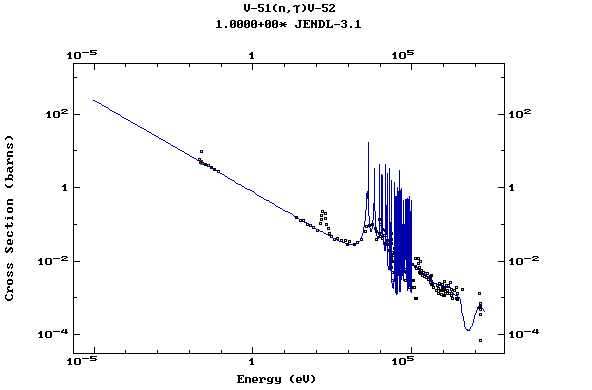
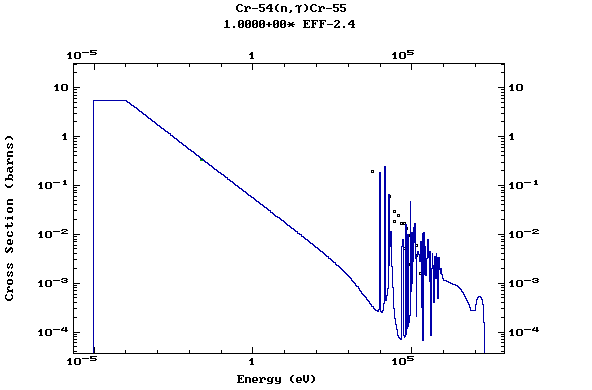
Z=24, Cr
(Chromium)
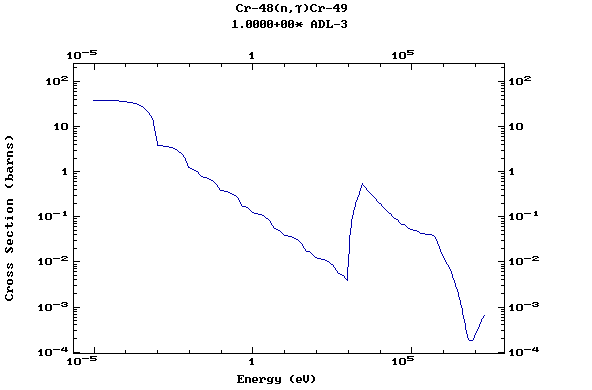
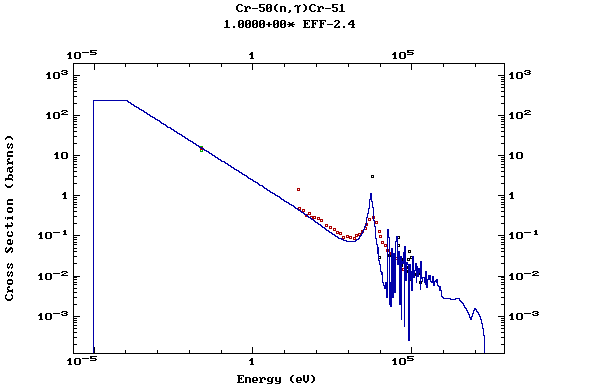
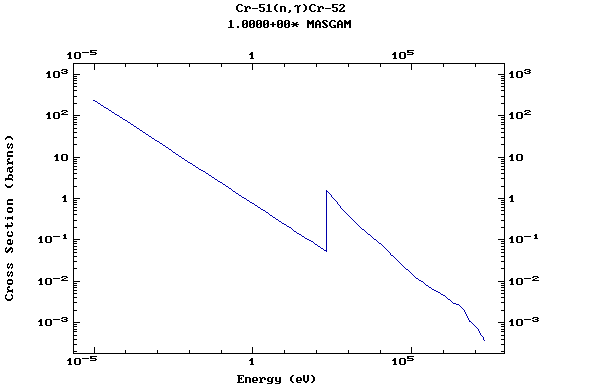
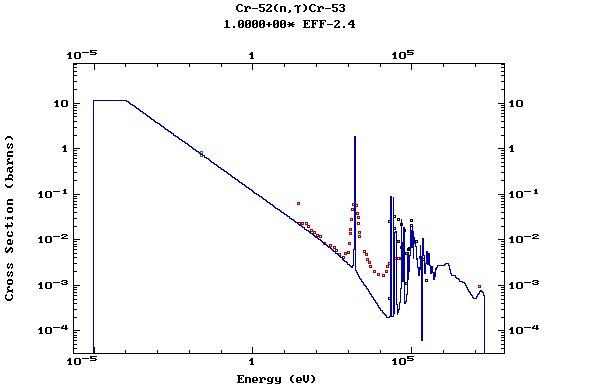
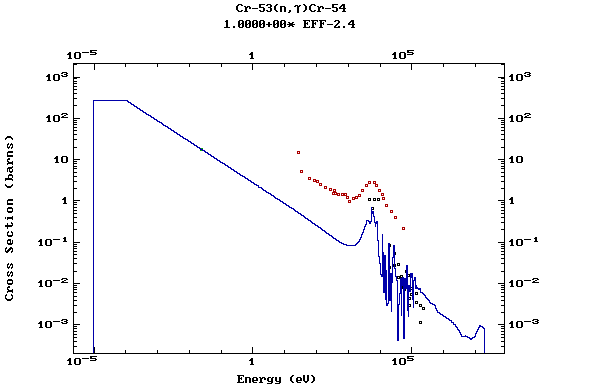
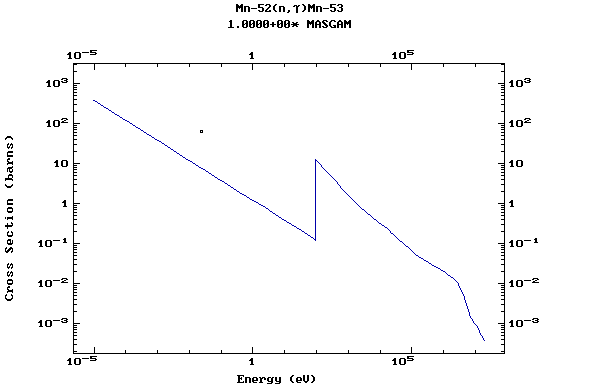
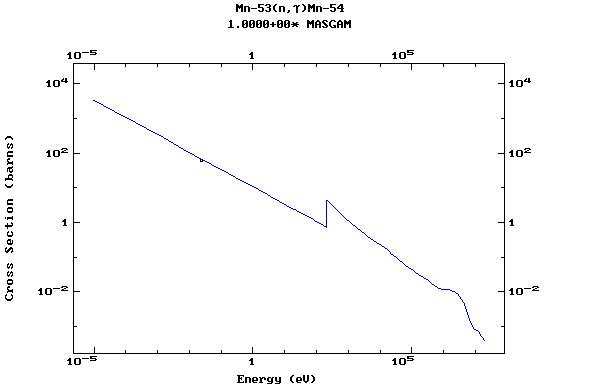
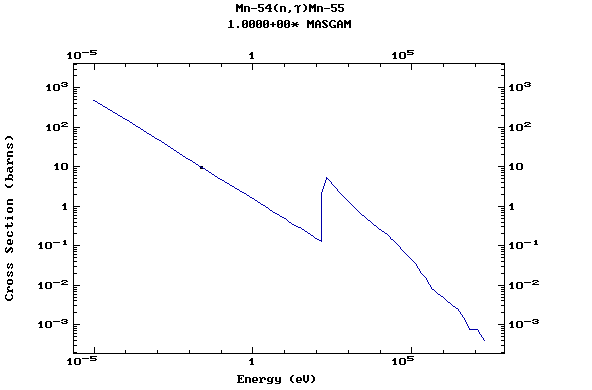
Z=25, Mn
(Manganese)
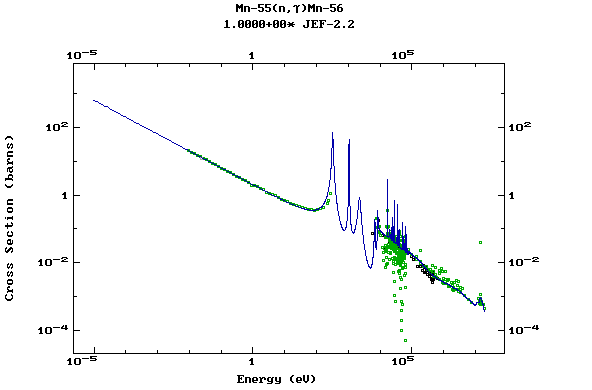
Z=26, Fe
(Iron)
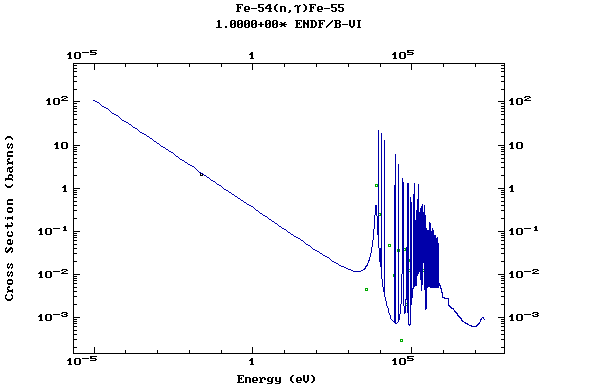
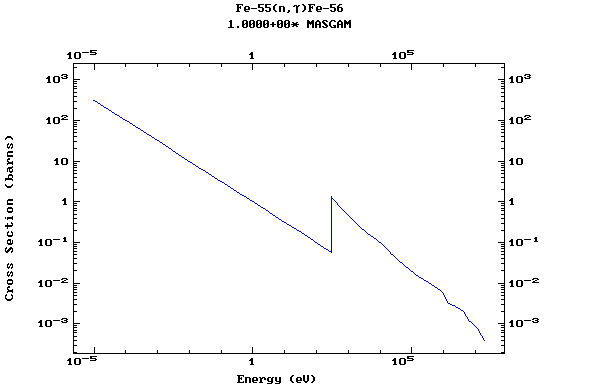
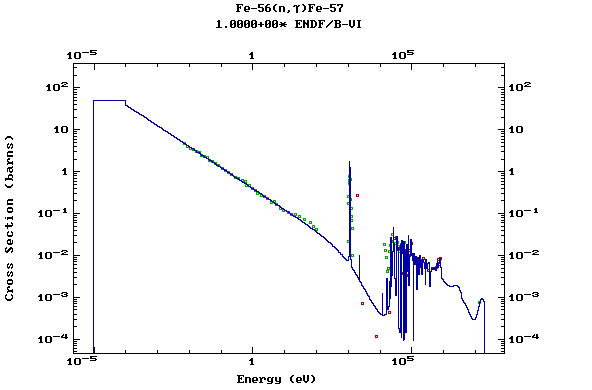
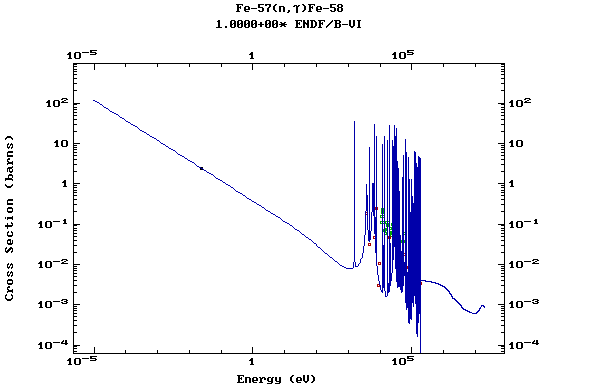
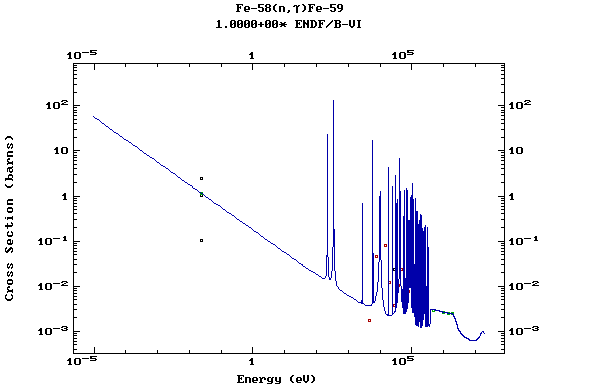
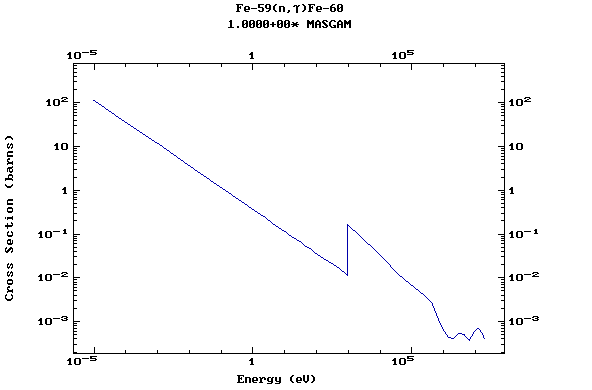
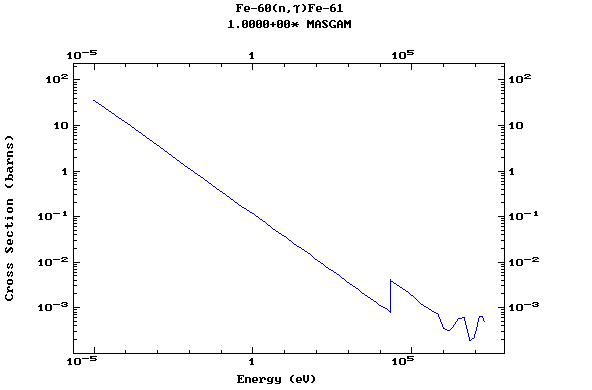
Z=27, Co
(Cobalt)
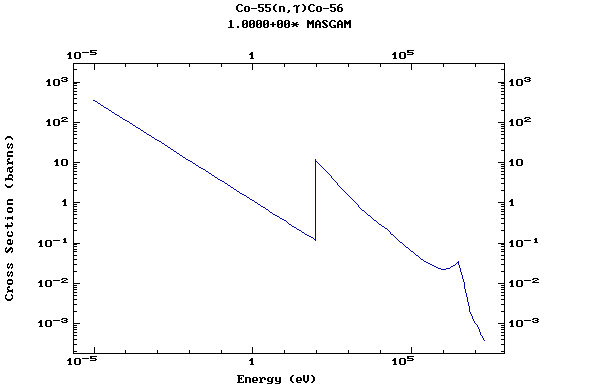
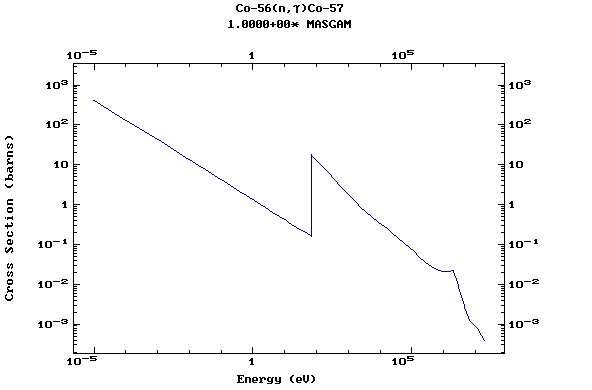
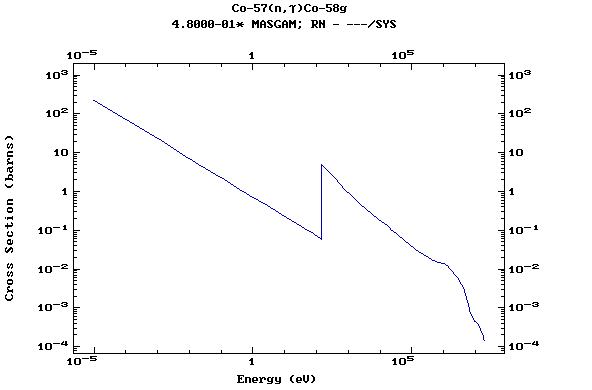
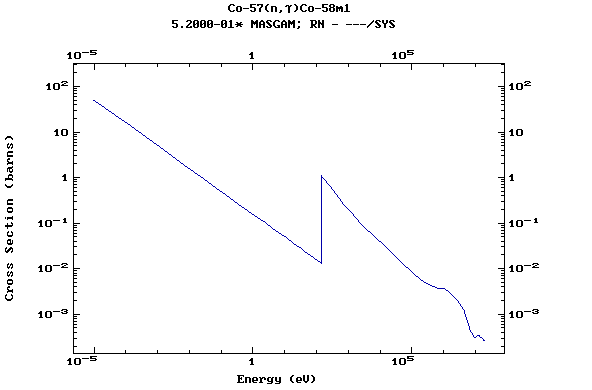
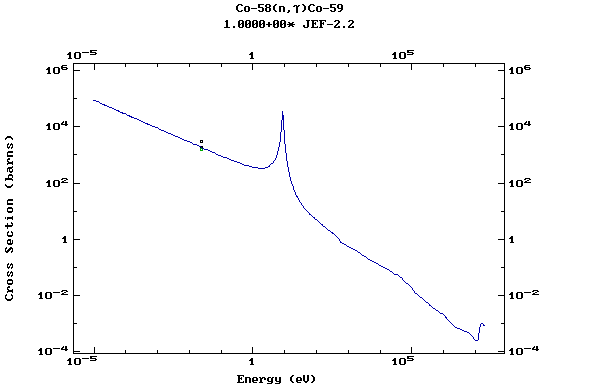
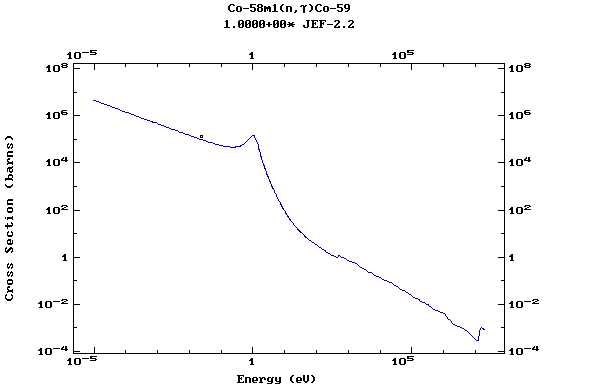
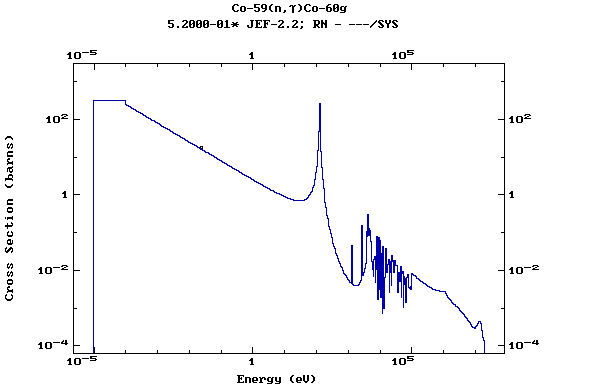
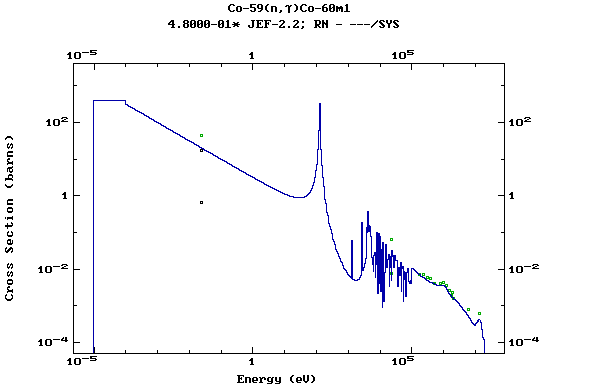
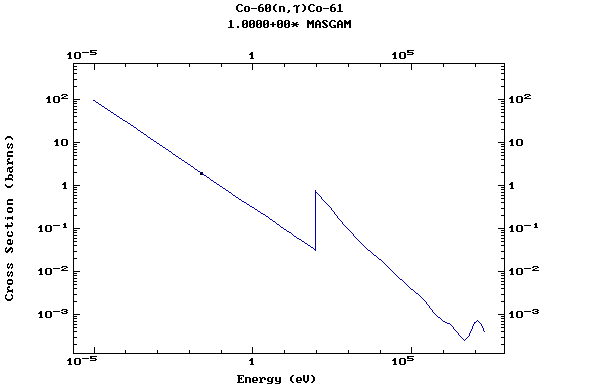
Z=28, Ni
(Nickel)
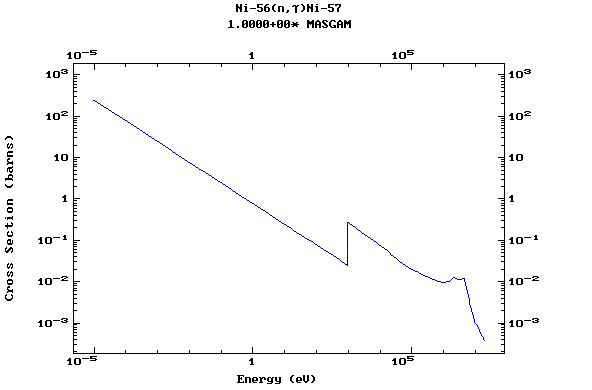
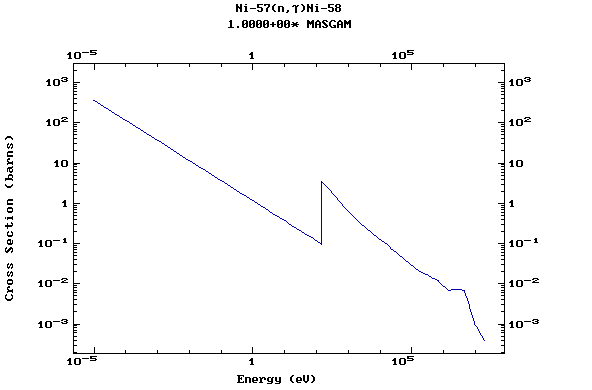
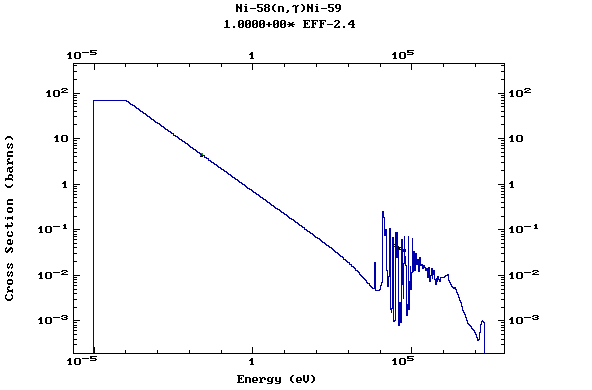
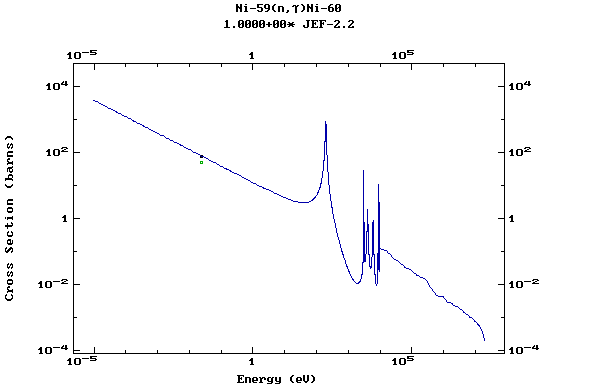
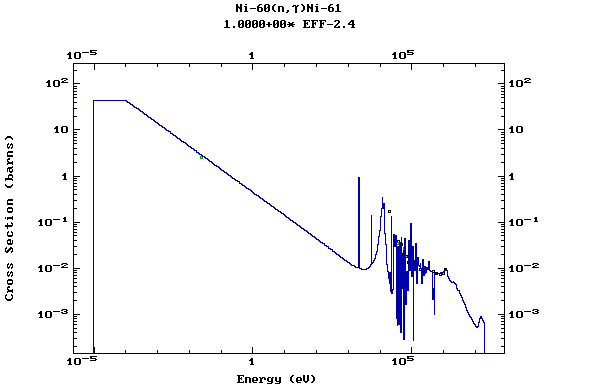
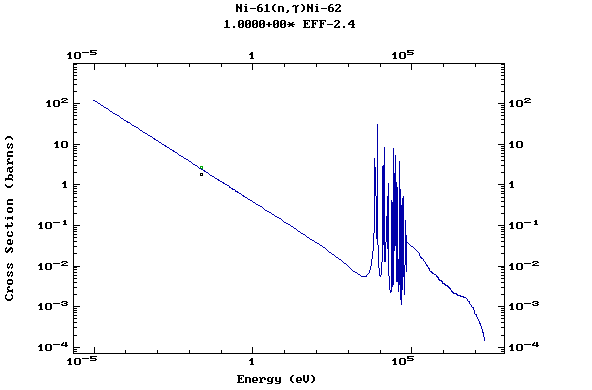
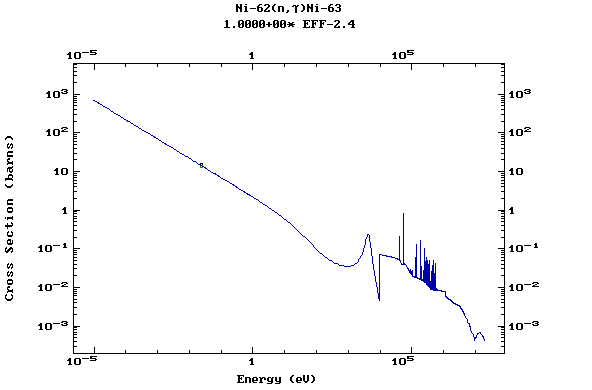
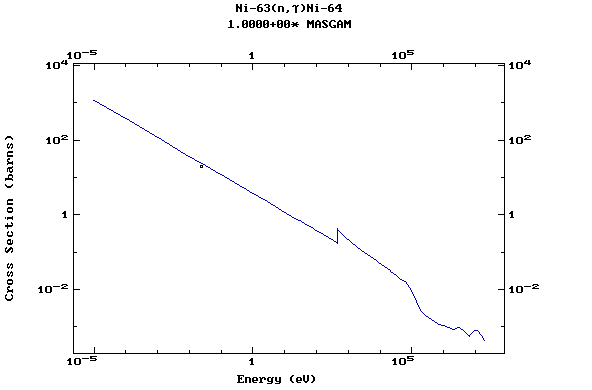
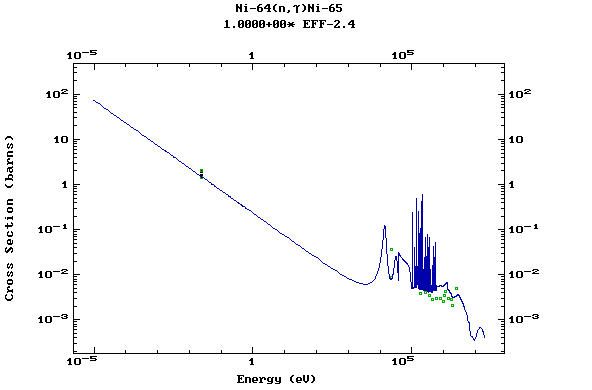
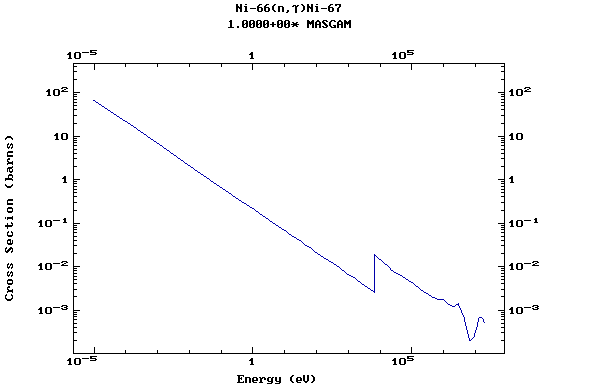
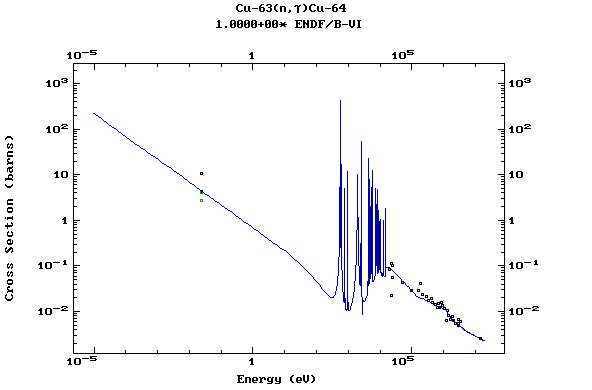
Z=29, Cu
(Copper)
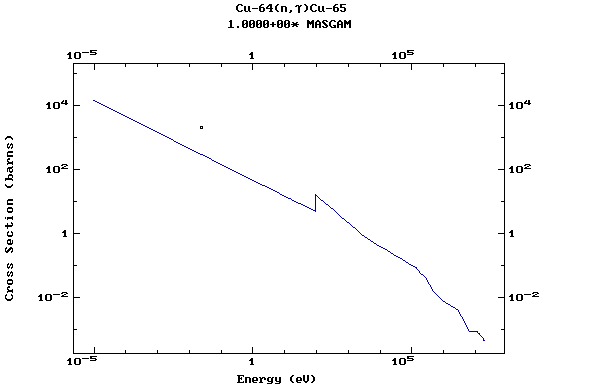
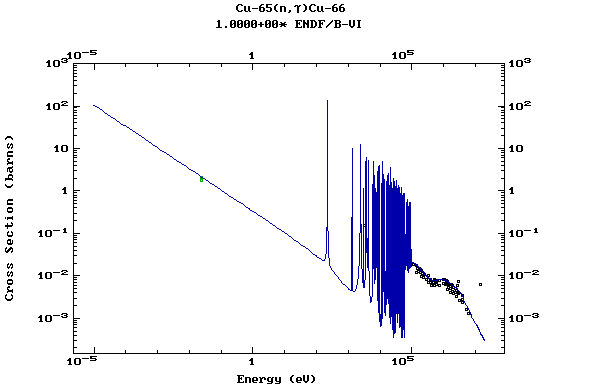
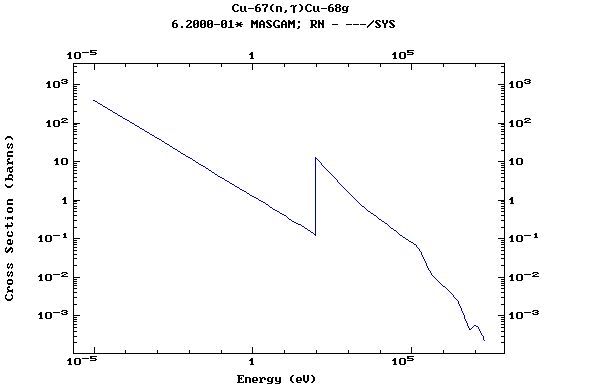
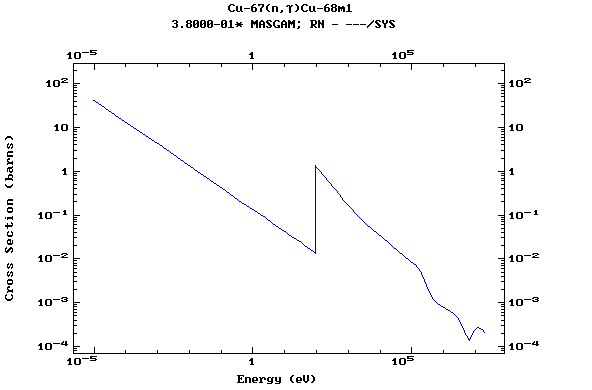
Z=30, Zn
(Zinc)
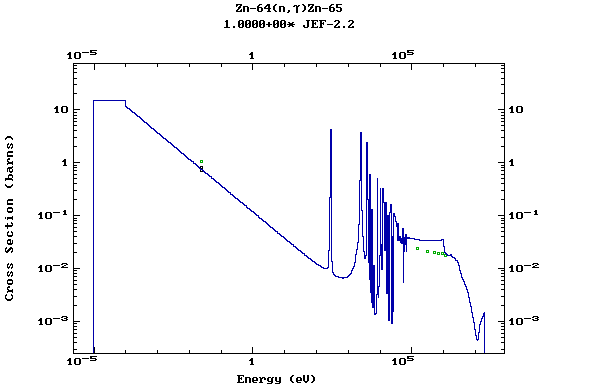
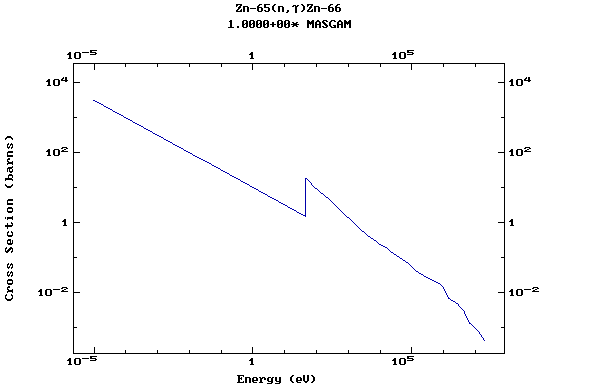
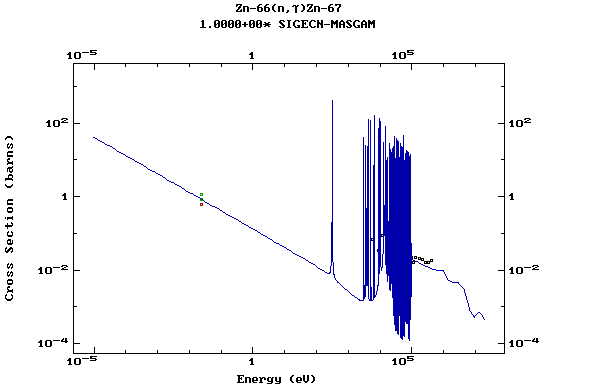
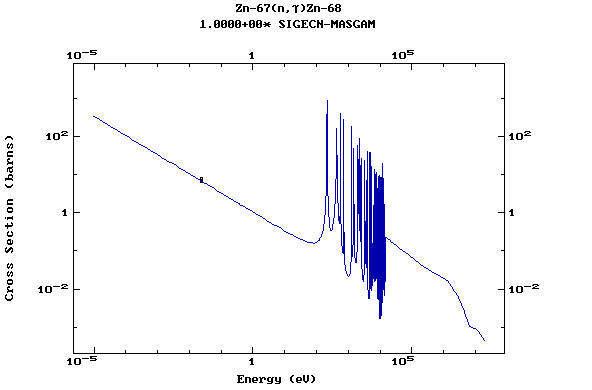
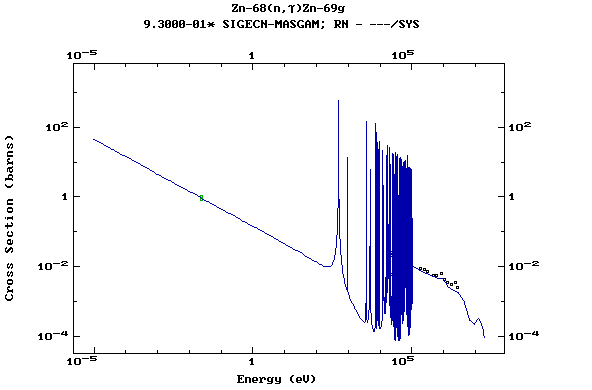
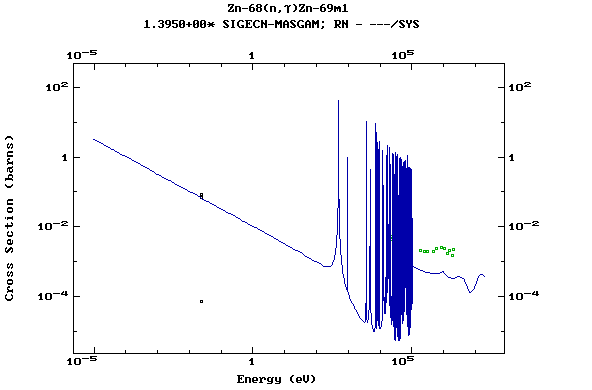
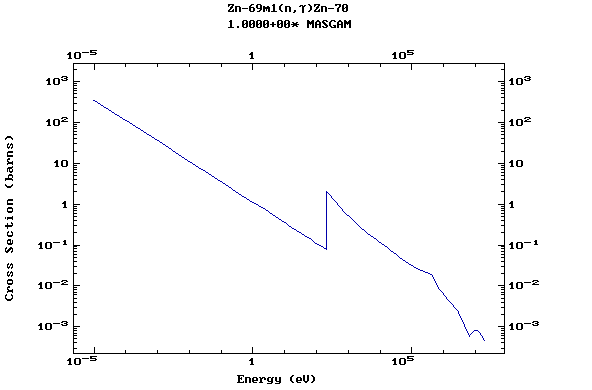
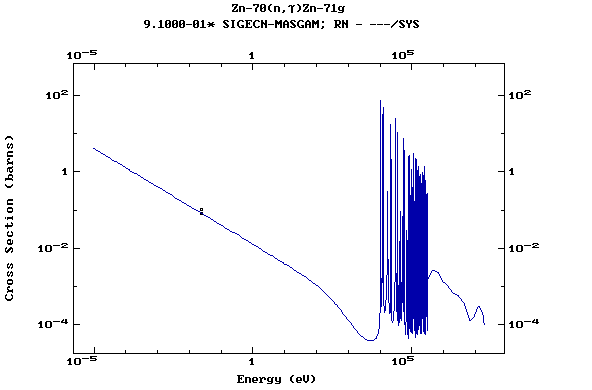
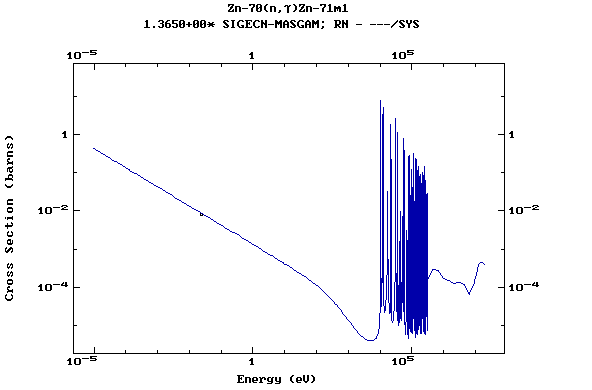
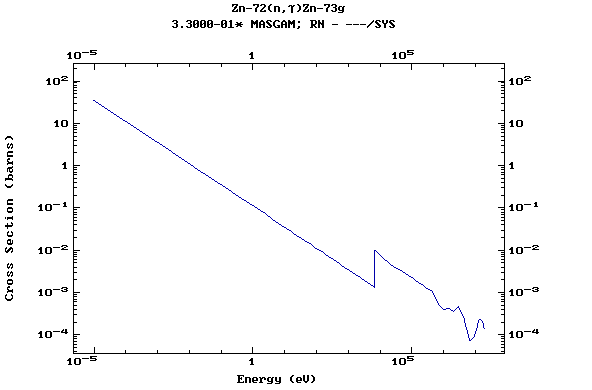
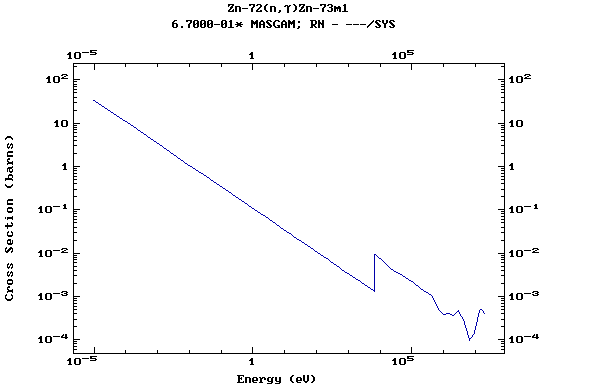
Z=31, Ga
(Gallium)
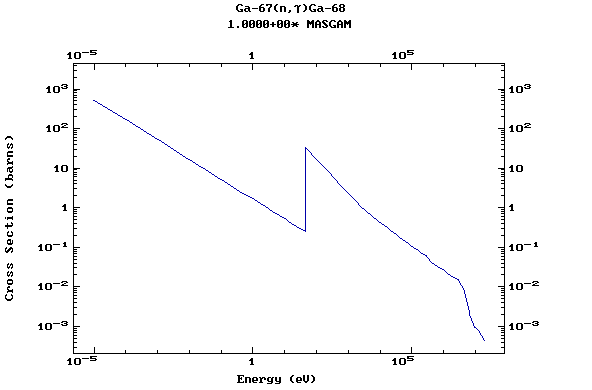
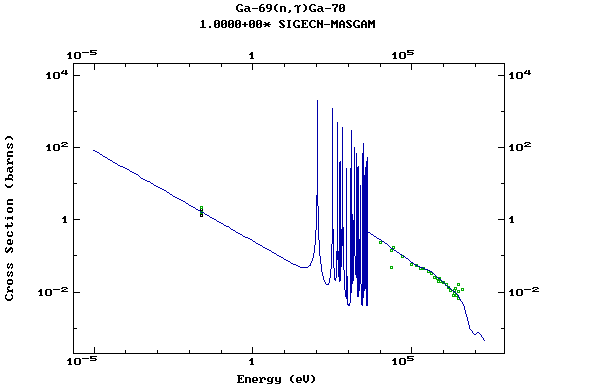
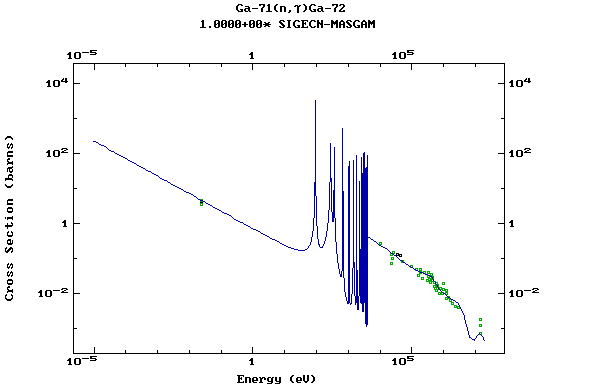
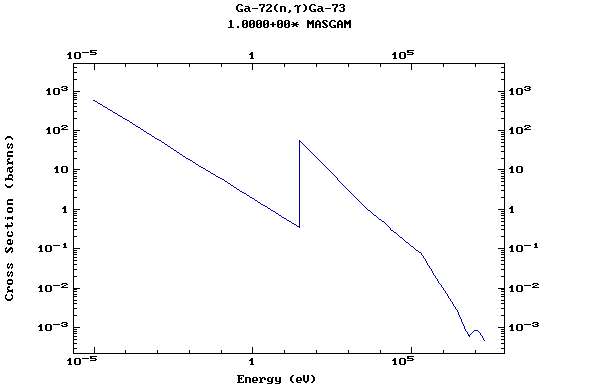
Z=32, Ge
(Germanium)
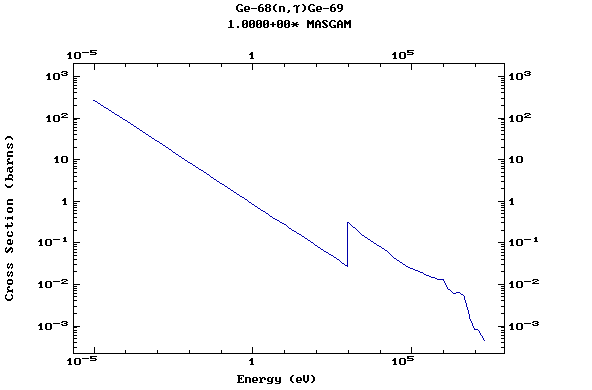
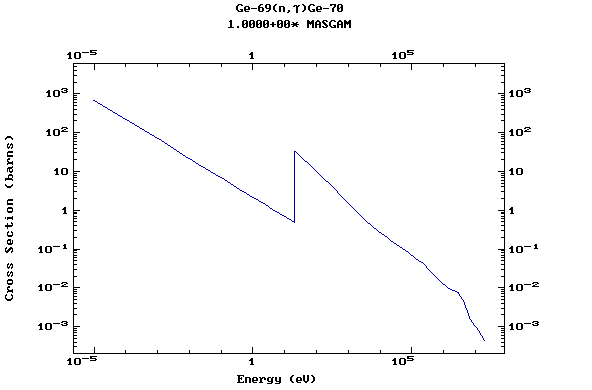
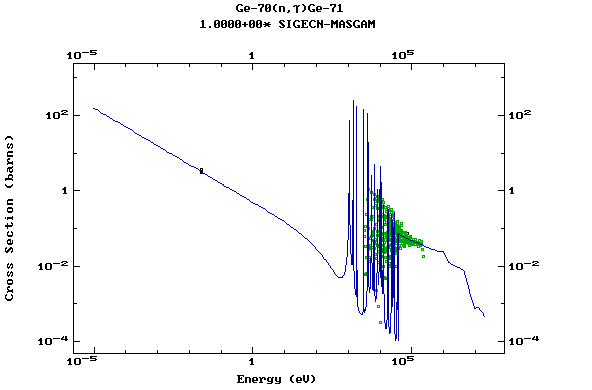
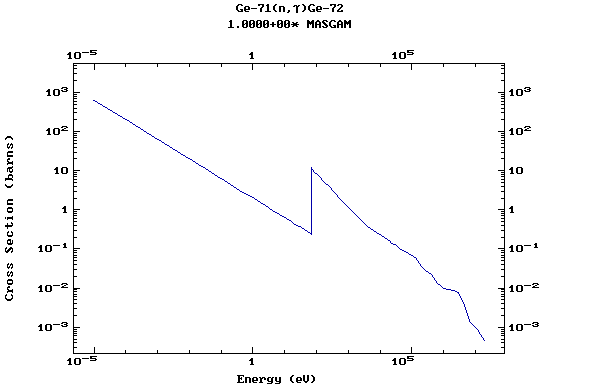
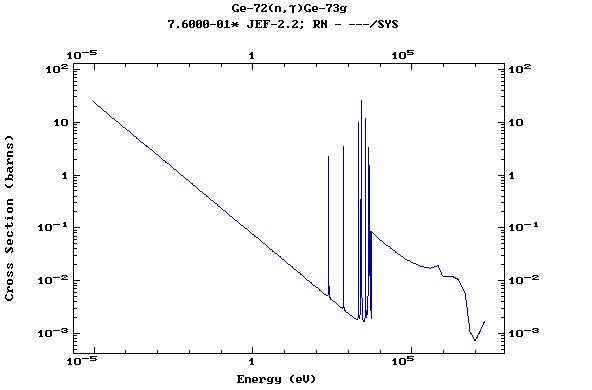
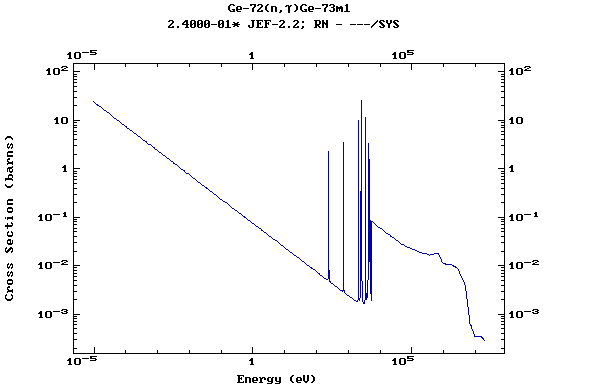
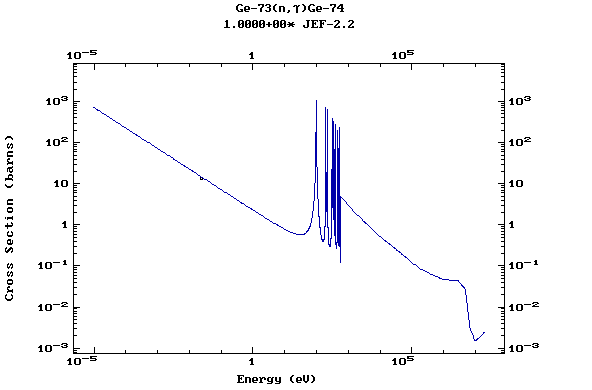
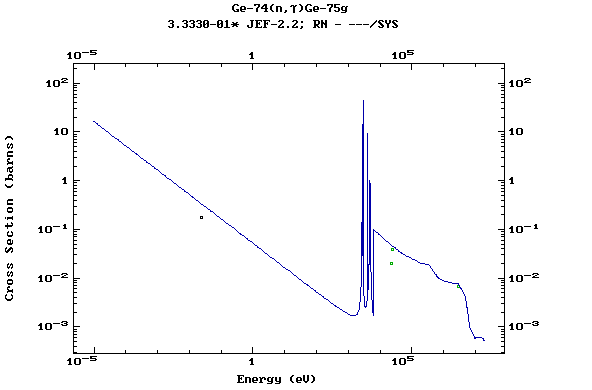
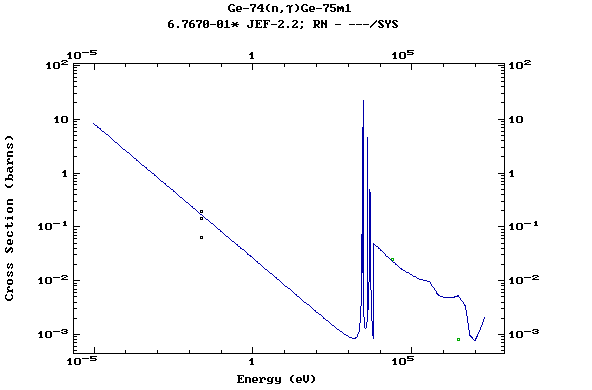
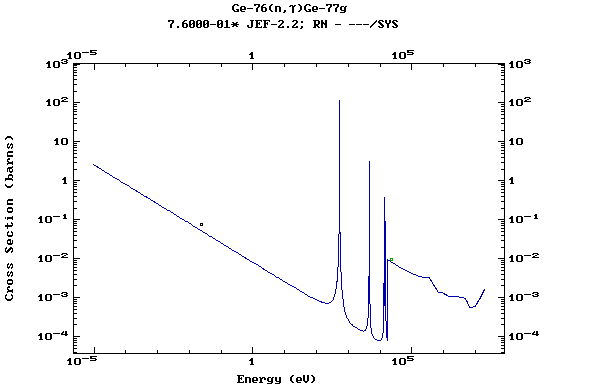
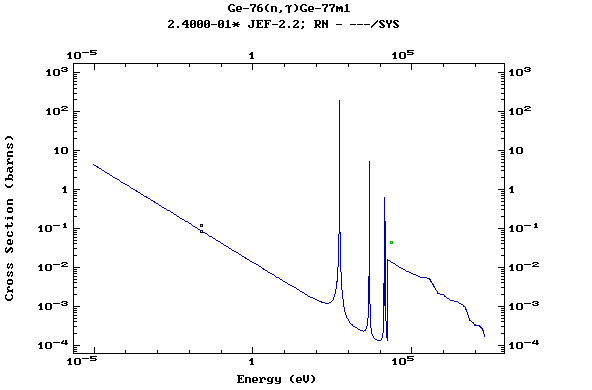
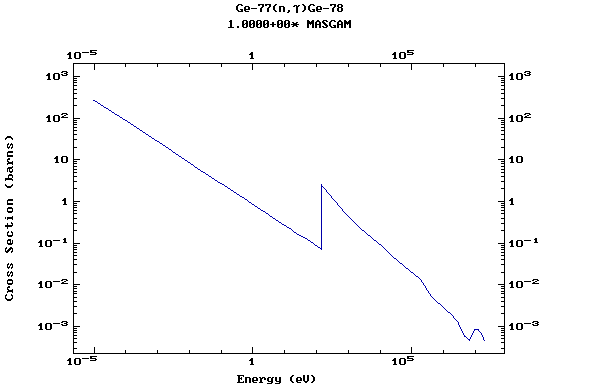
Z=33, As
(Arsenic)
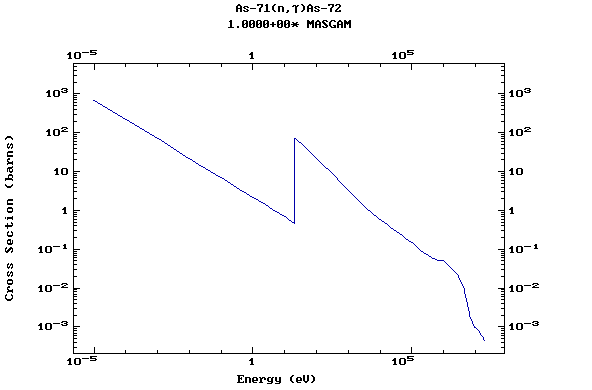
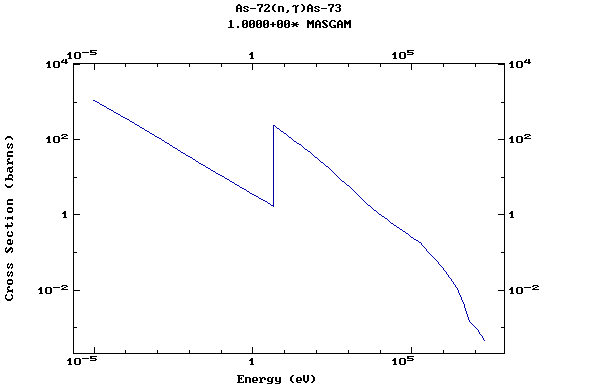
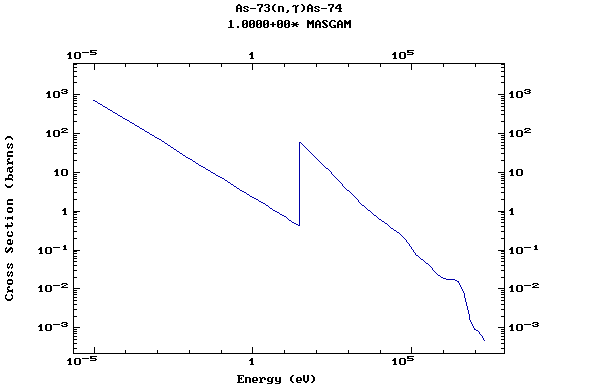
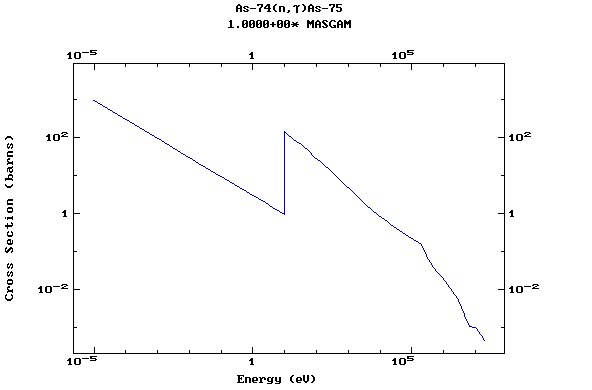
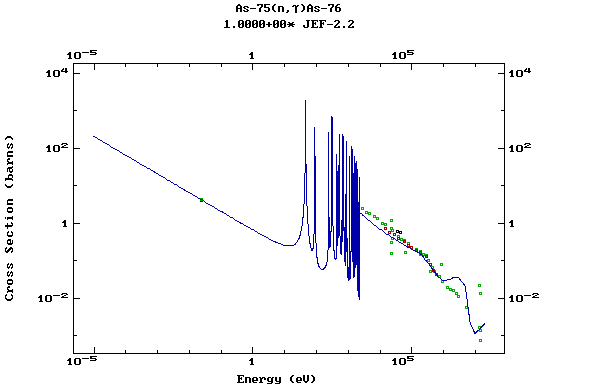
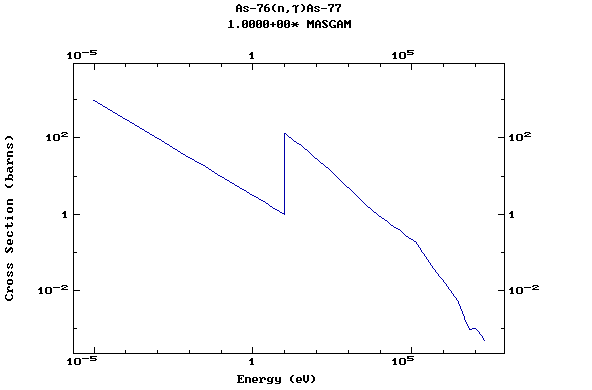
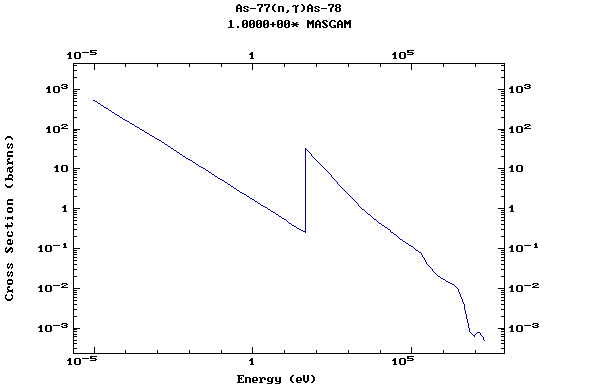
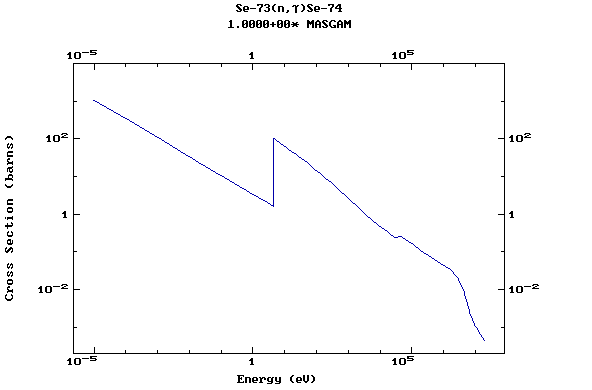
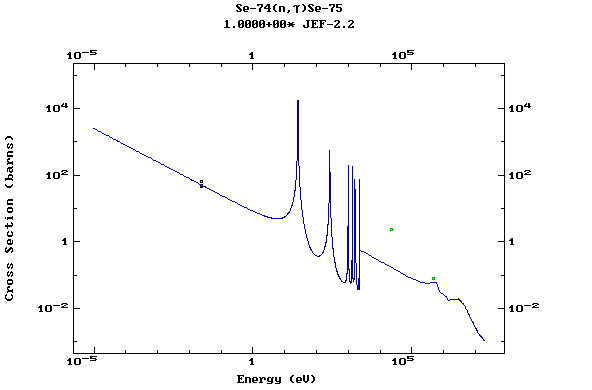
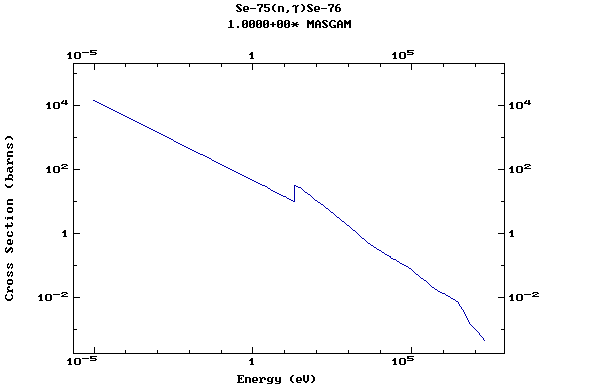
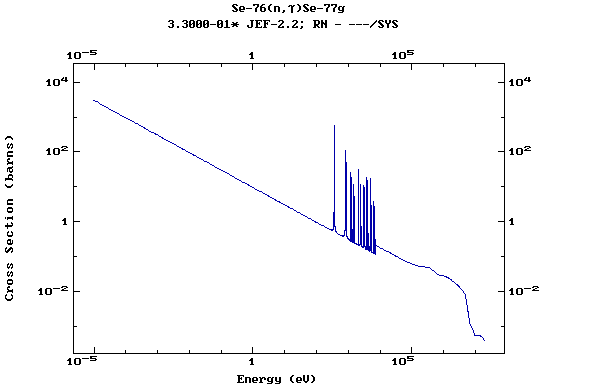
Z=34, Se
(Selenium)
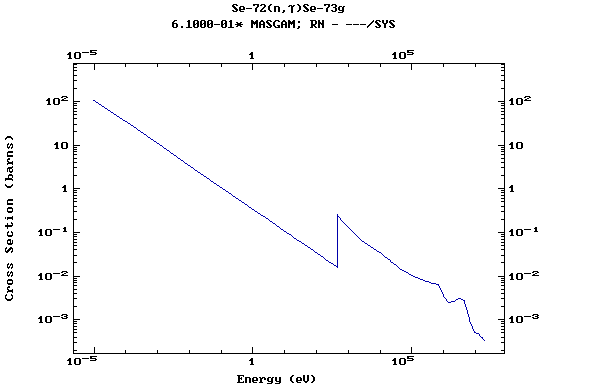
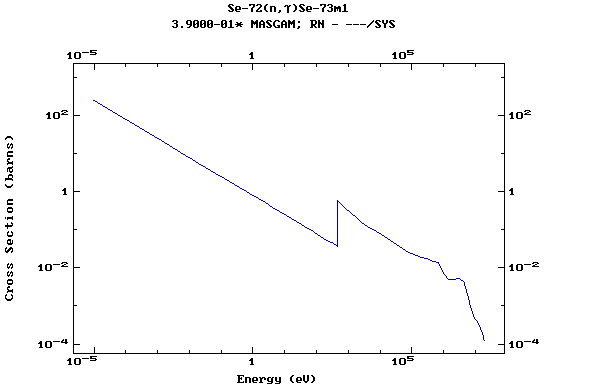
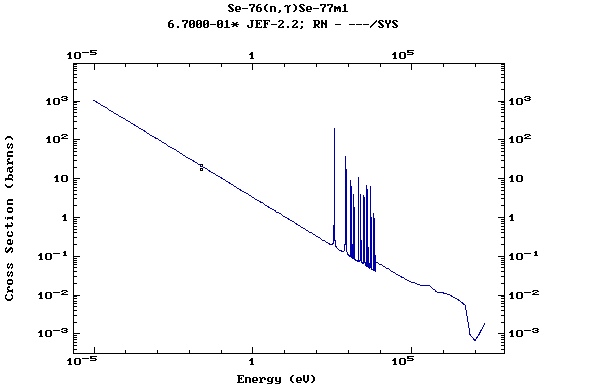
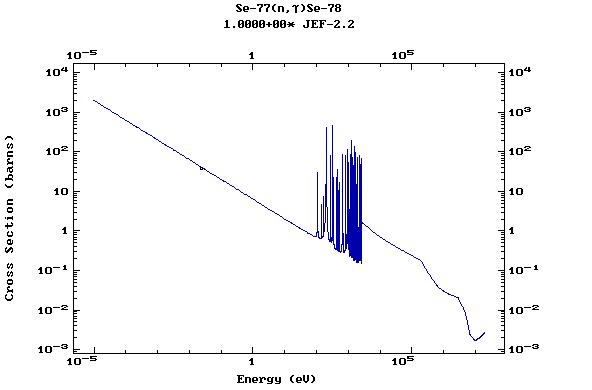
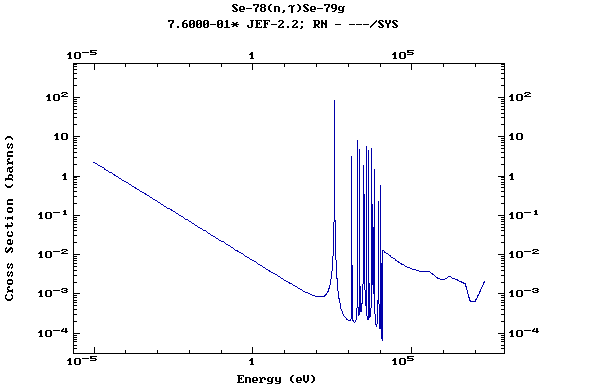
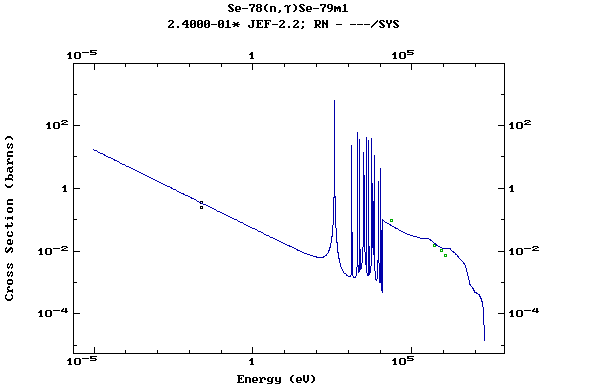
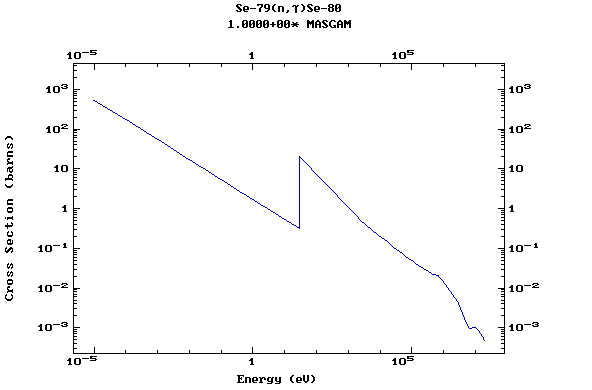
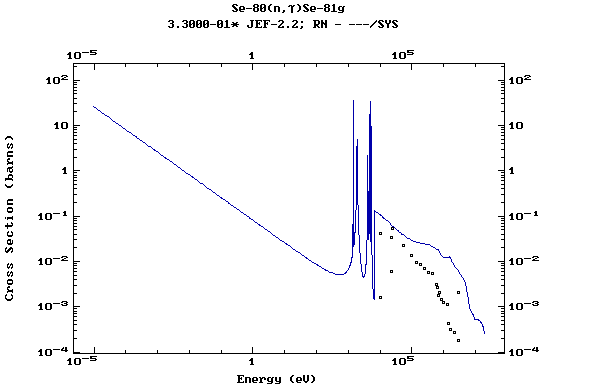
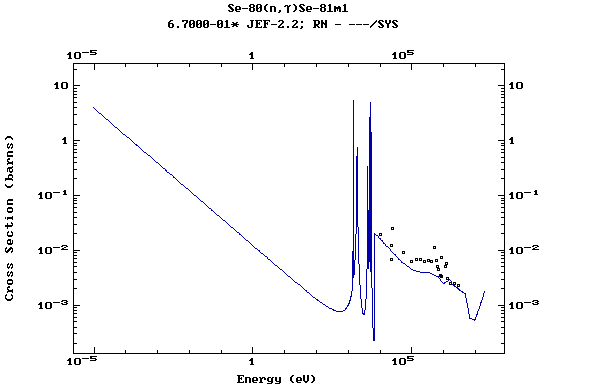
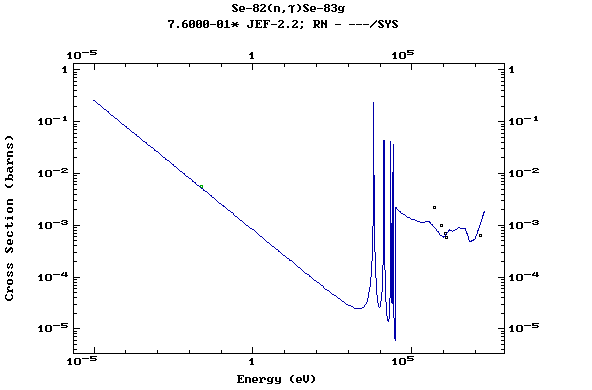
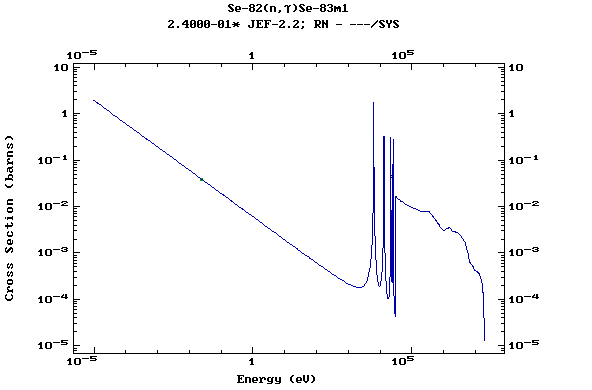
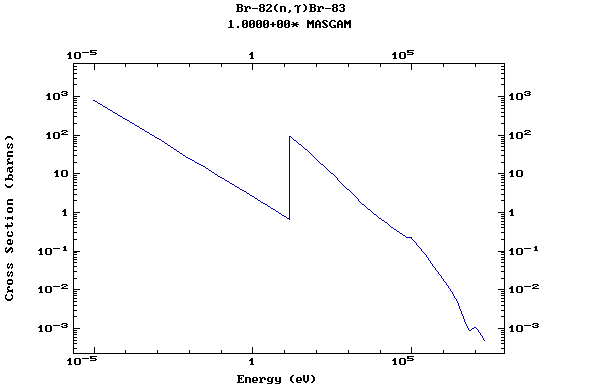
Z=35, Br
(Bromine)
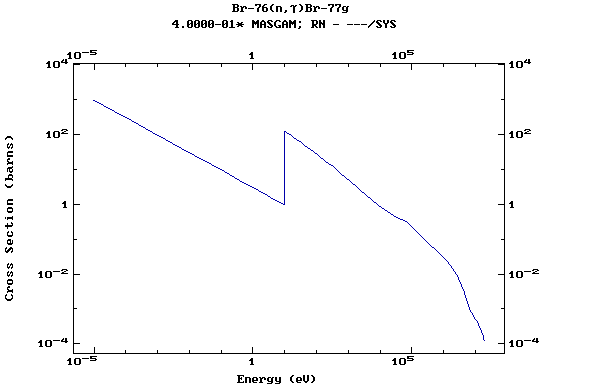
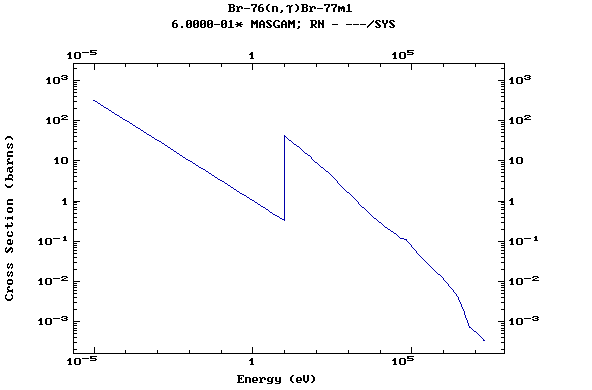
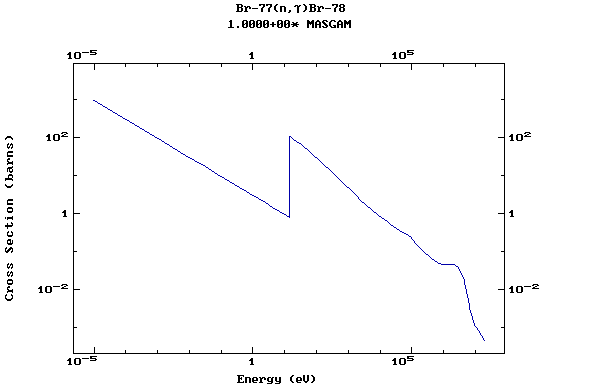
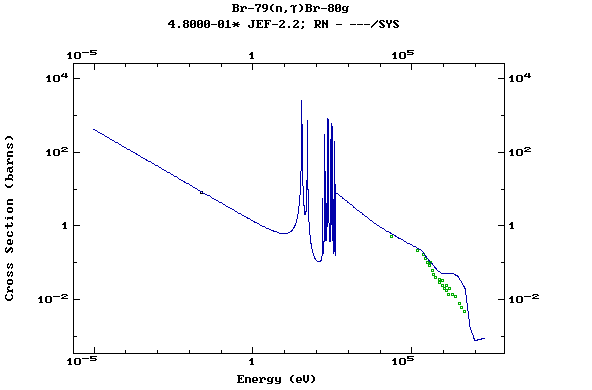
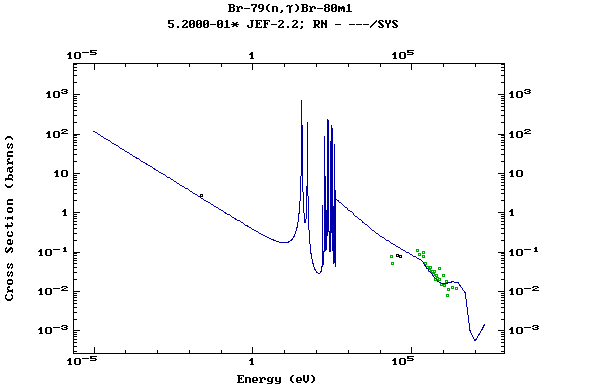
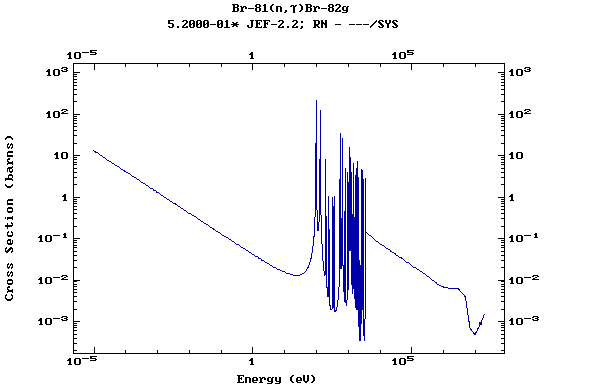
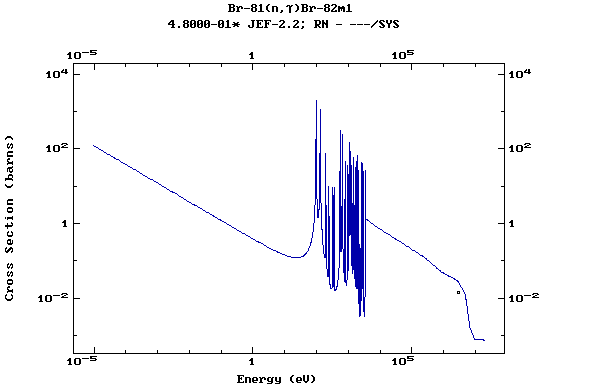
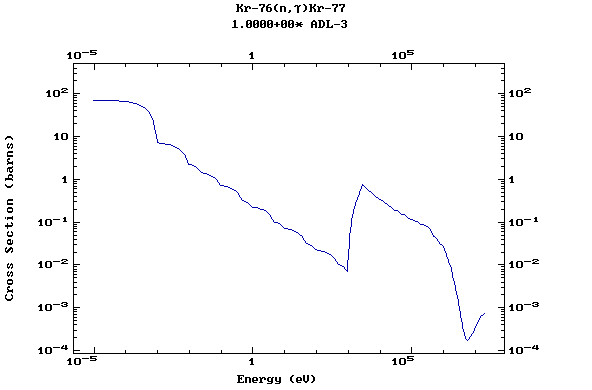
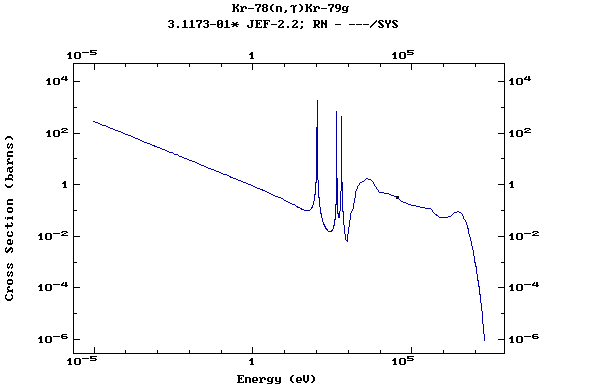
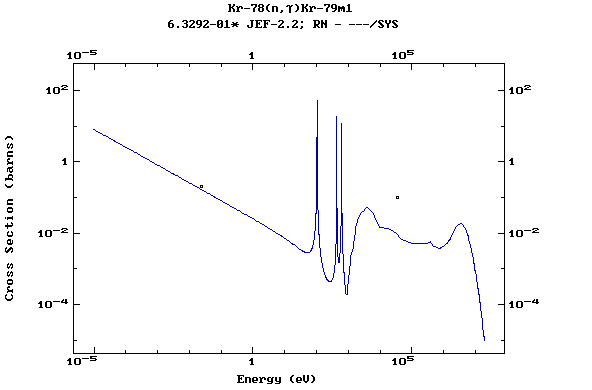
Z=36, Kr
(Krypton)
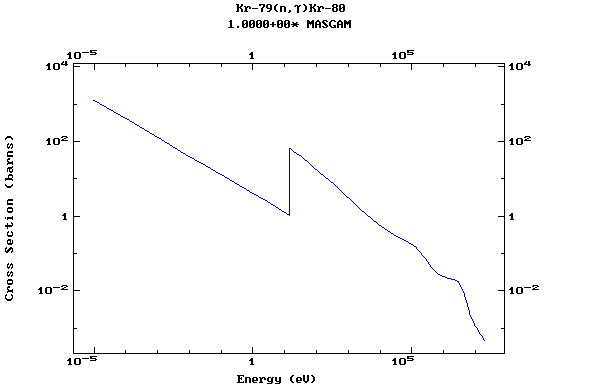
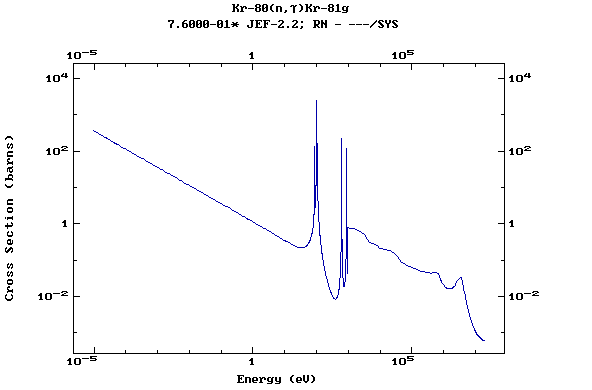
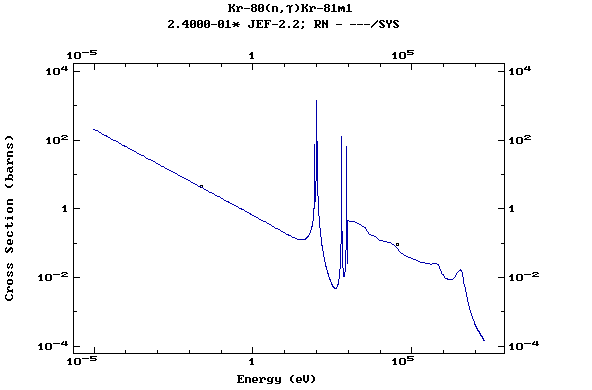
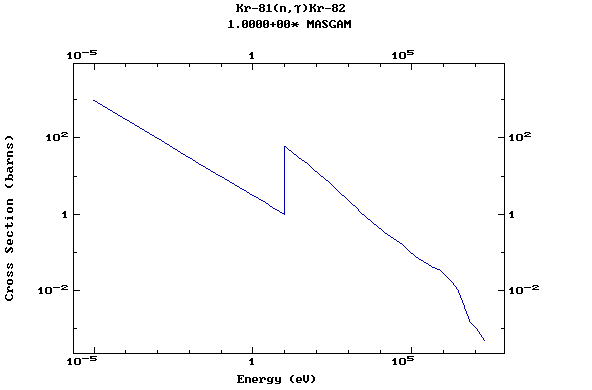
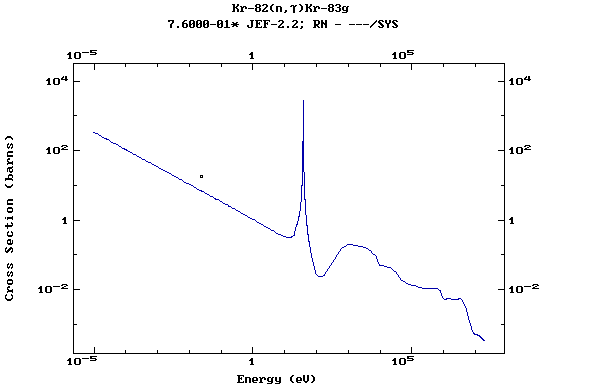
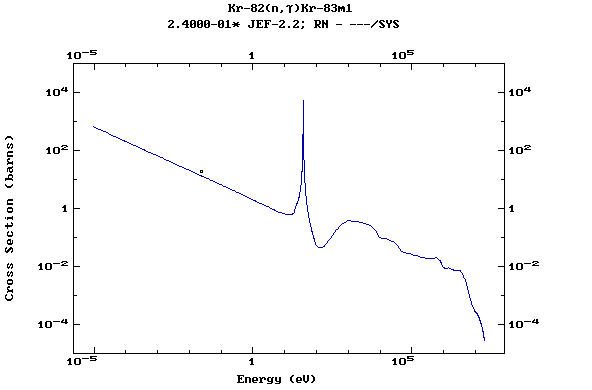
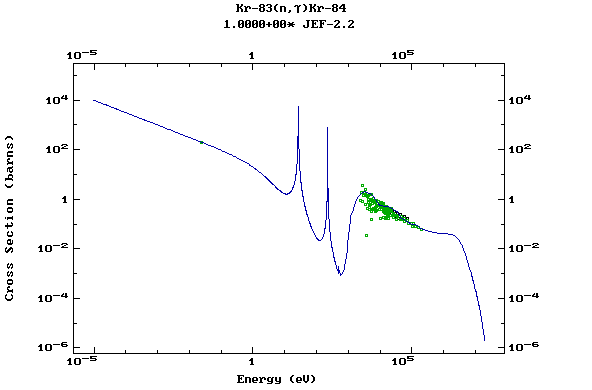
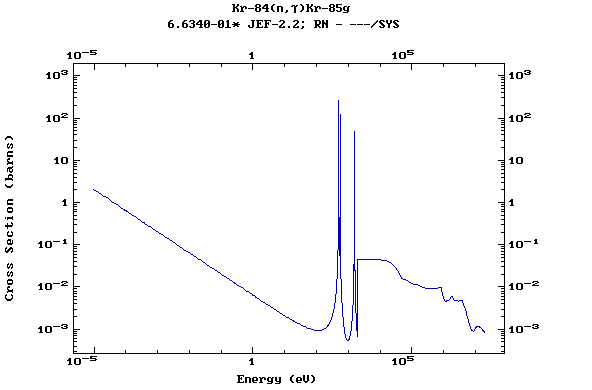
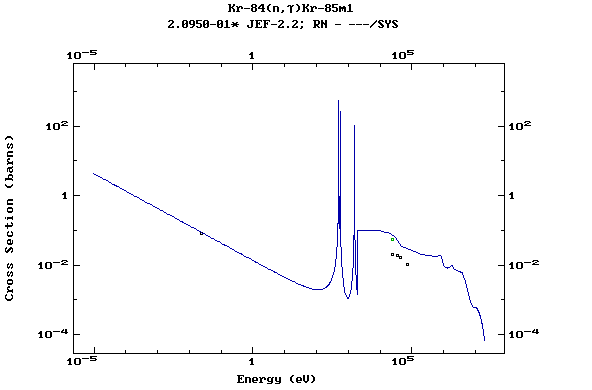
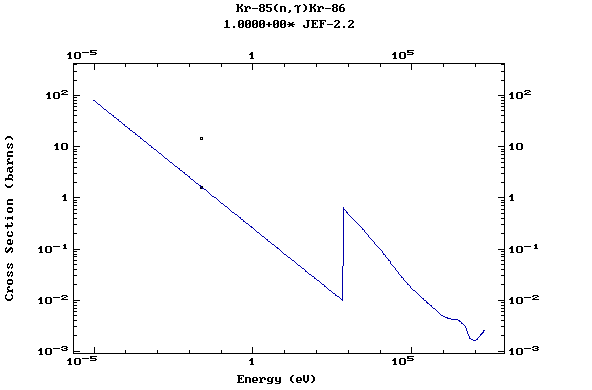
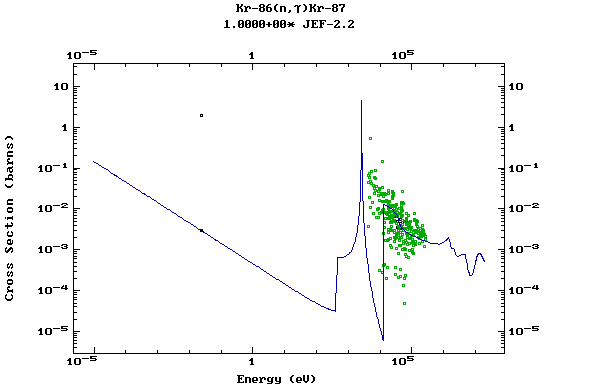
Z=37, Rb
(Rubidium)
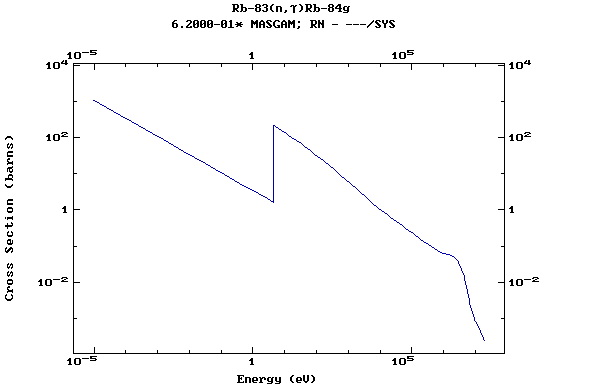
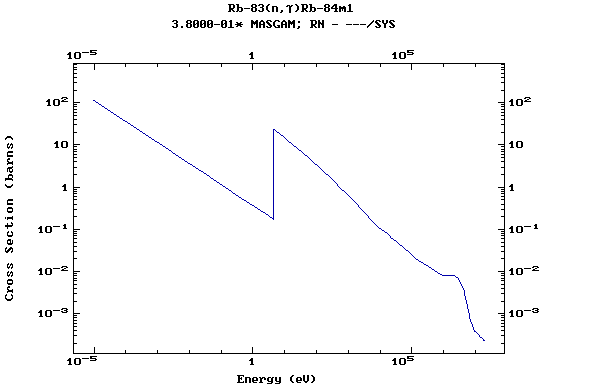
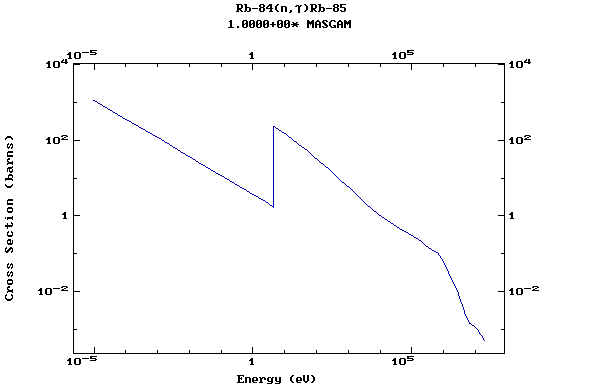
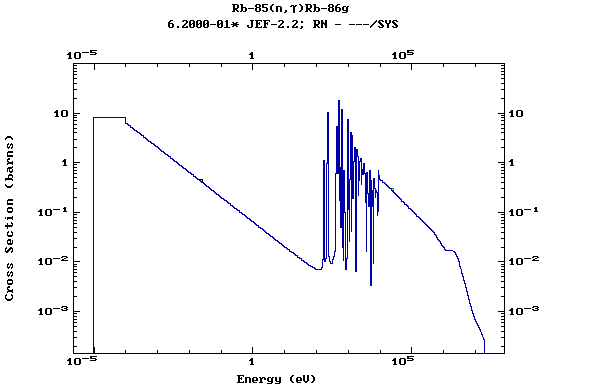
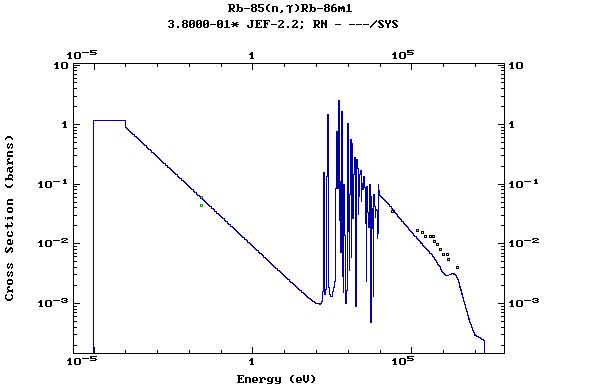
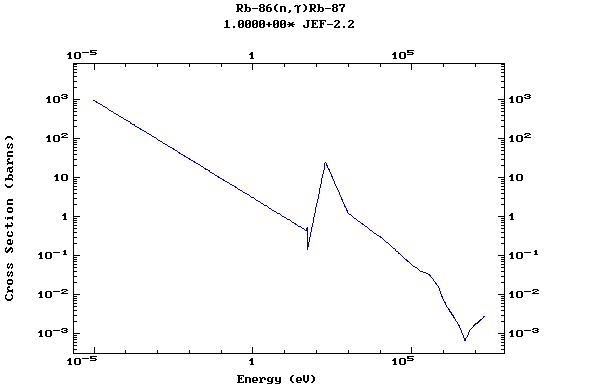
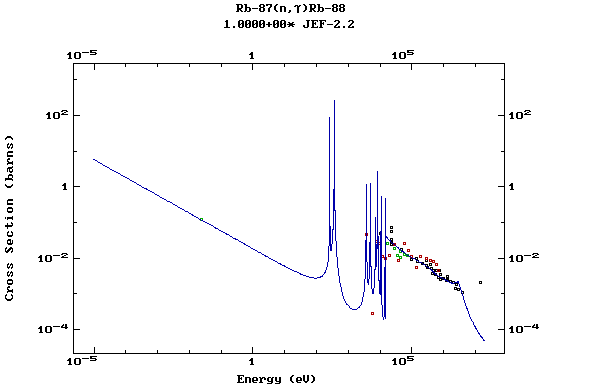
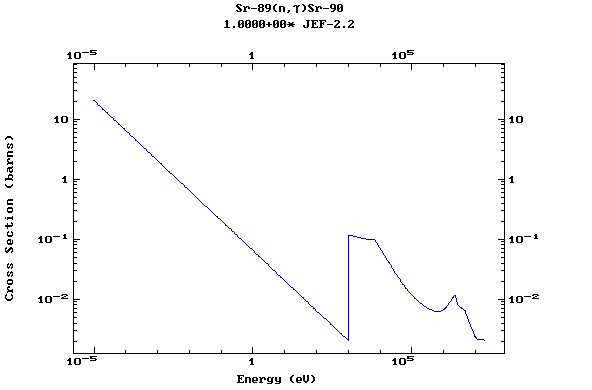
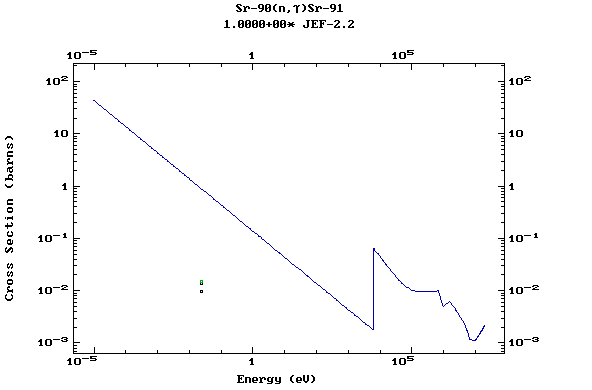
Z=38, Sr
(Strontium)
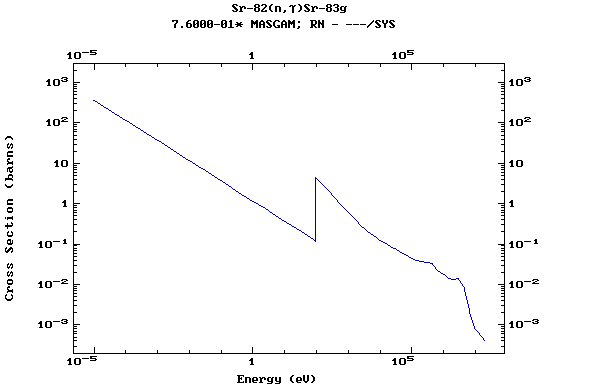
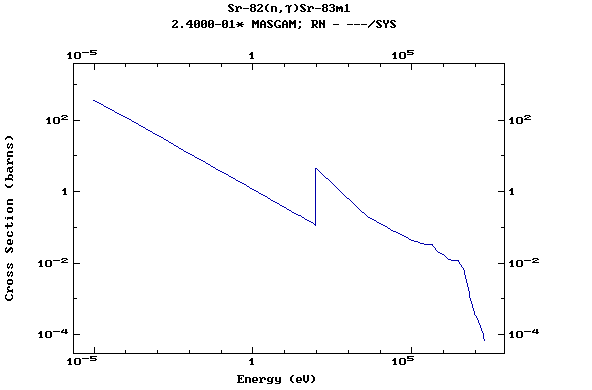
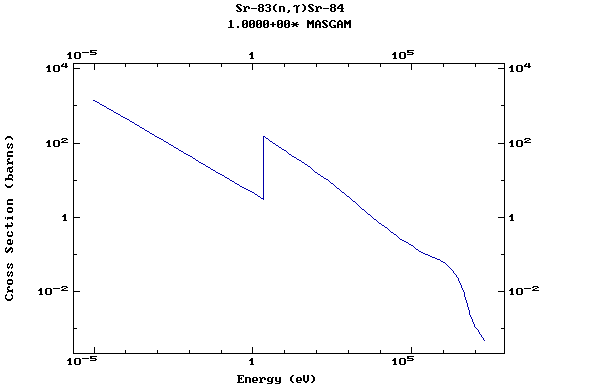
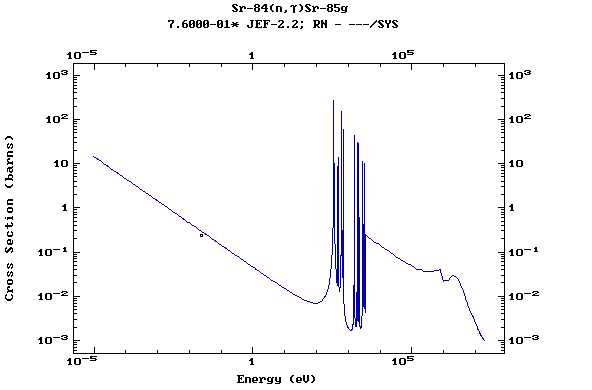
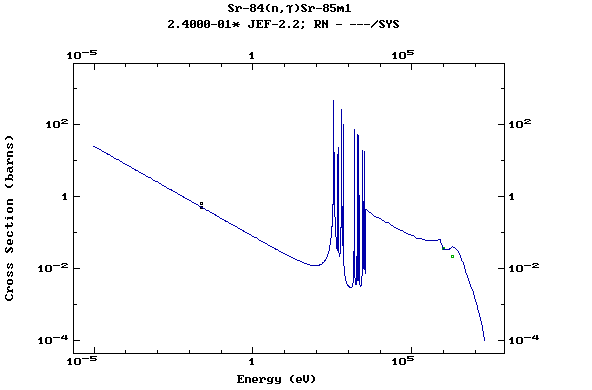
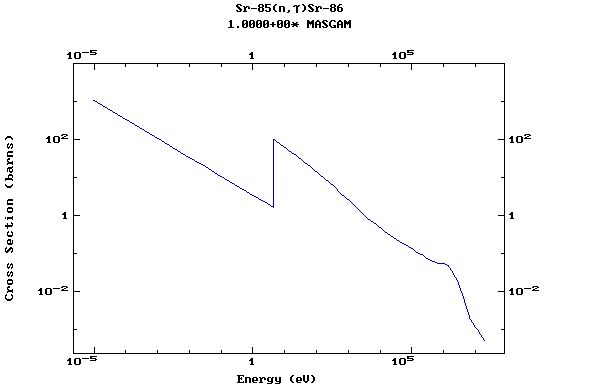
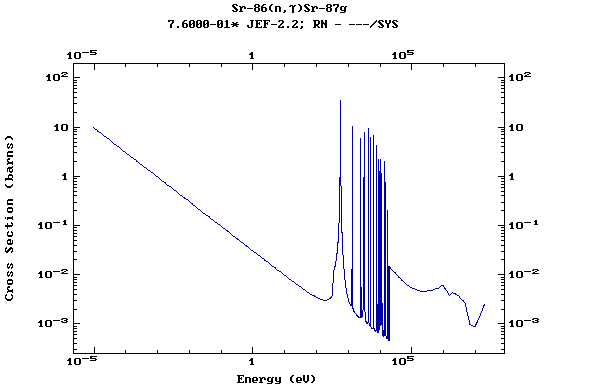
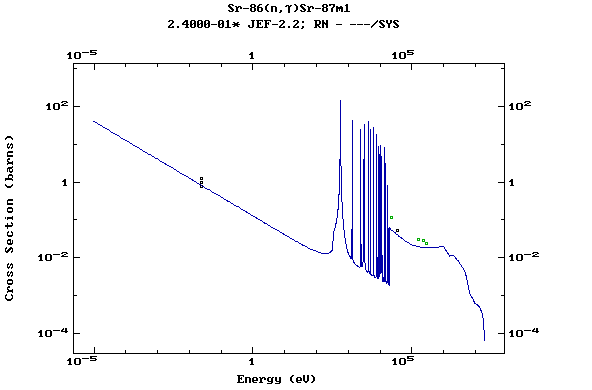
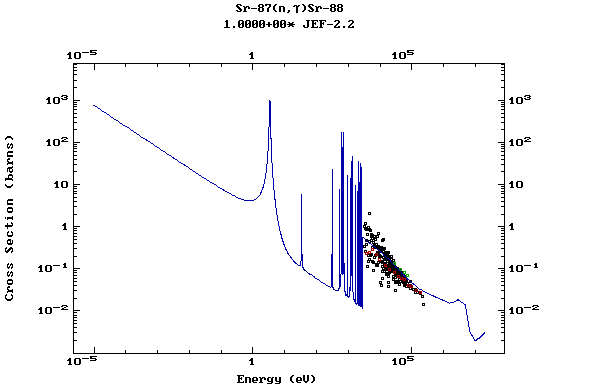
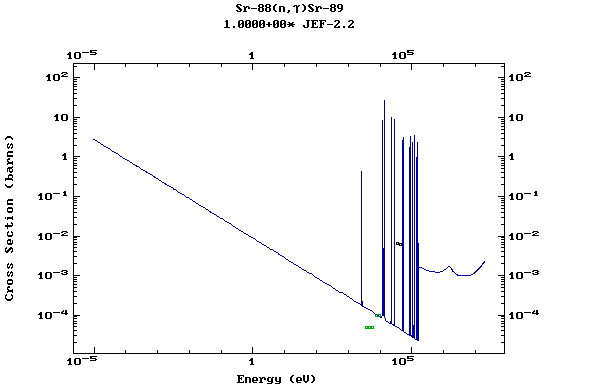
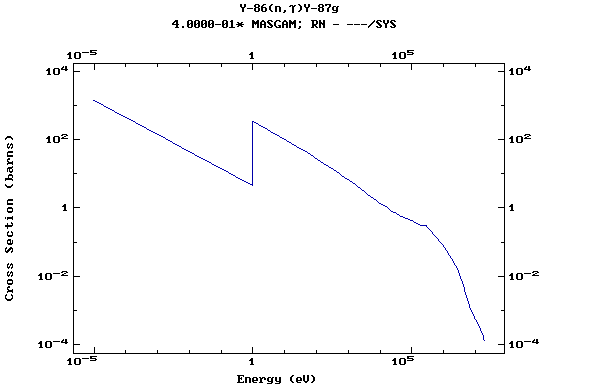
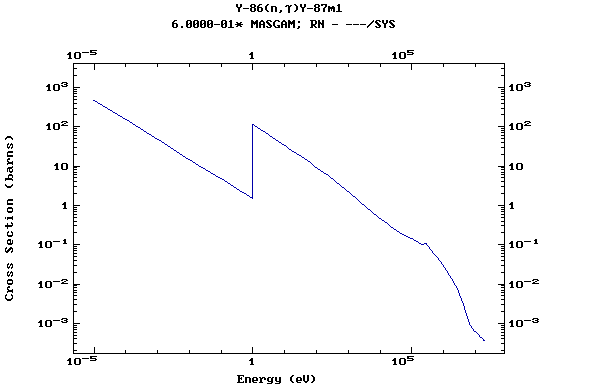
Z=39, Y
(Yttrium)
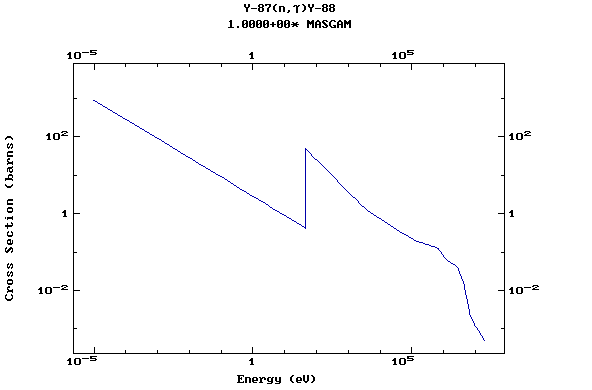
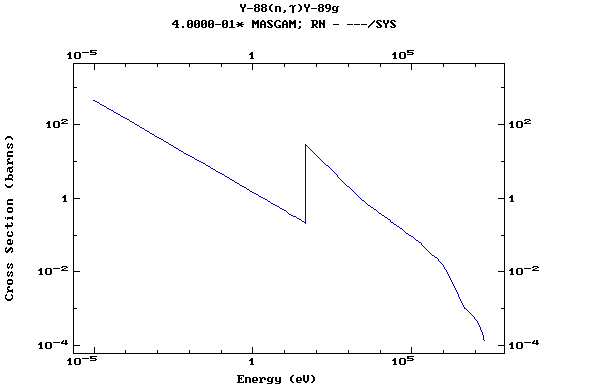
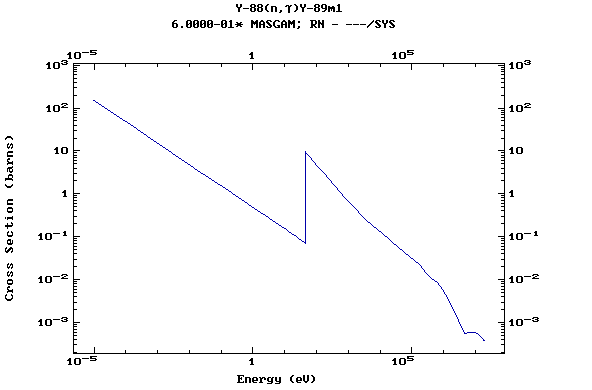
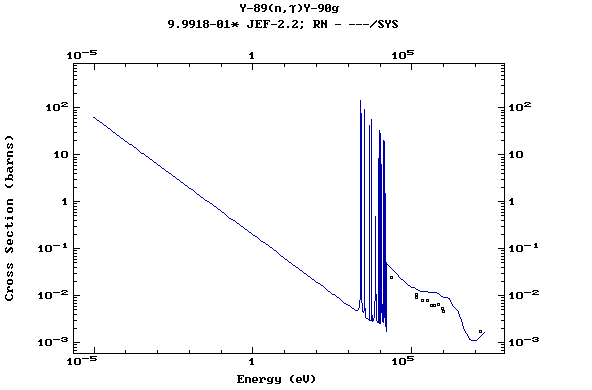
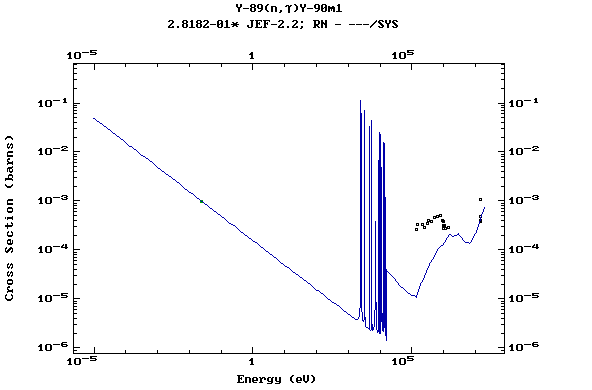
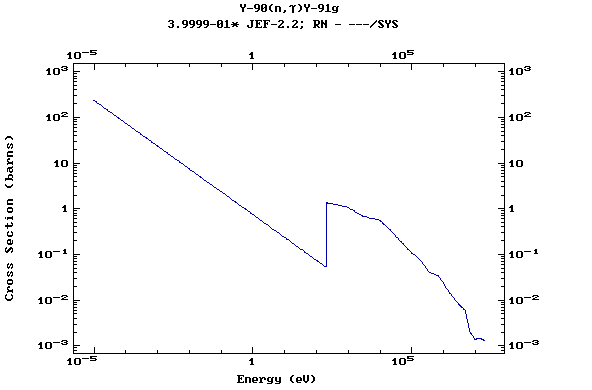
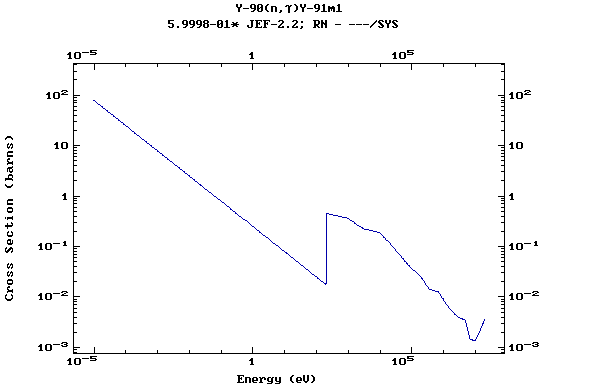
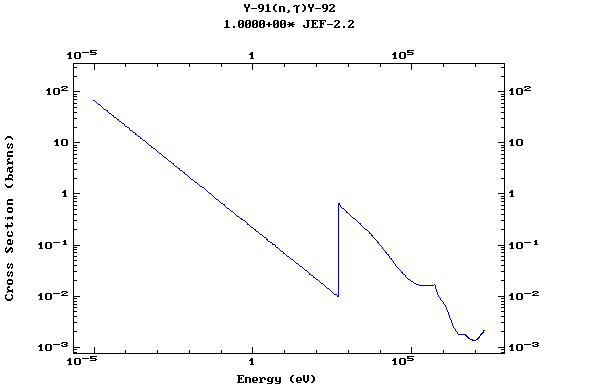
Z=40, Zr
(Zirconium)
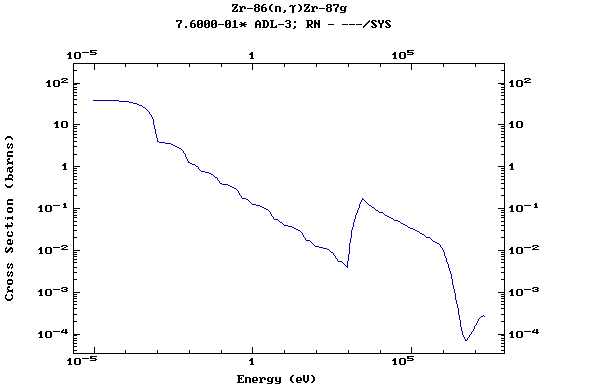
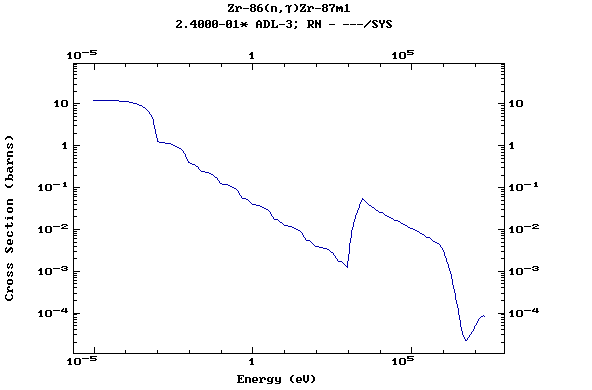
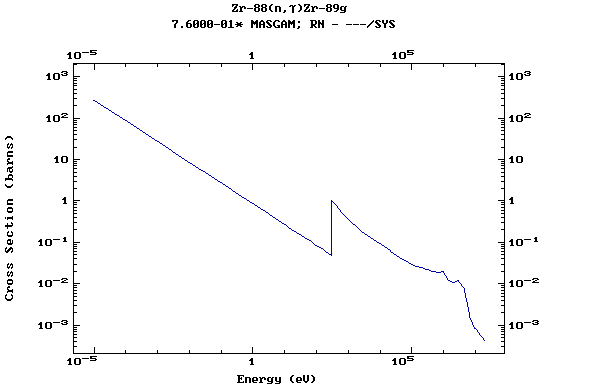
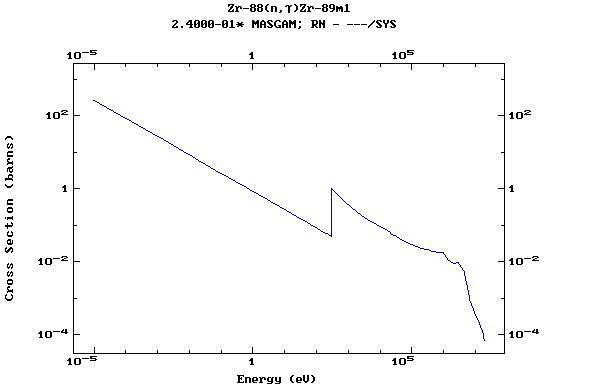
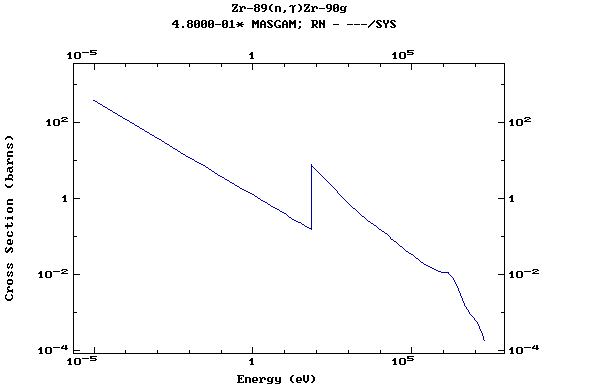
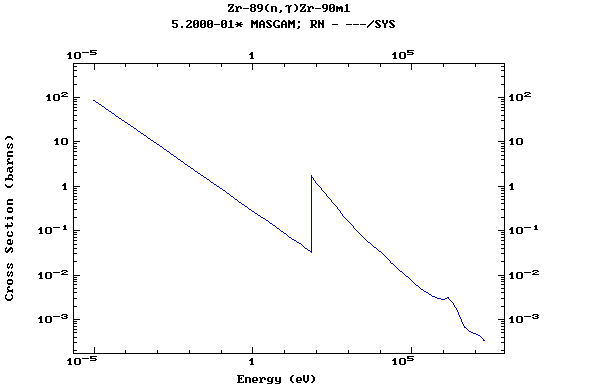
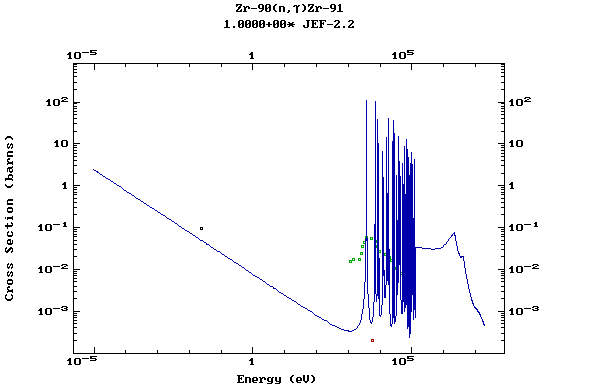
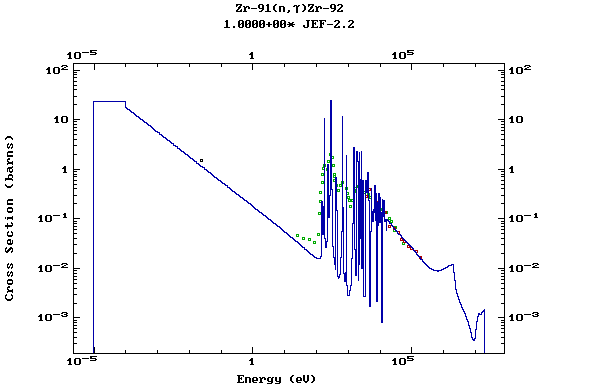
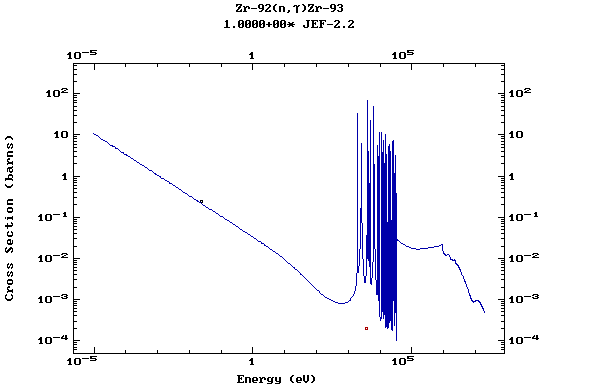
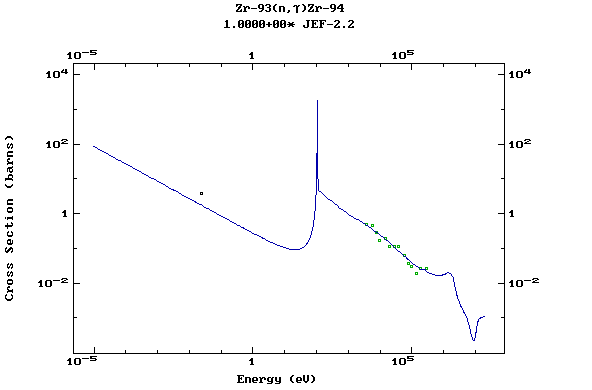
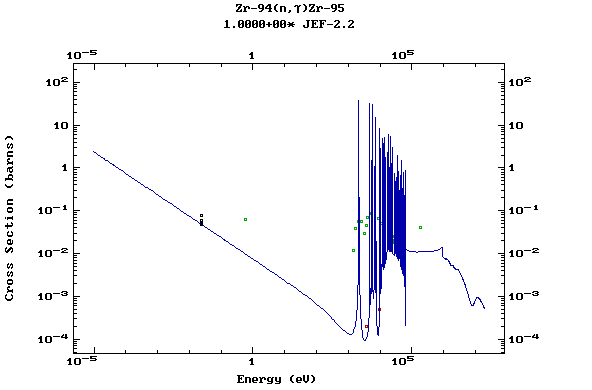
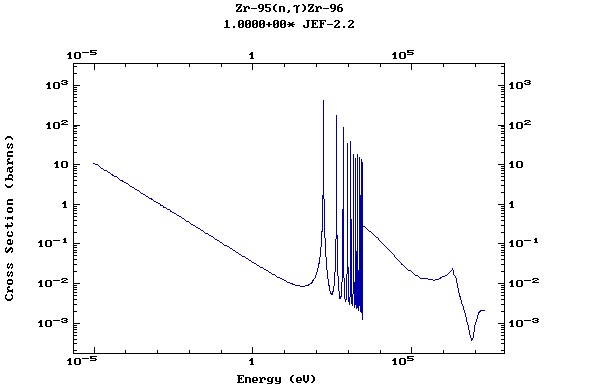
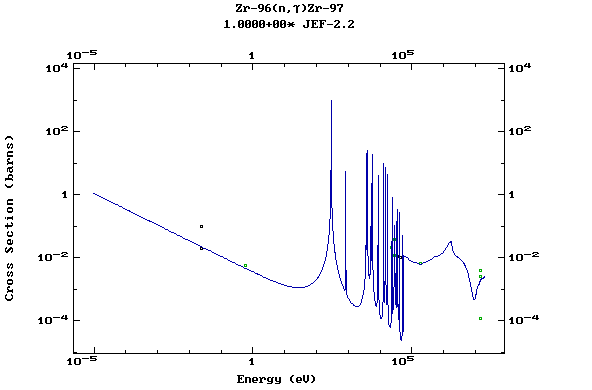
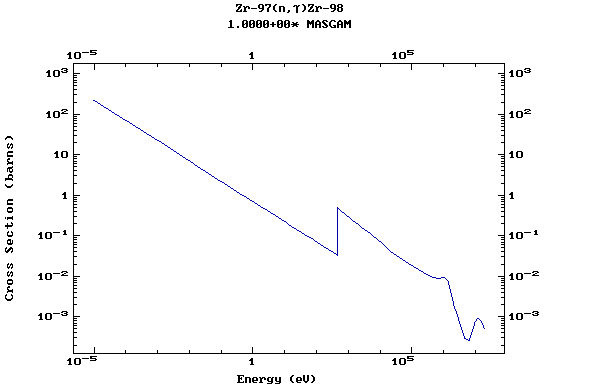
Z=41, Nb
(Niobium)
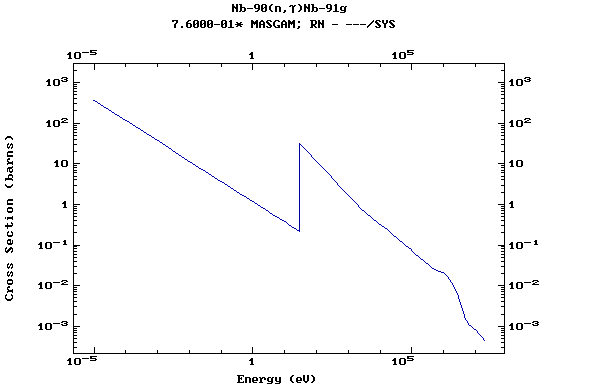
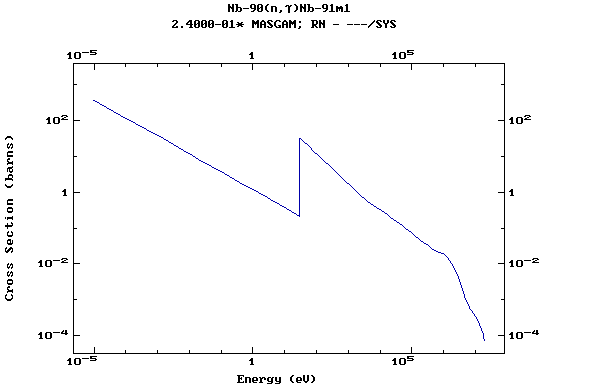
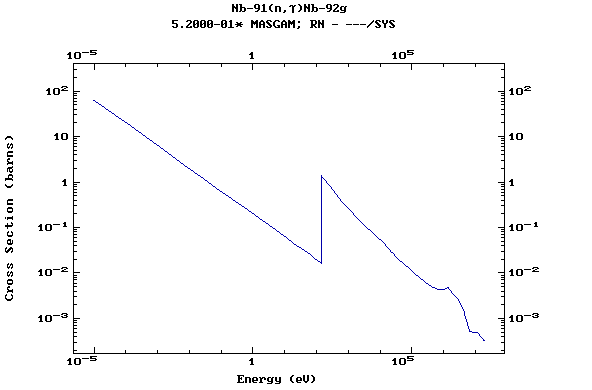
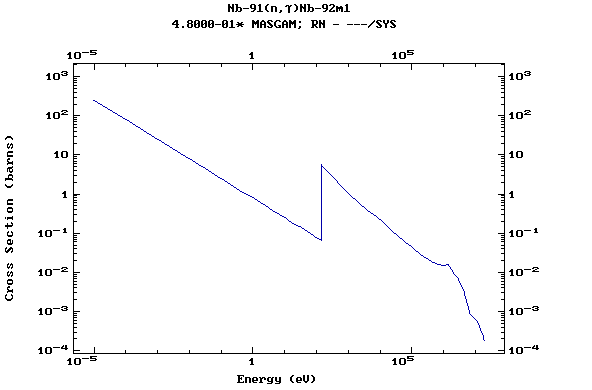
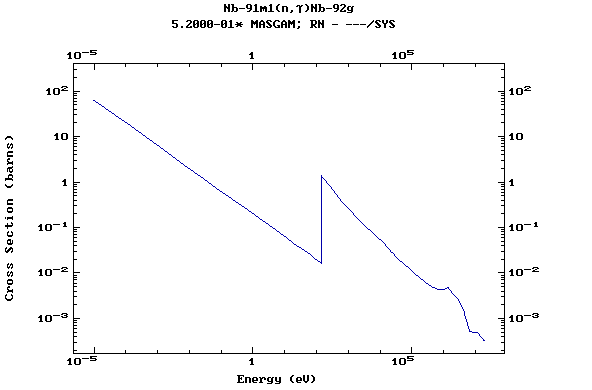
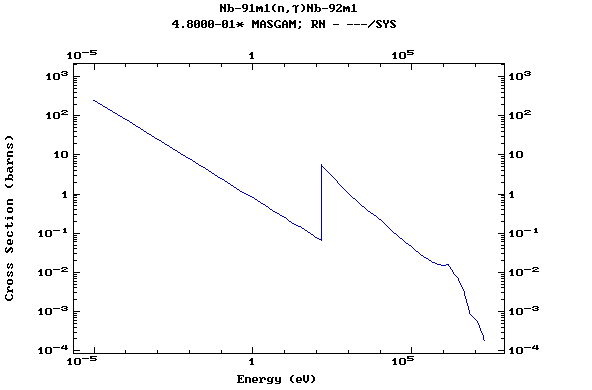
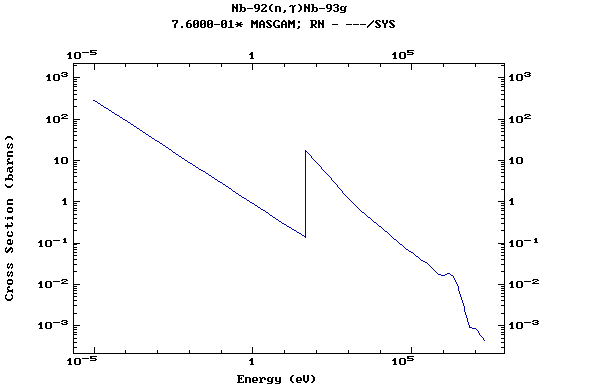
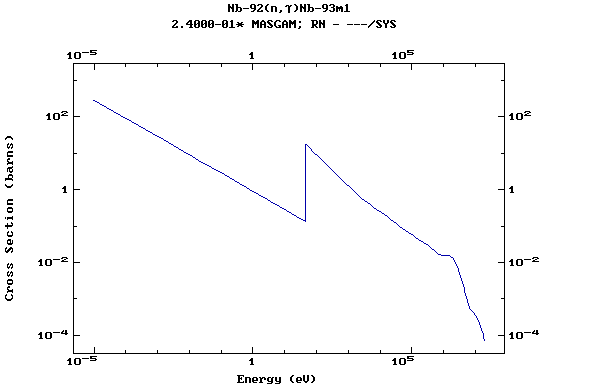
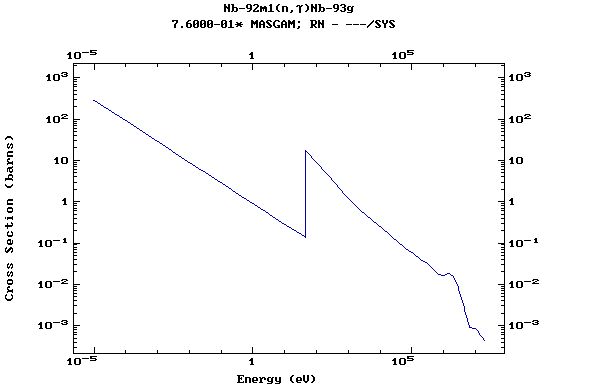
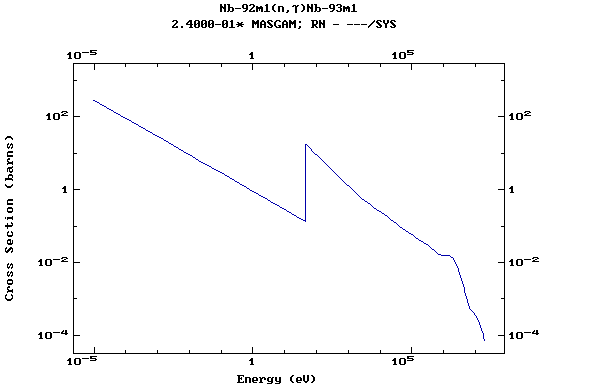
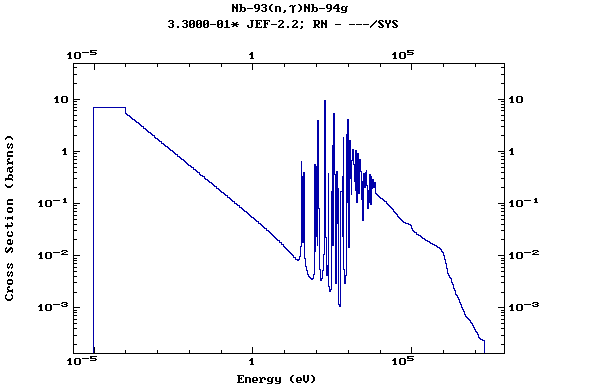
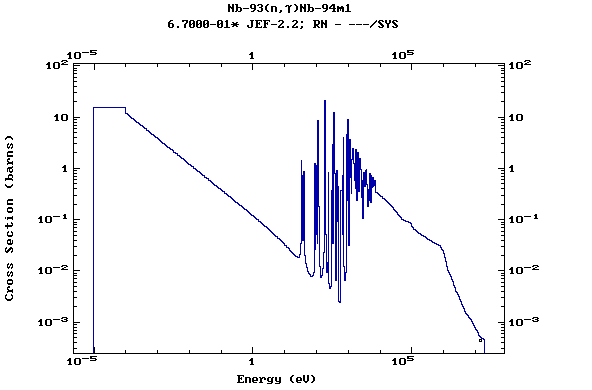
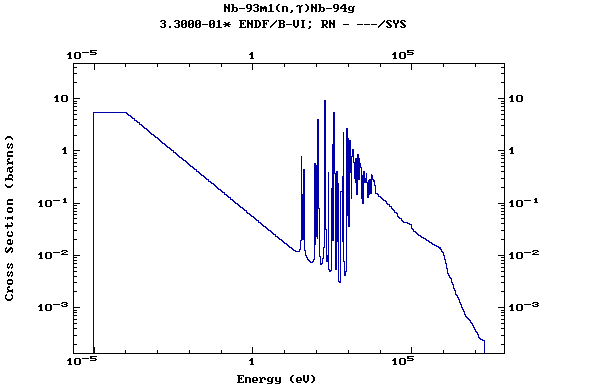
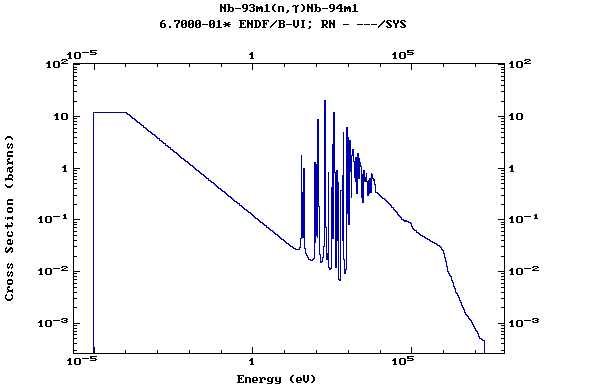
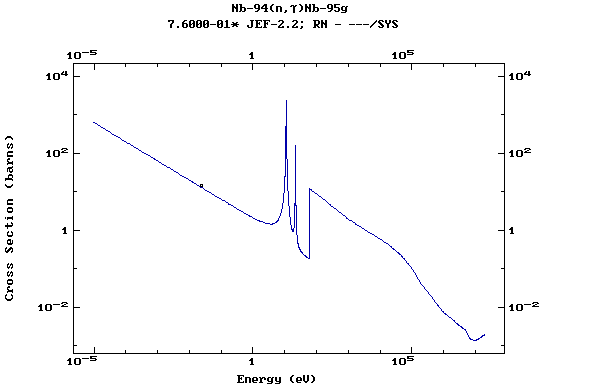
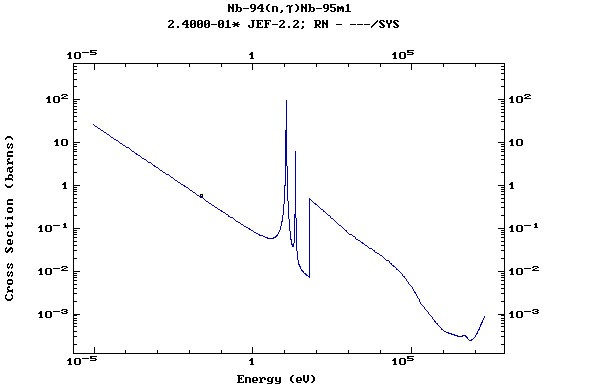
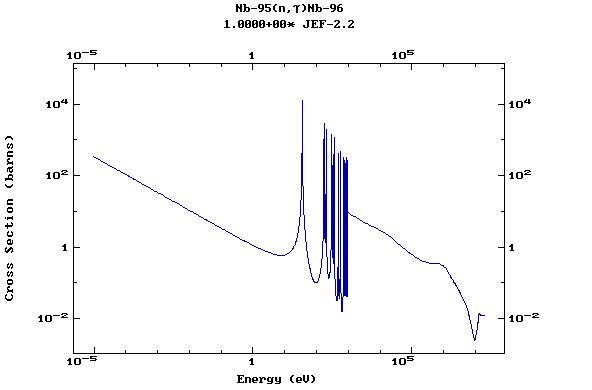
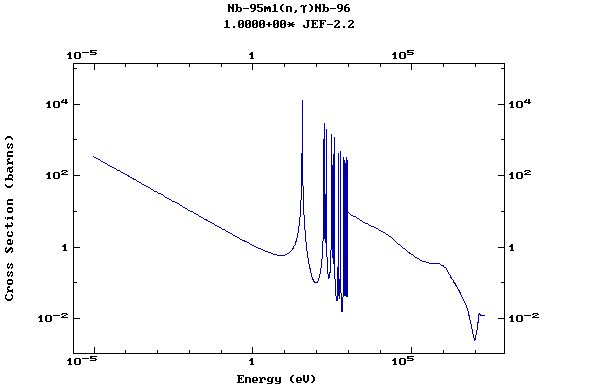
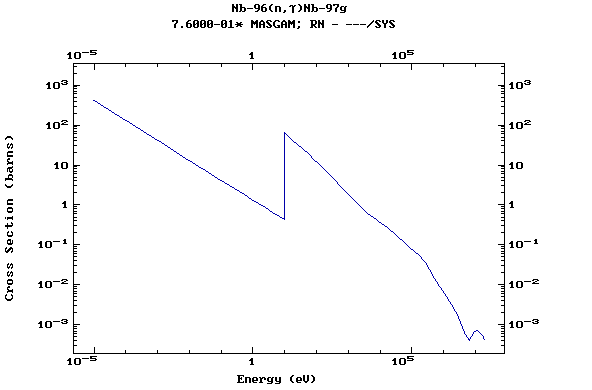
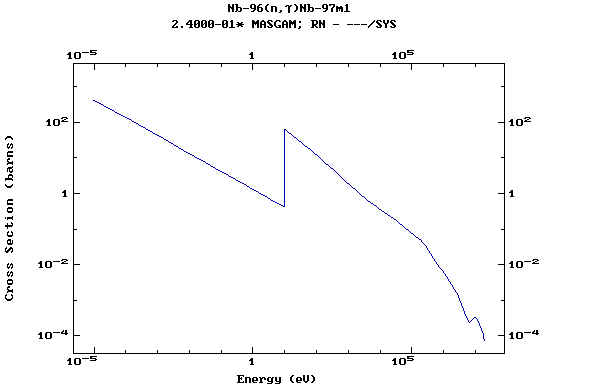
Z=42, Mo
(Molybdenum)
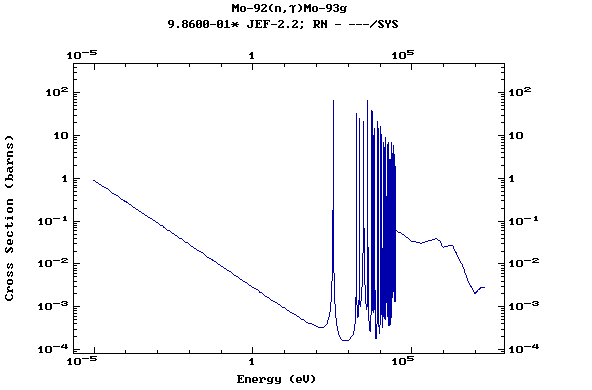
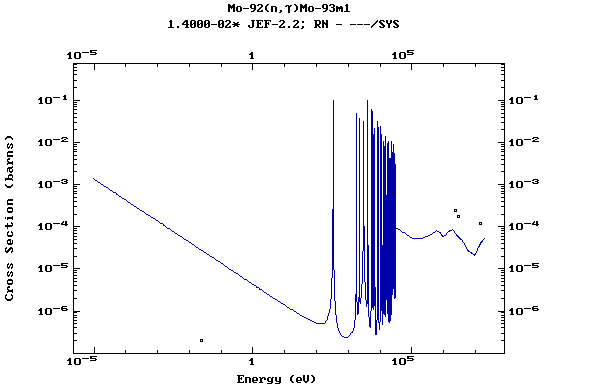
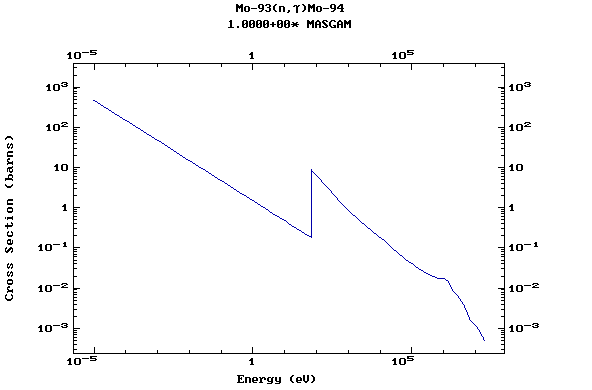
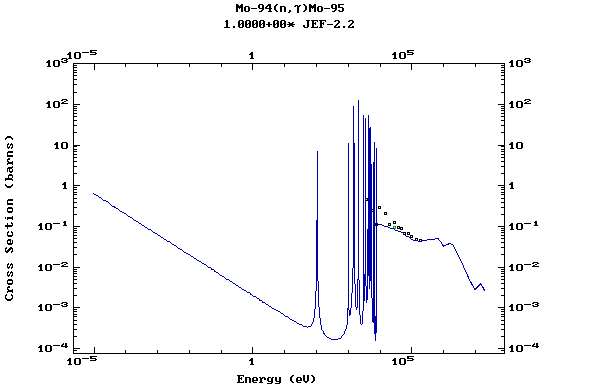
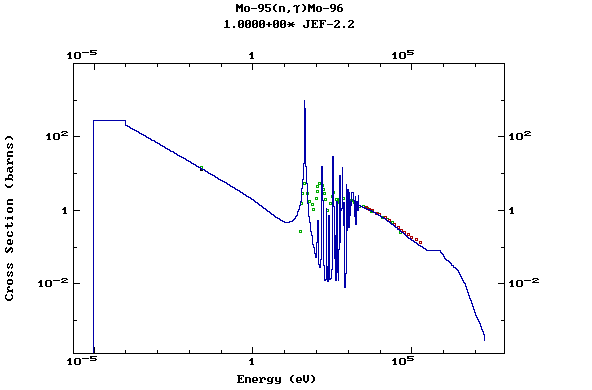
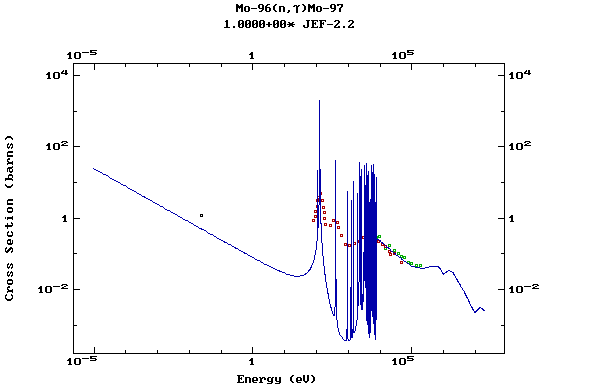
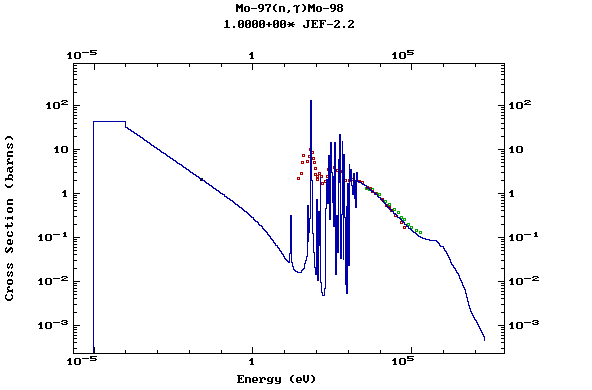
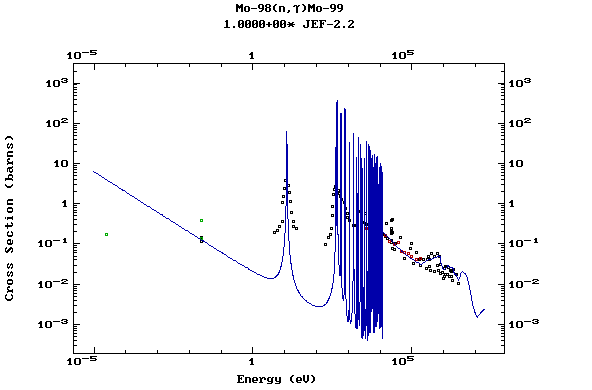
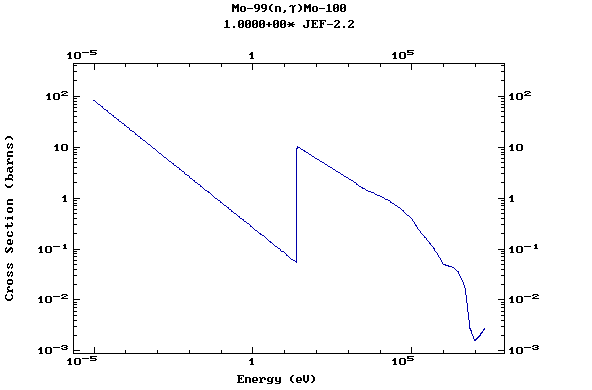
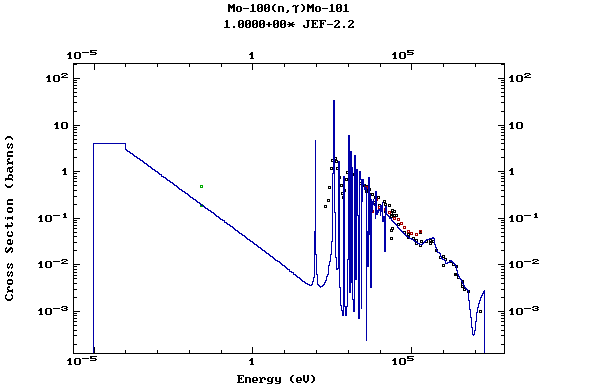
Z=43, Tc
(Technetium)
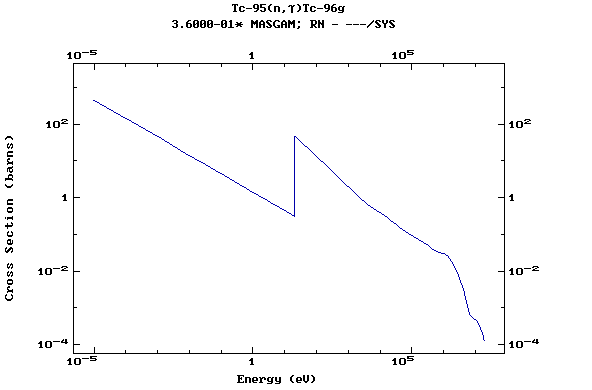
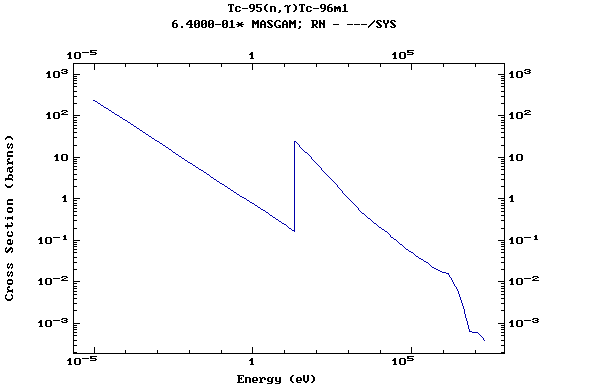
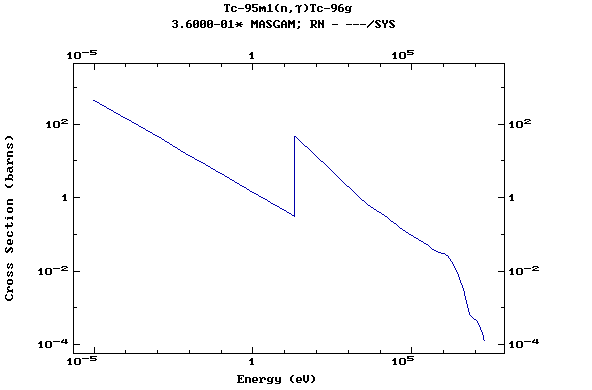
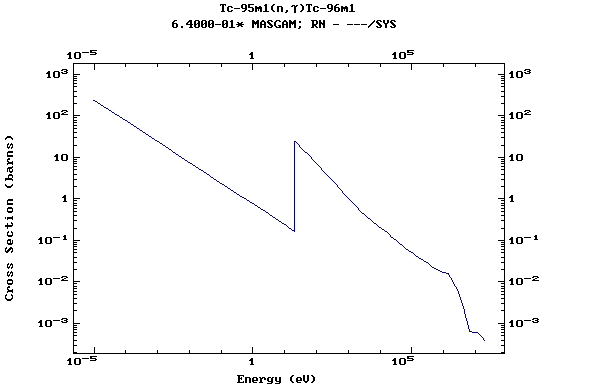
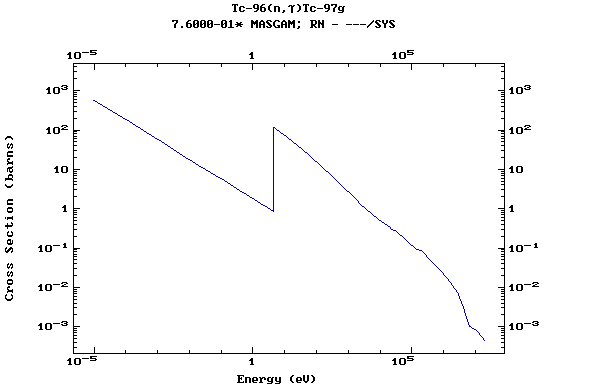
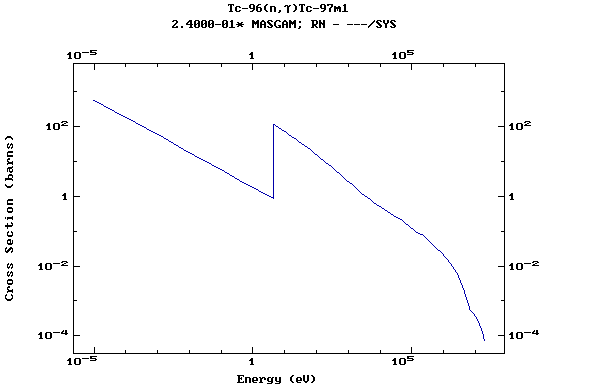
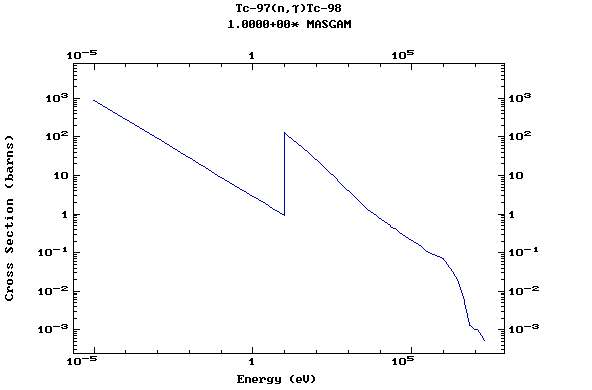
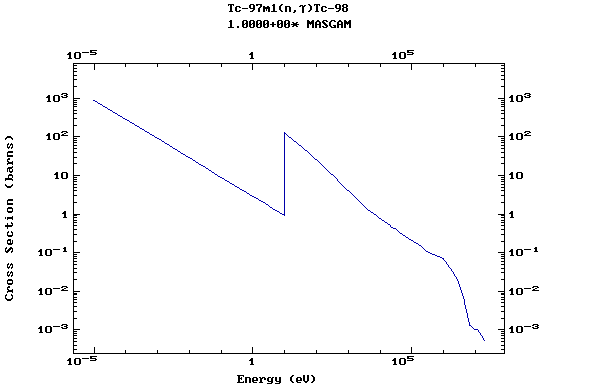
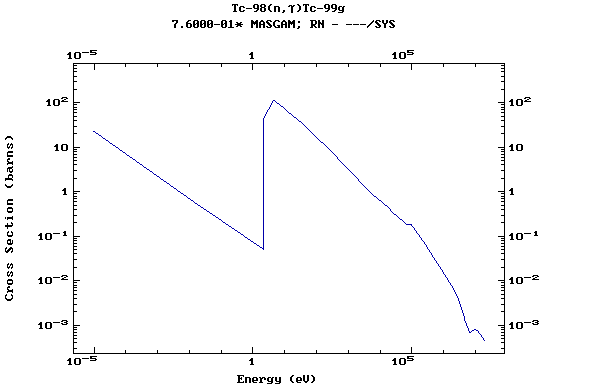
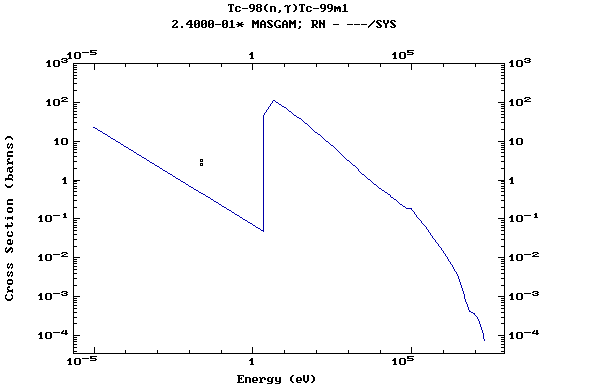
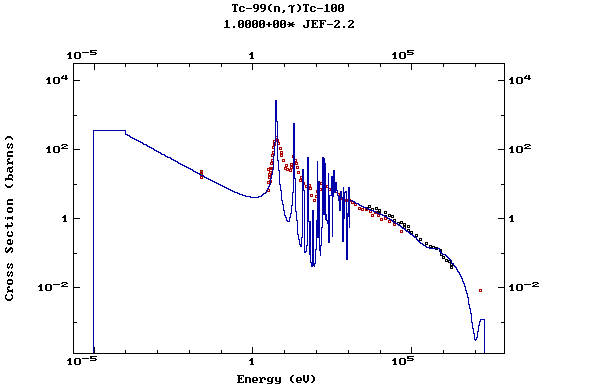
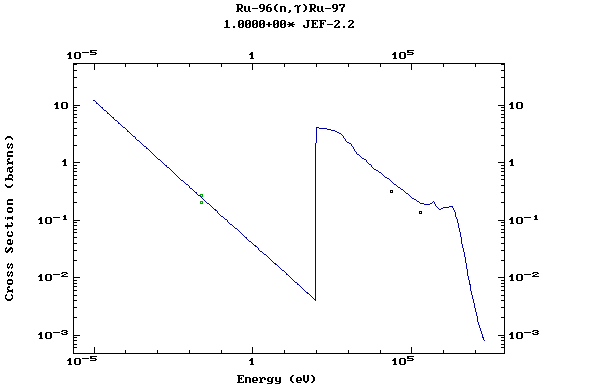
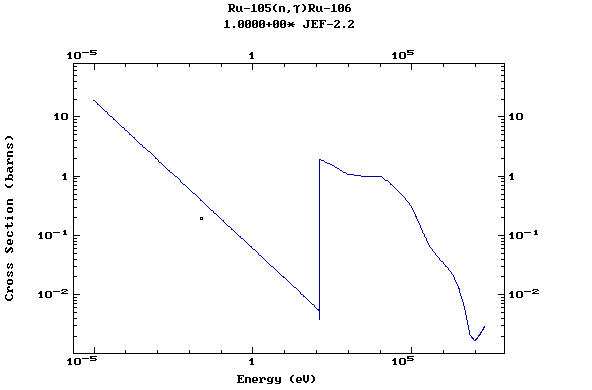
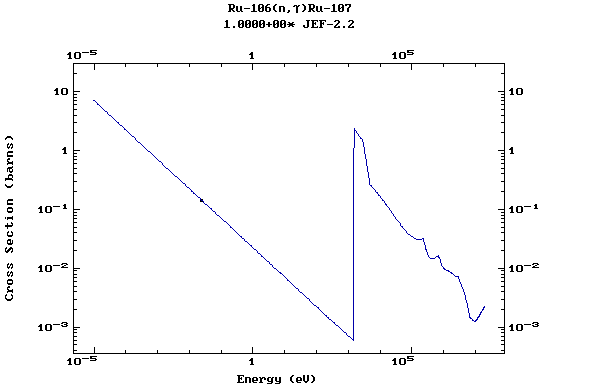
Z=44, Ru
(Ruthenium)
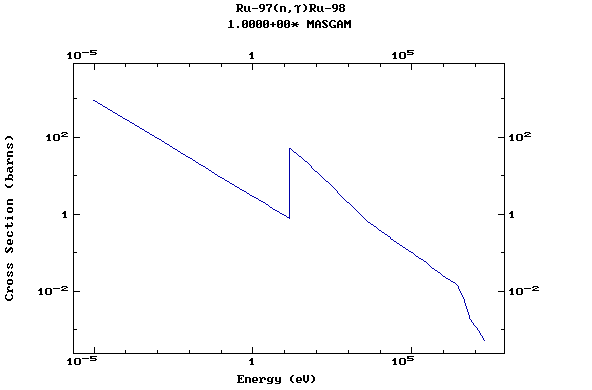
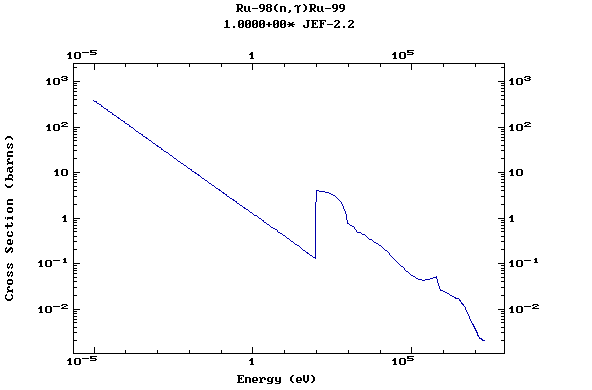
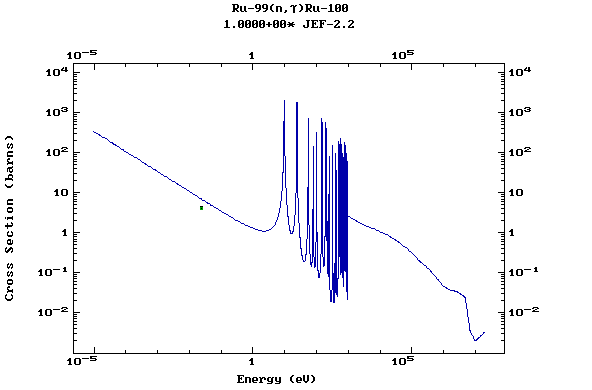
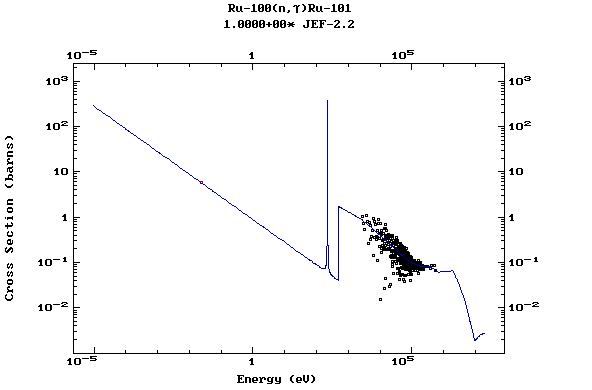
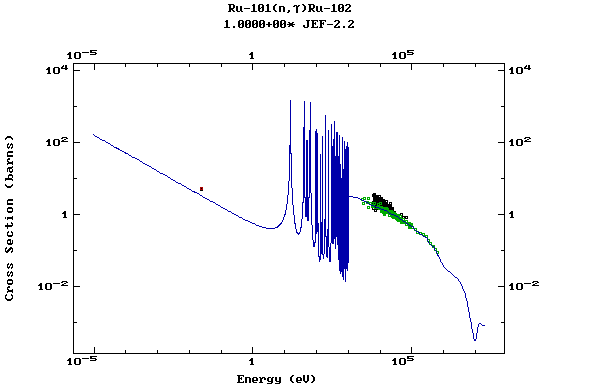
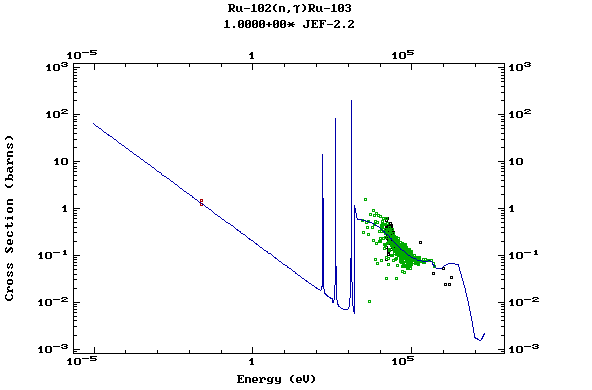
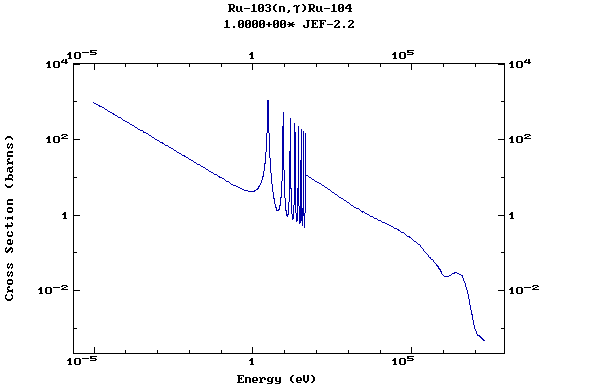
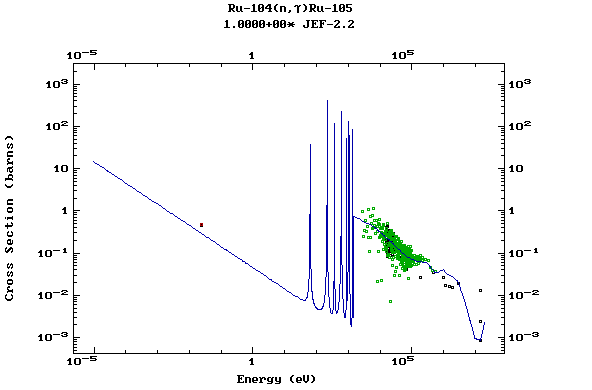
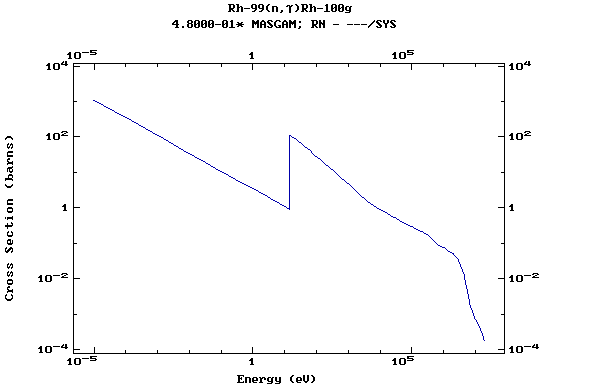
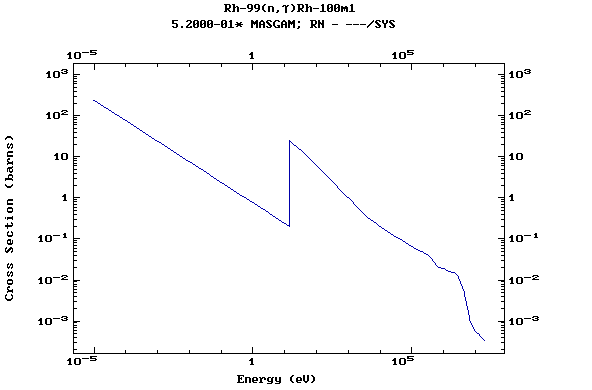
Z=45, Rh
(Rhodium)
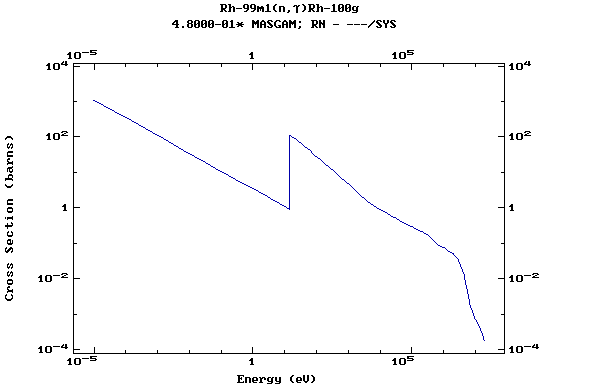
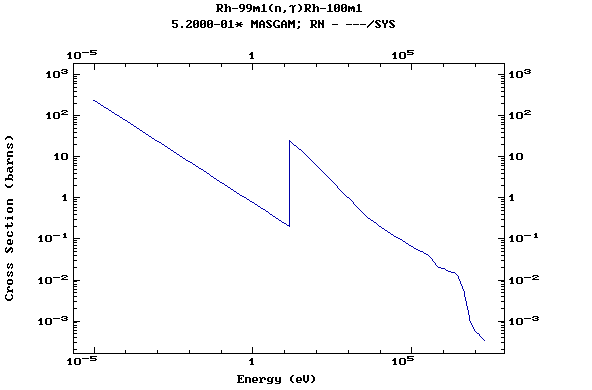
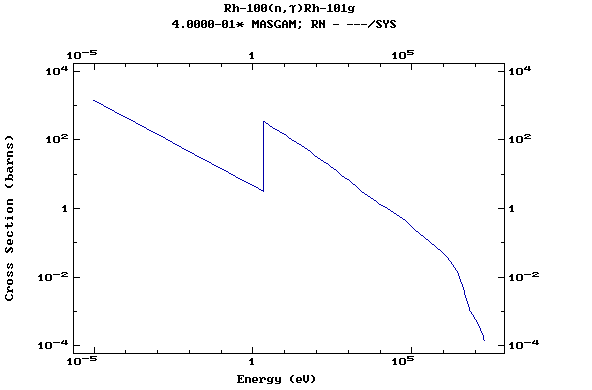
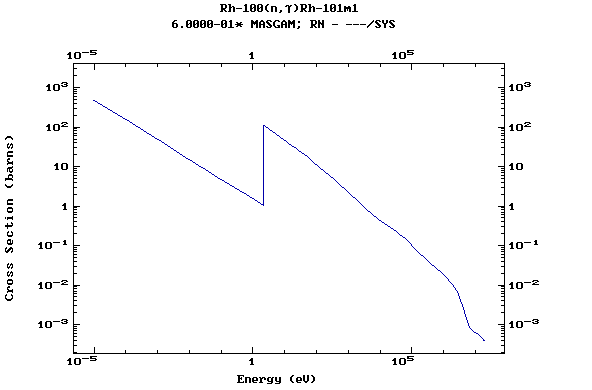
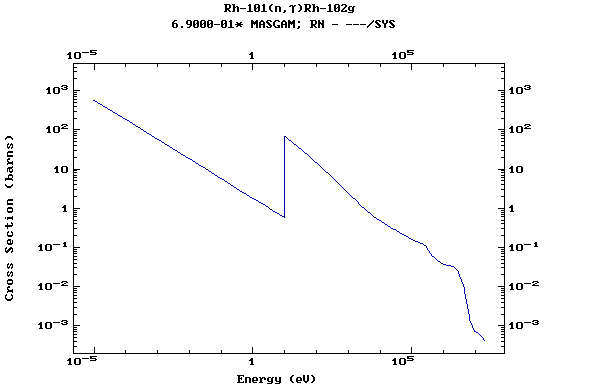
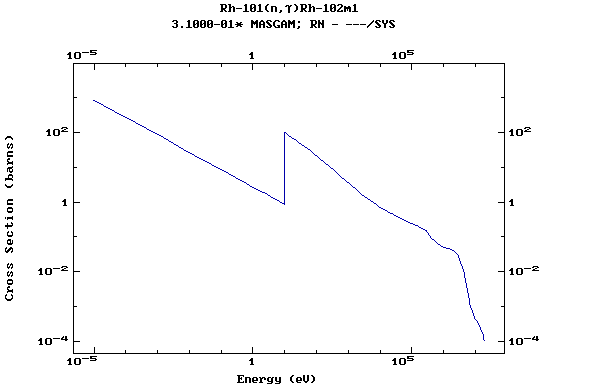
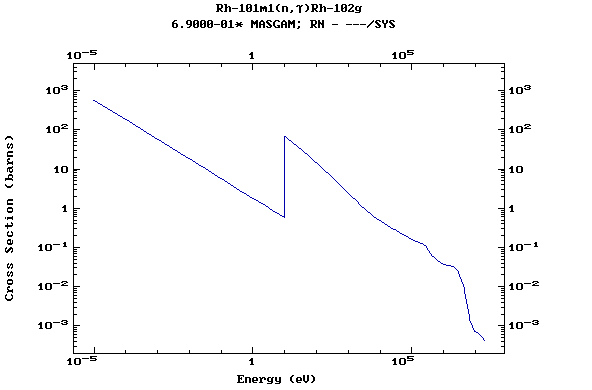
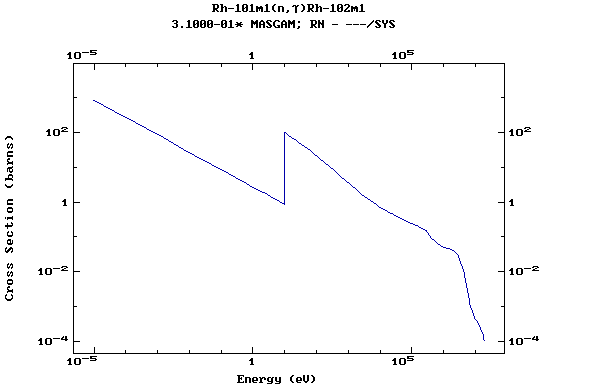
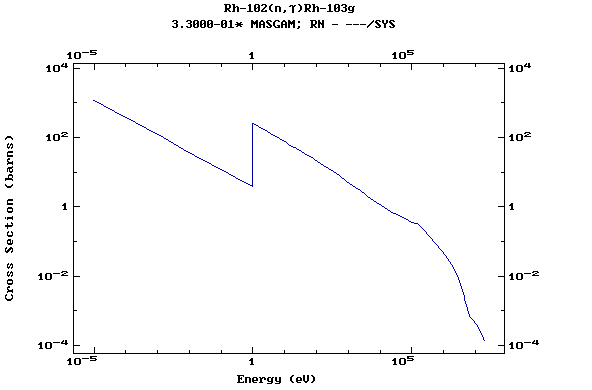
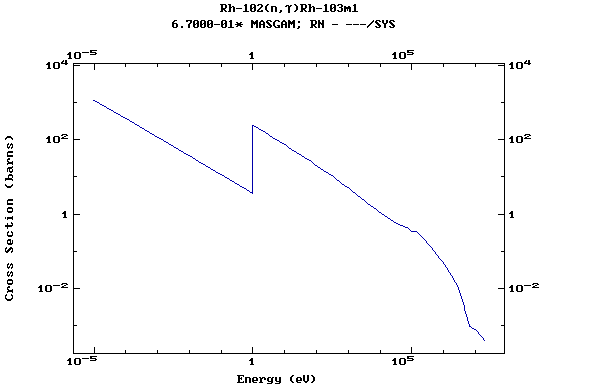
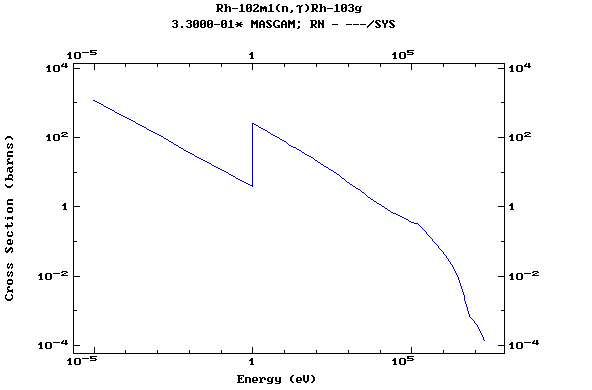
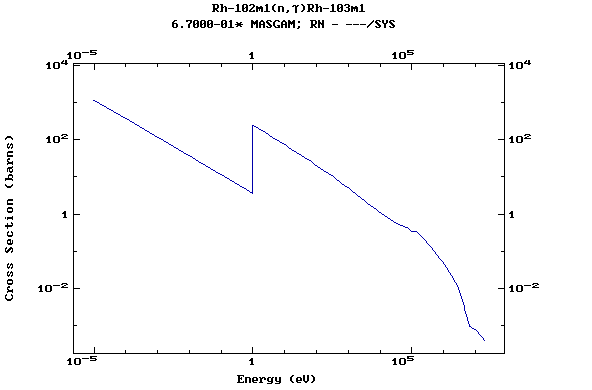
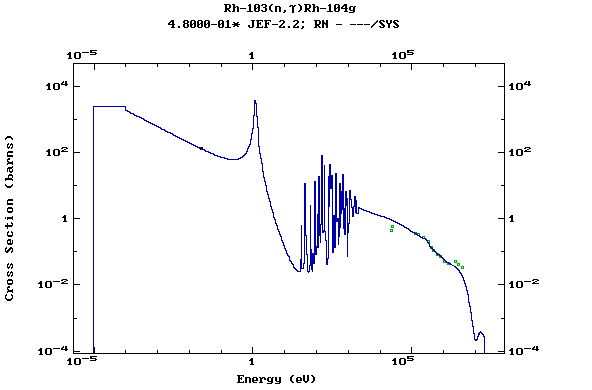
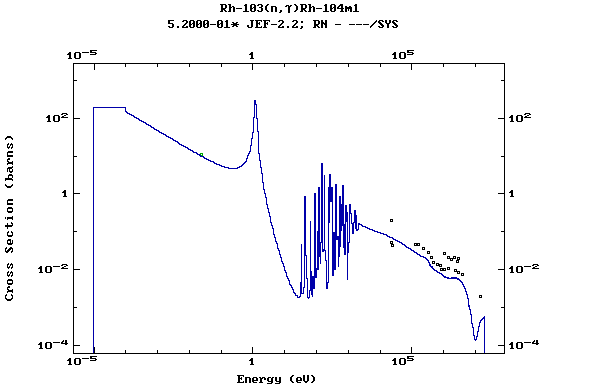
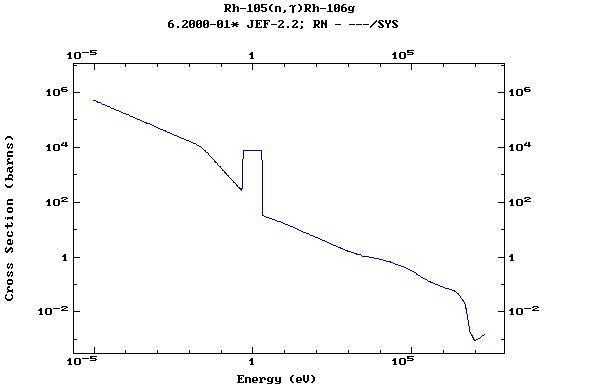
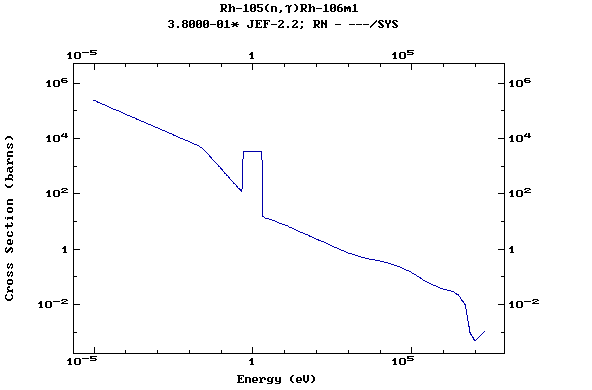
Z=46, Pd
(Palladium)
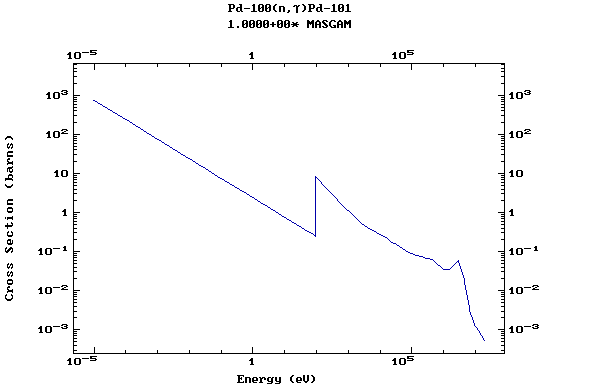

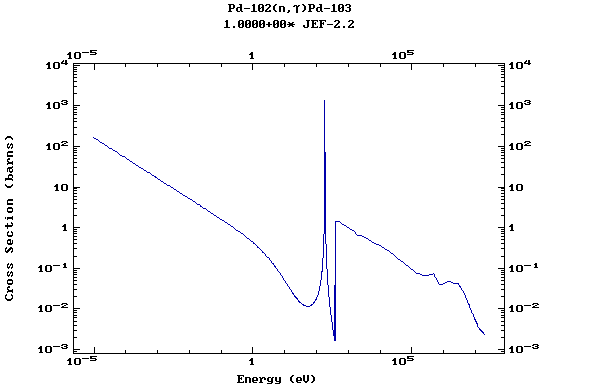
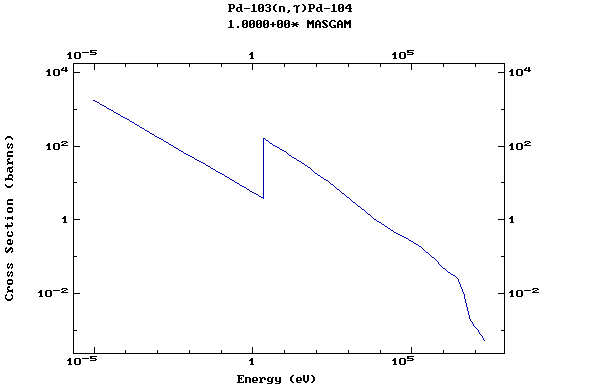
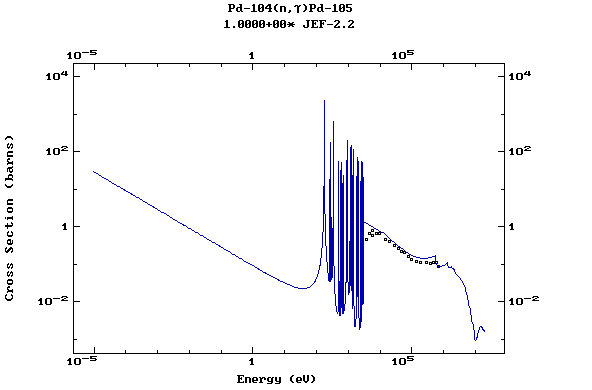
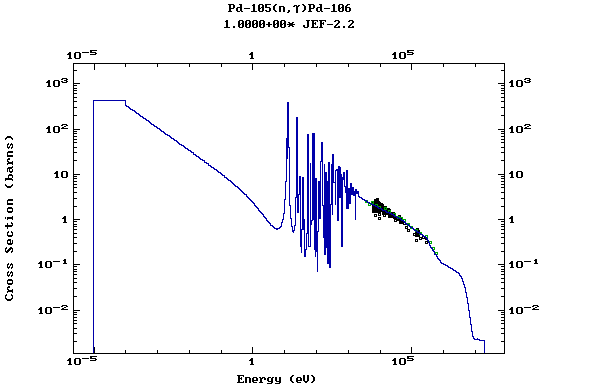
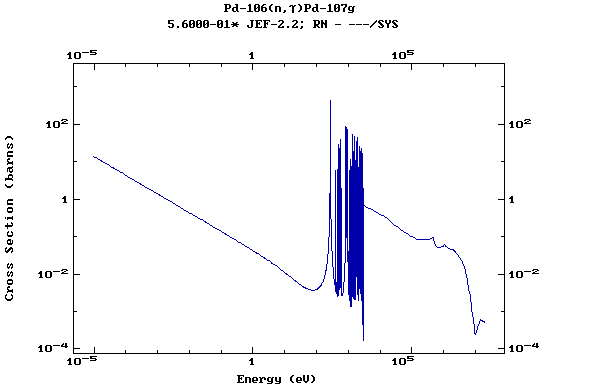
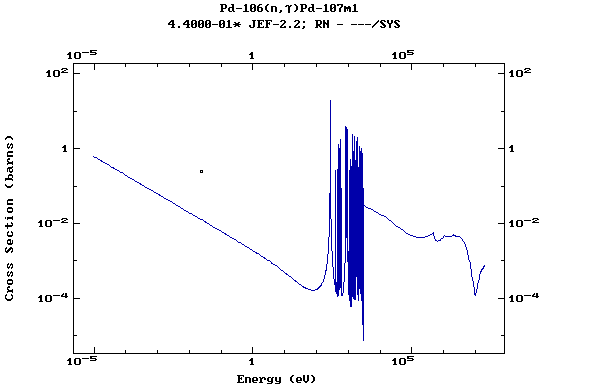
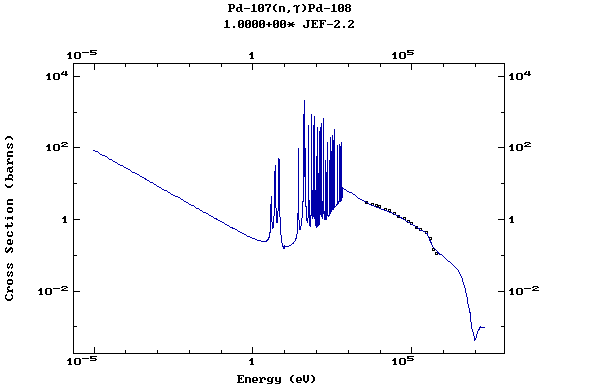
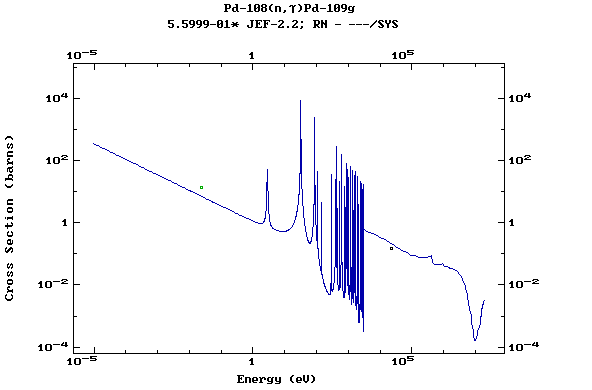
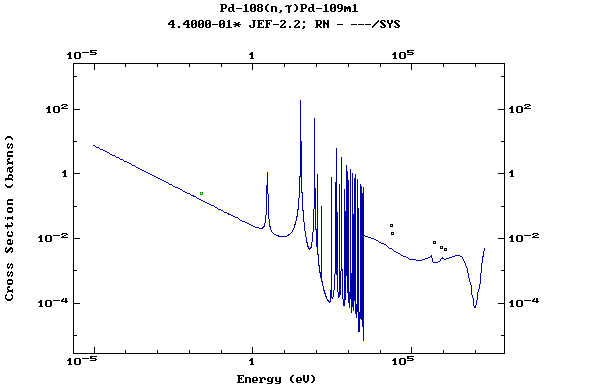
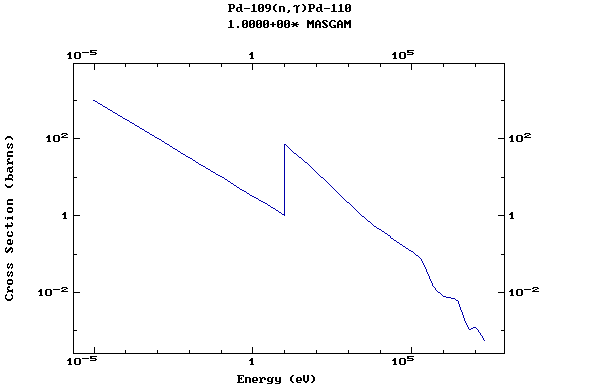
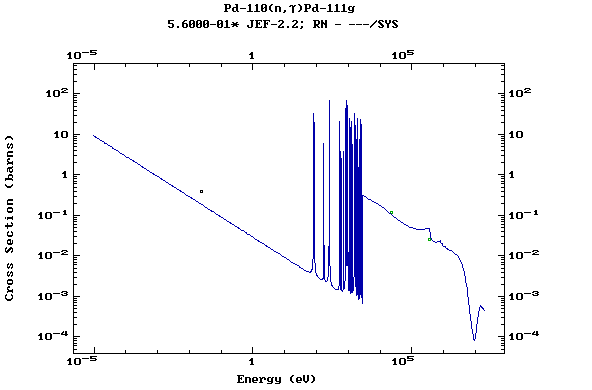
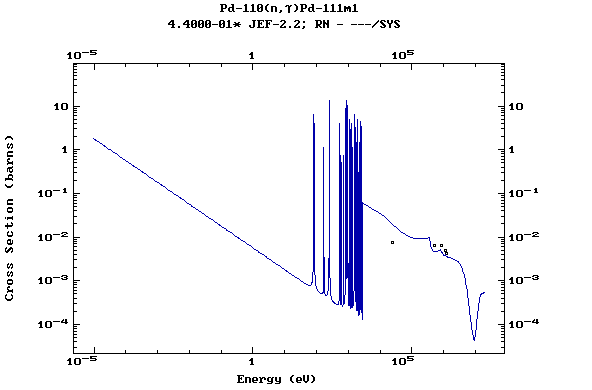
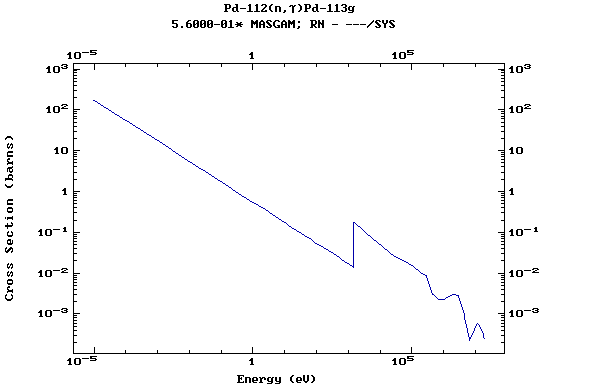
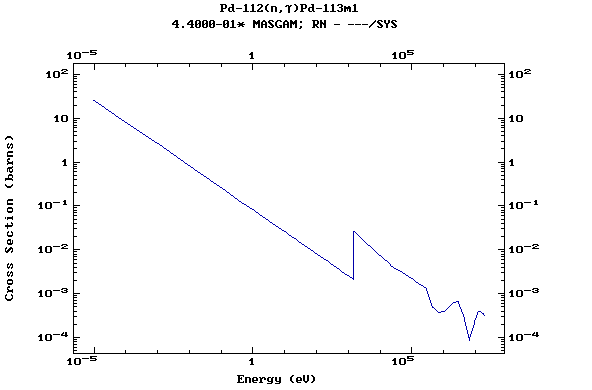
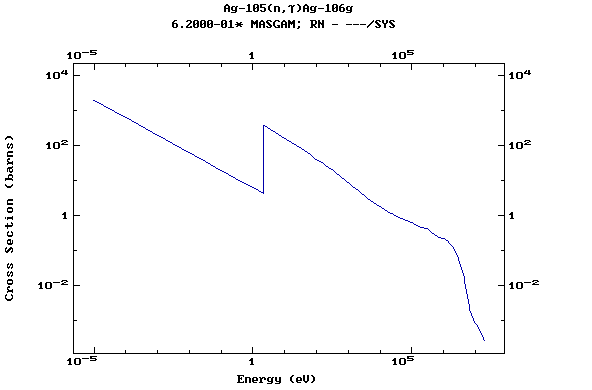
Z=47, Ag
(Silver)
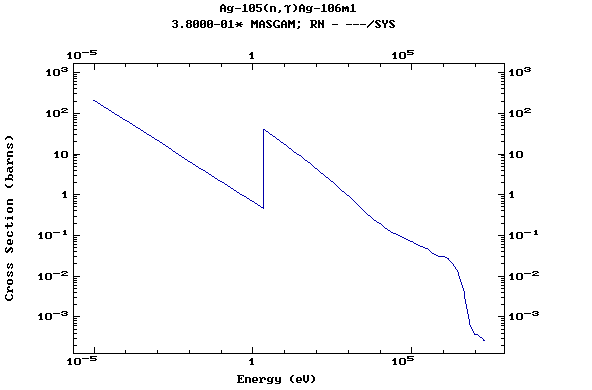
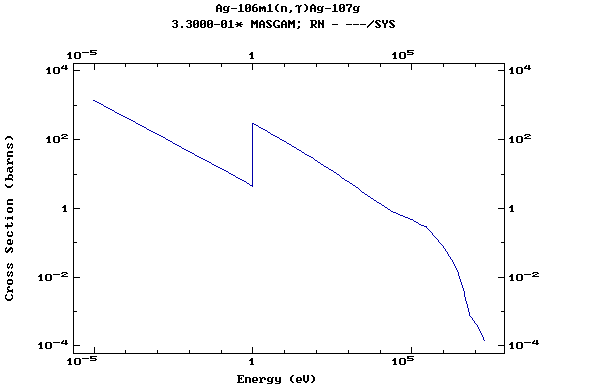
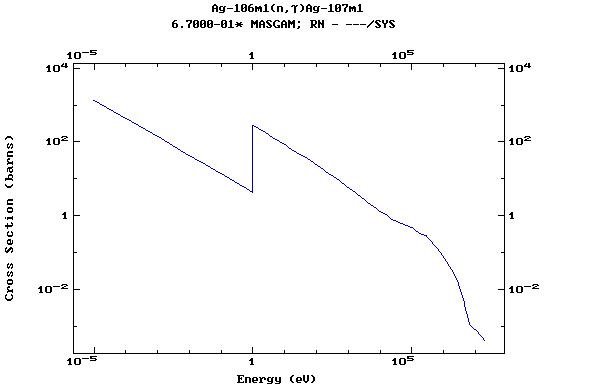
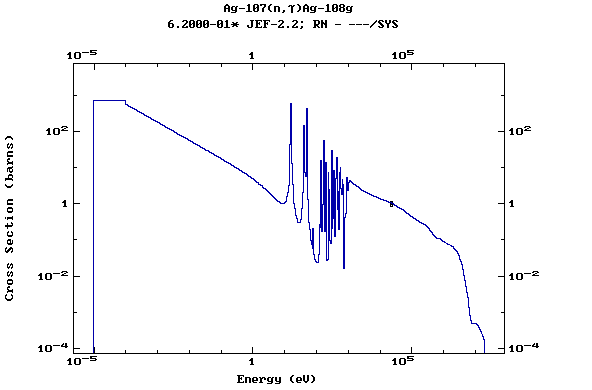
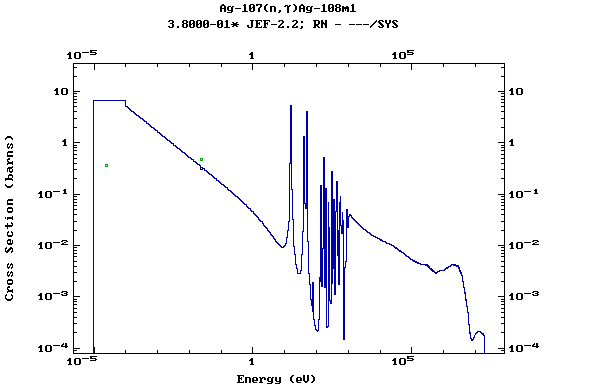
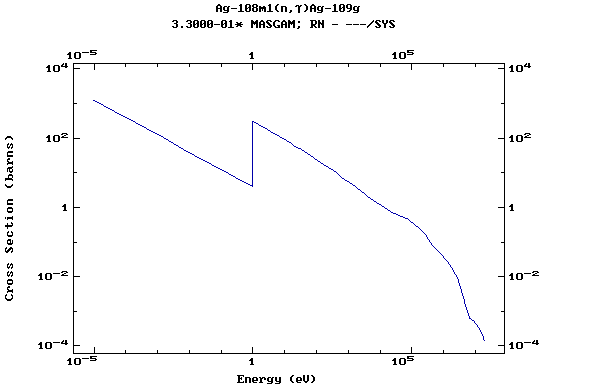
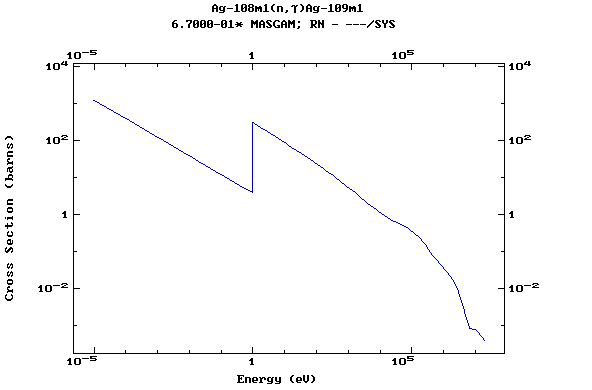
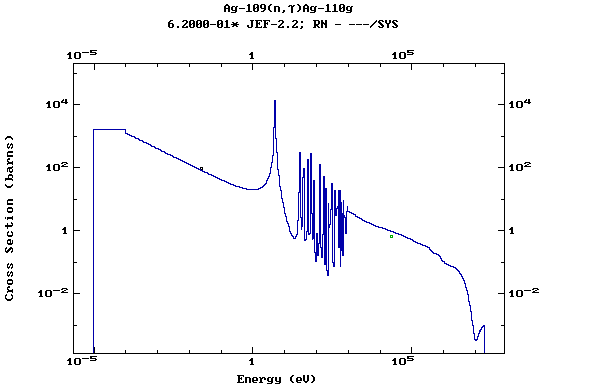
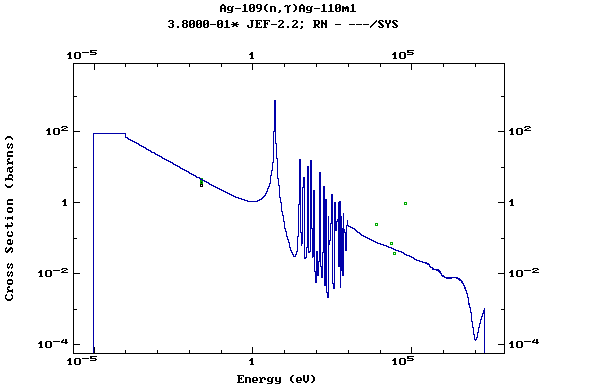
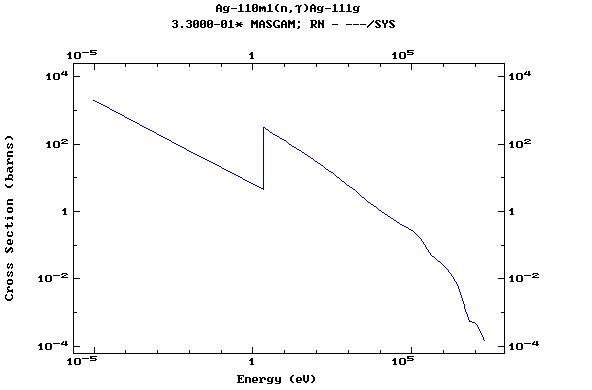
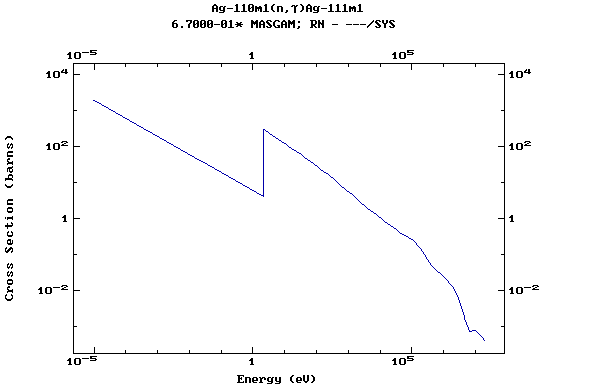
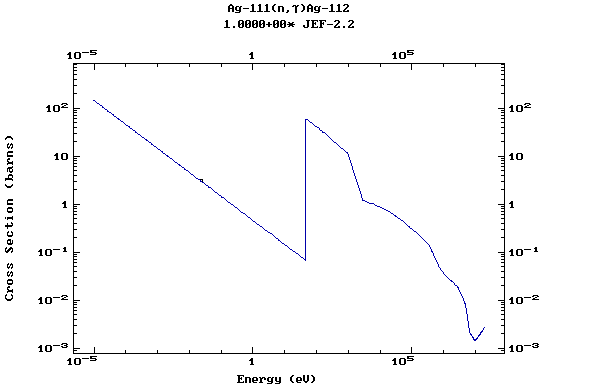
Z=48, Cd
(Cadmium)
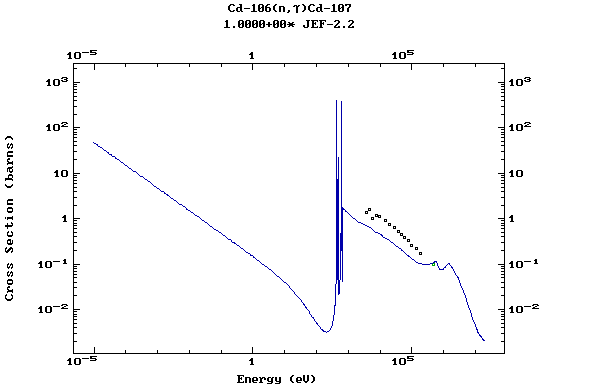
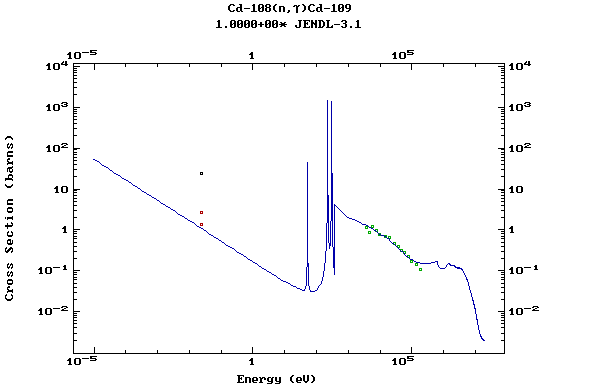
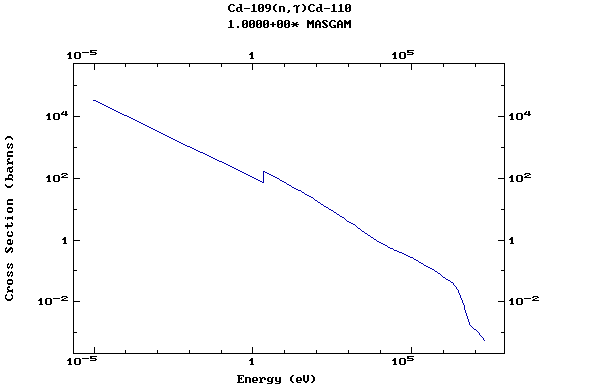
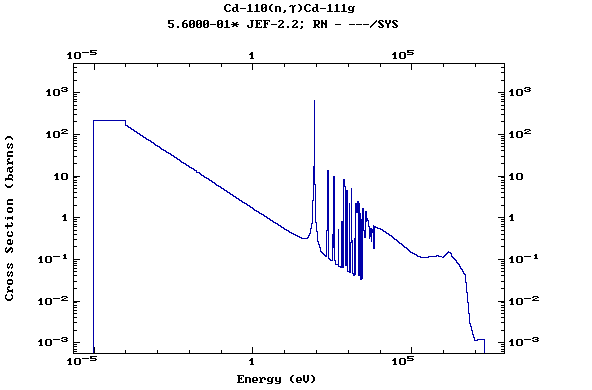
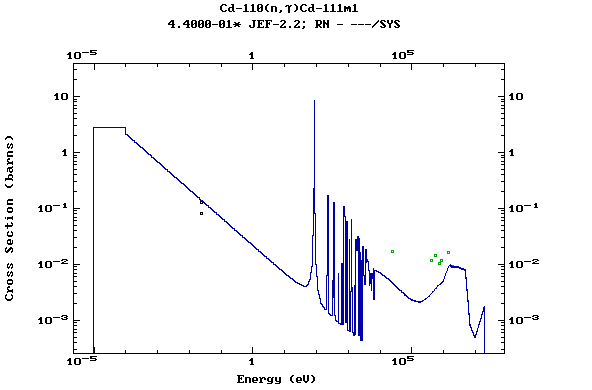
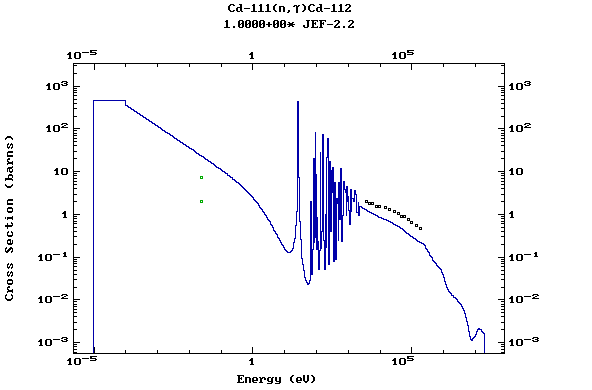
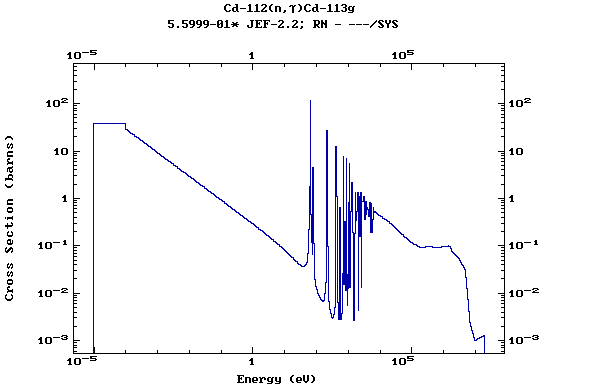
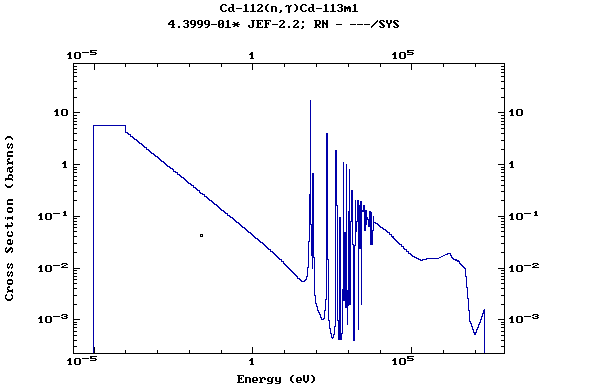
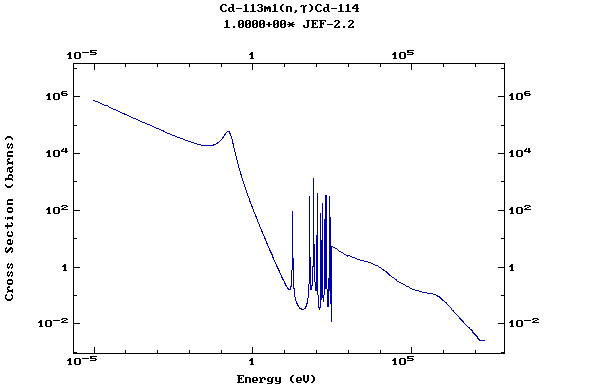
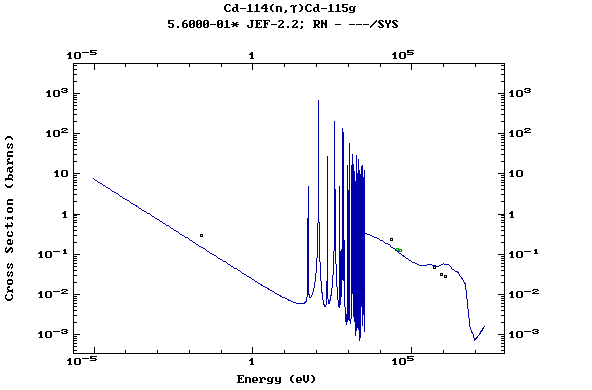
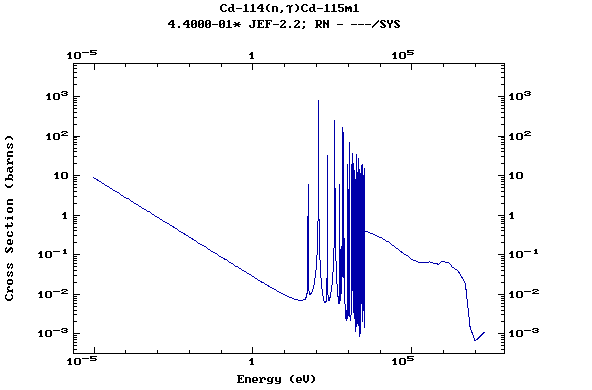
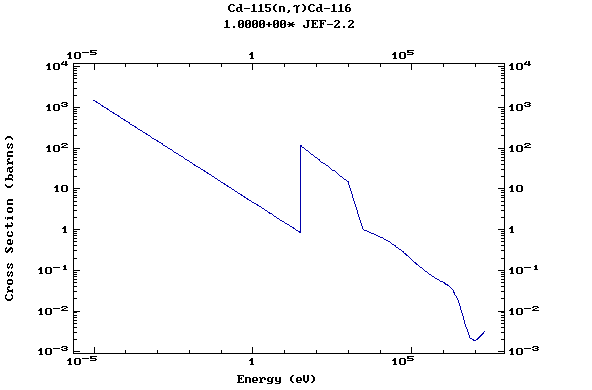
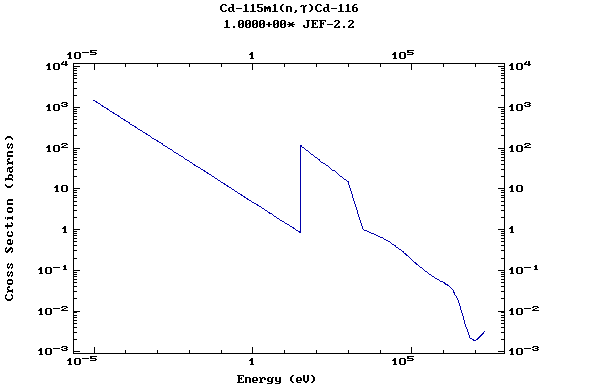
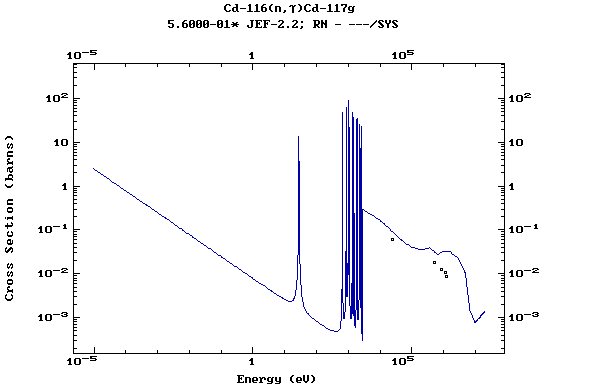
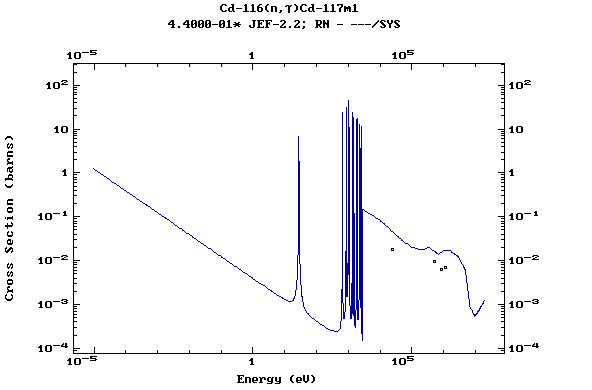
Z=49, In
(Indium)
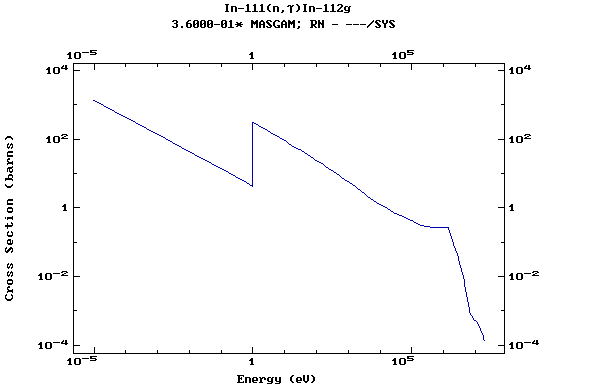
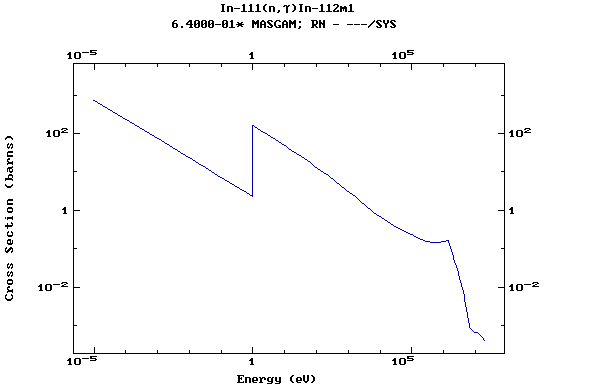
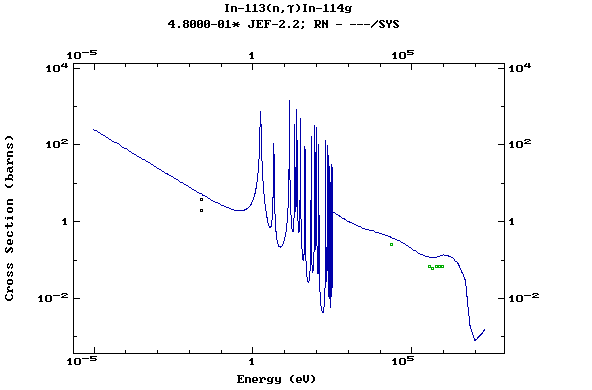
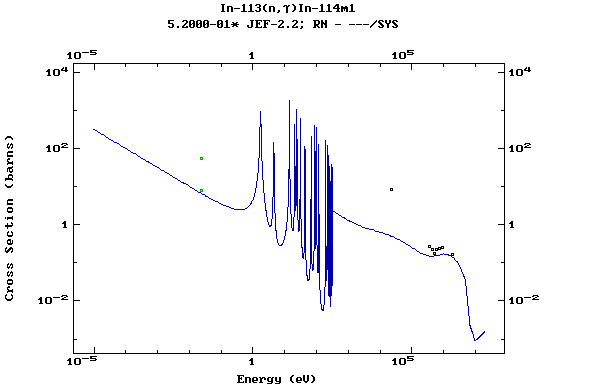
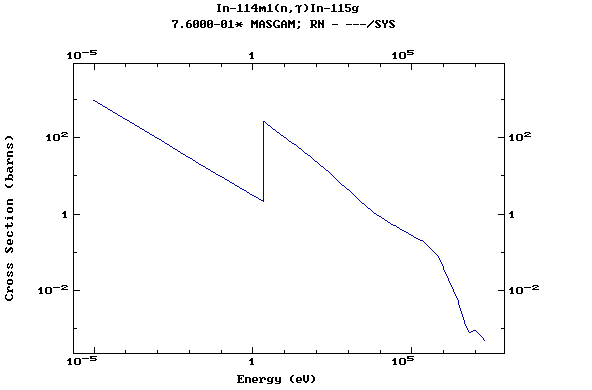
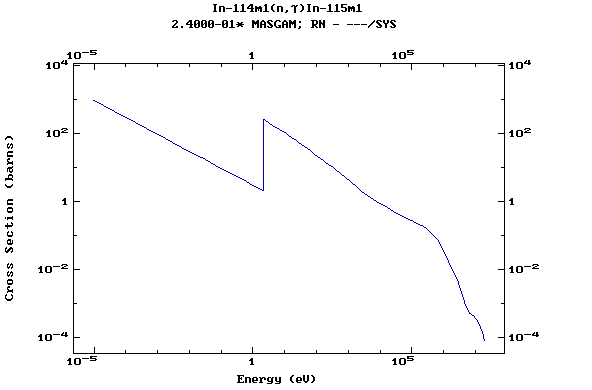
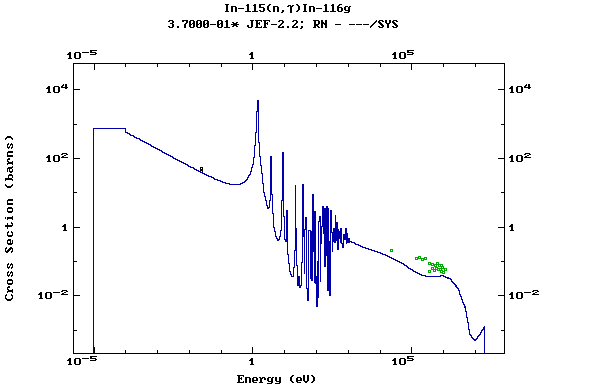
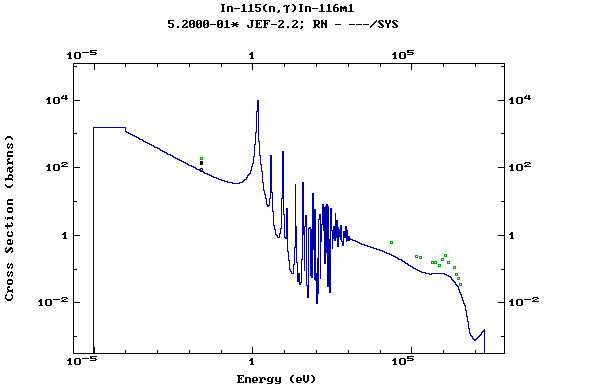
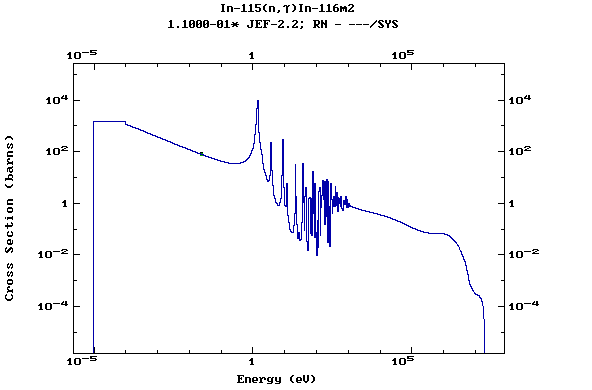
Z=50, Sn
(Tin)
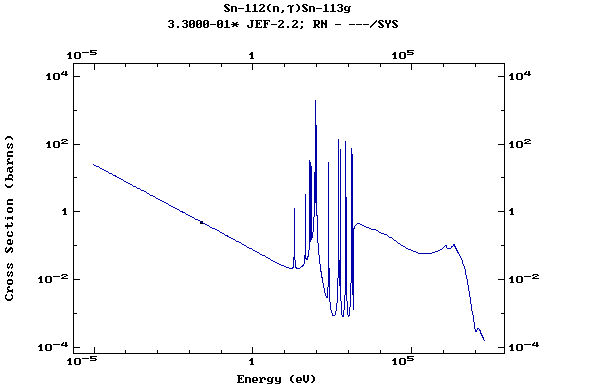
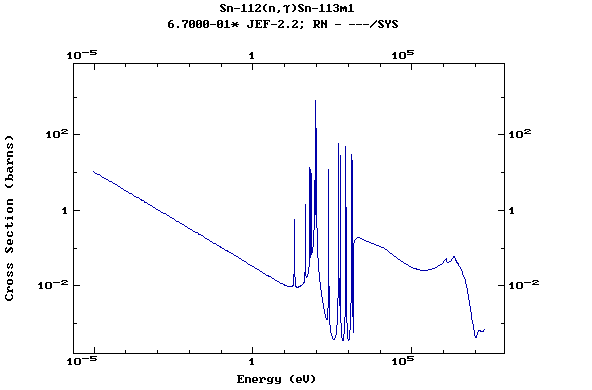
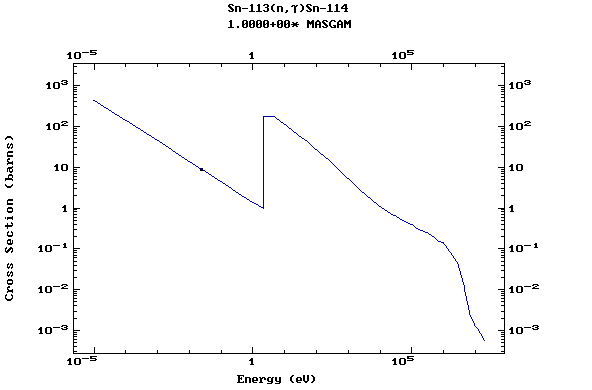
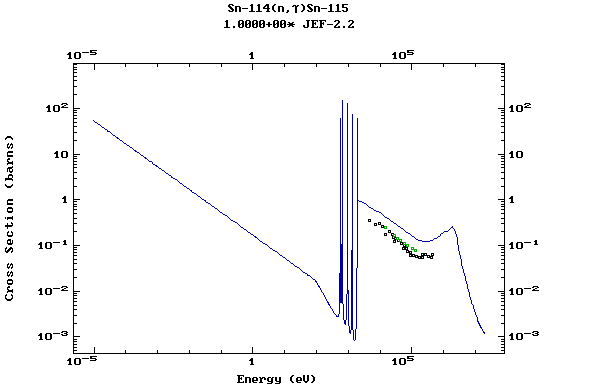
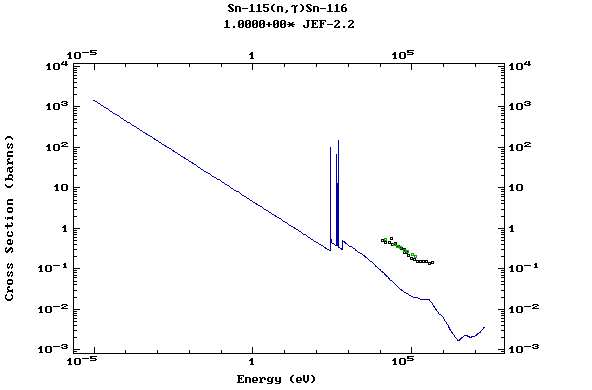
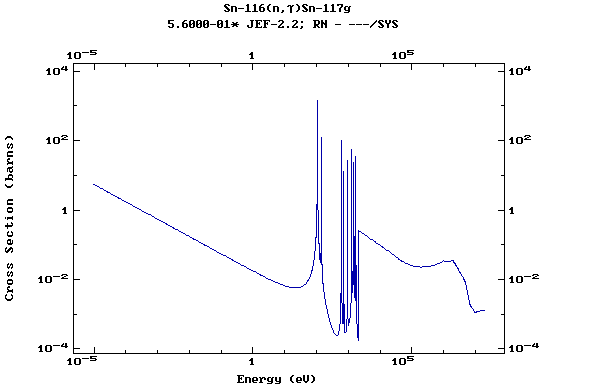
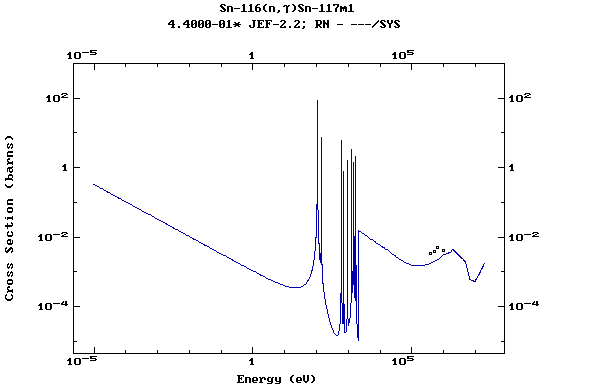
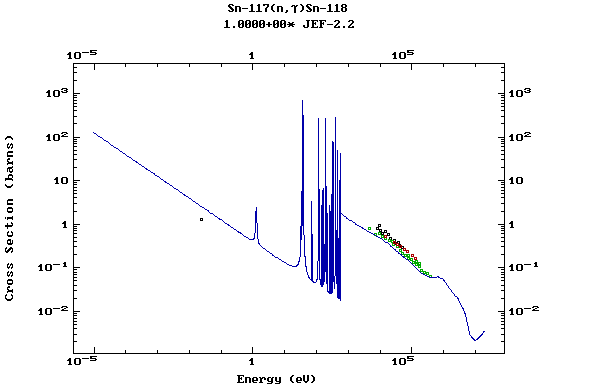
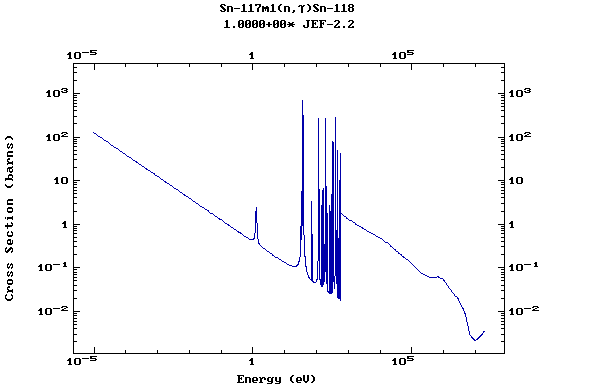
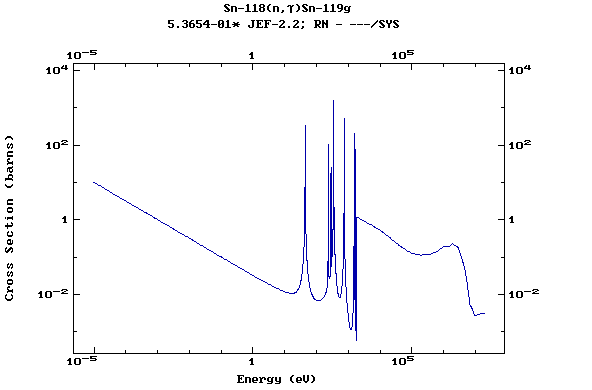
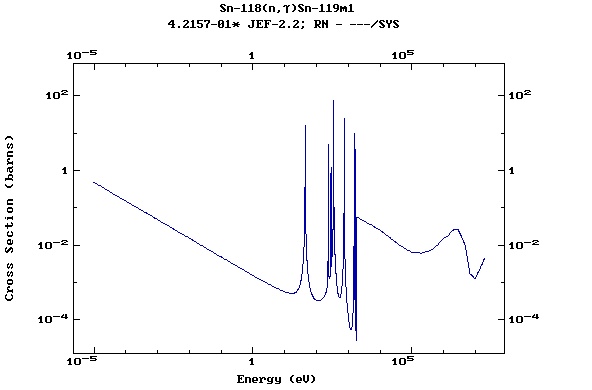
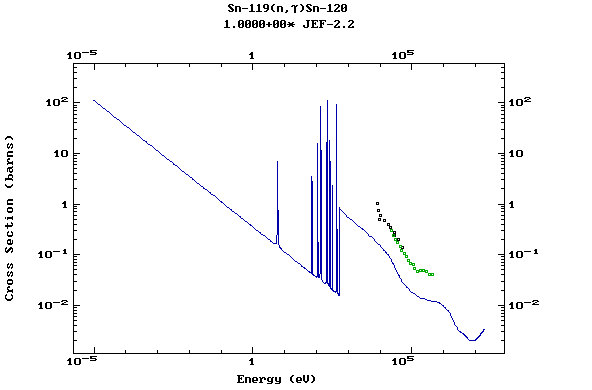
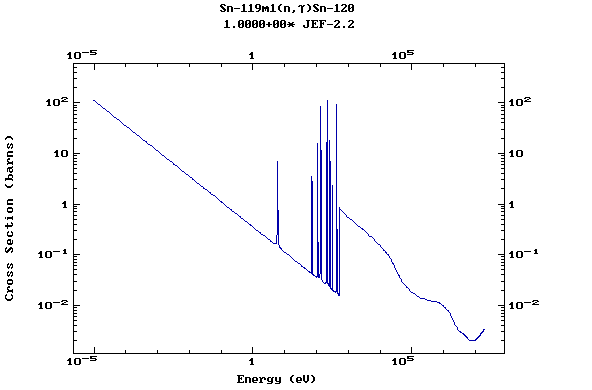
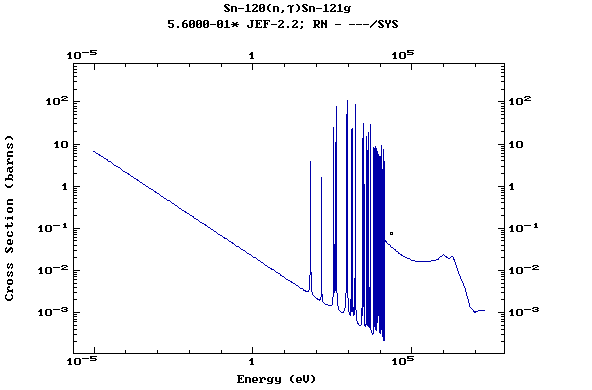
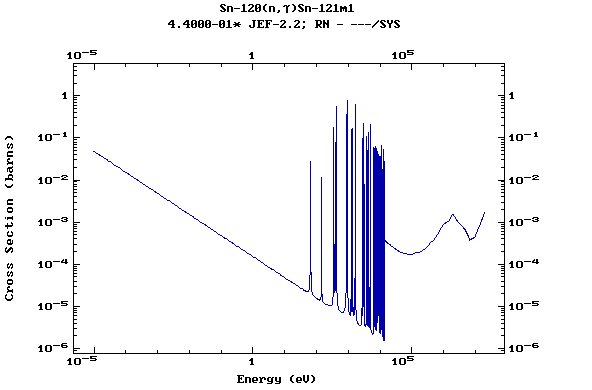
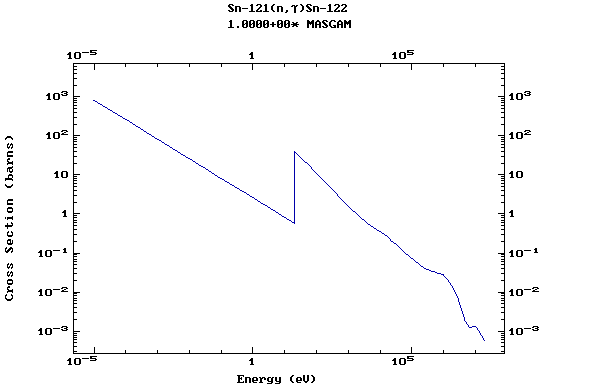
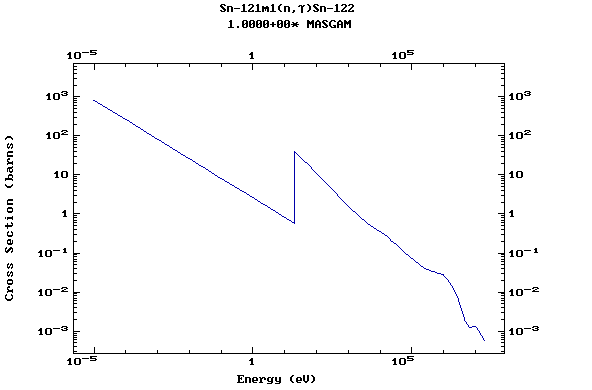
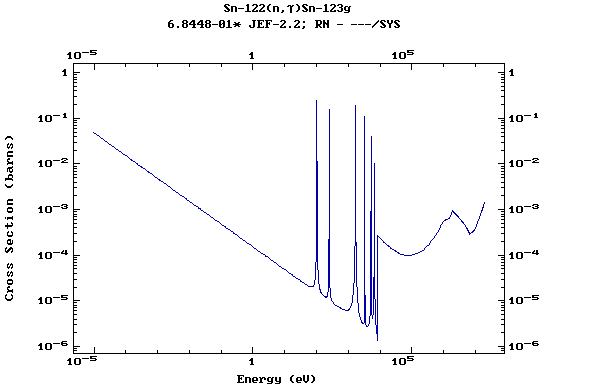
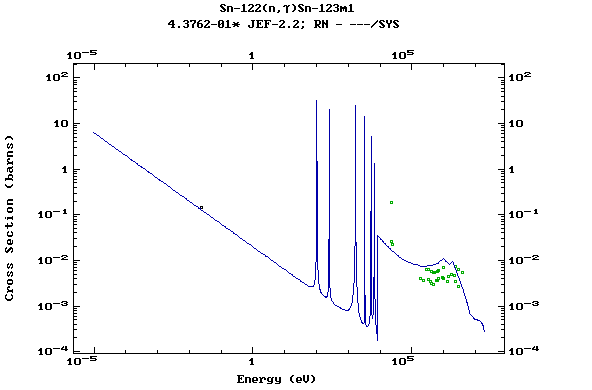
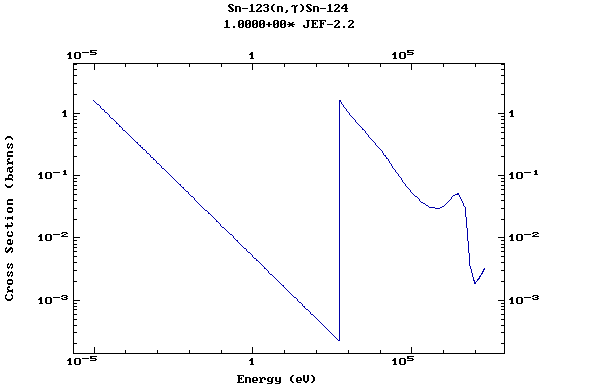
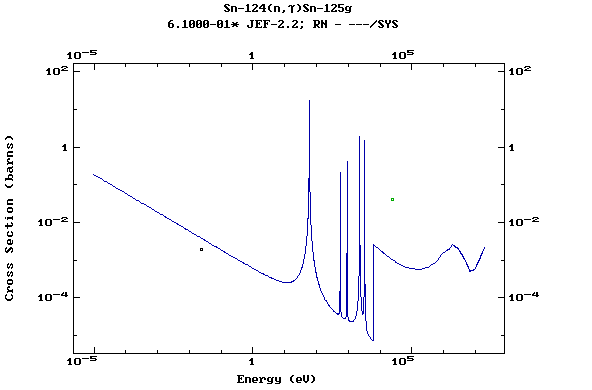
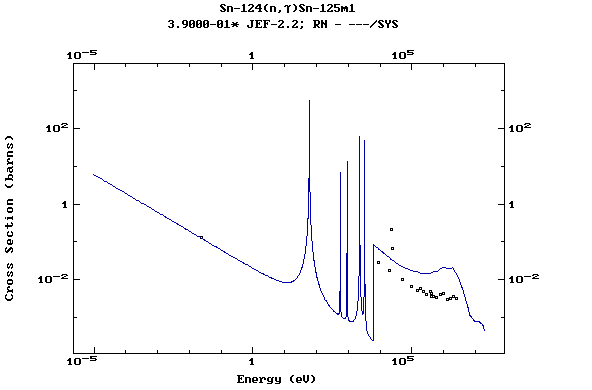
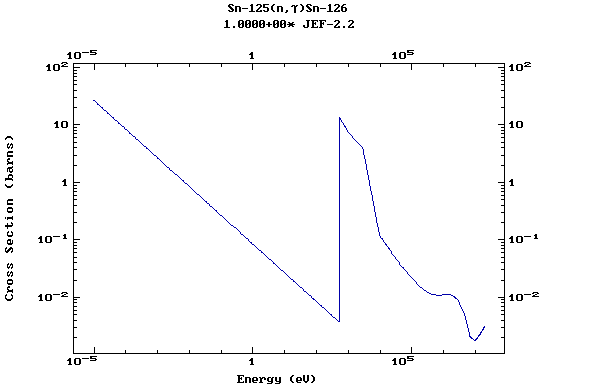
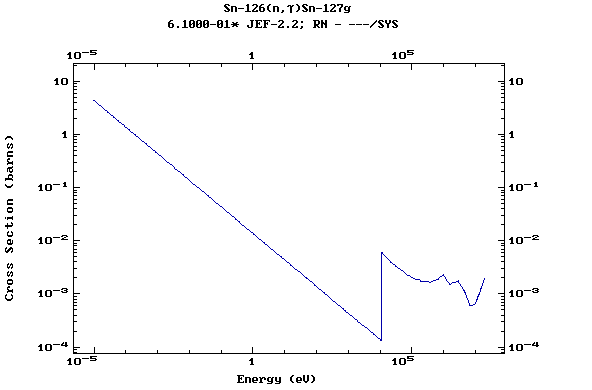
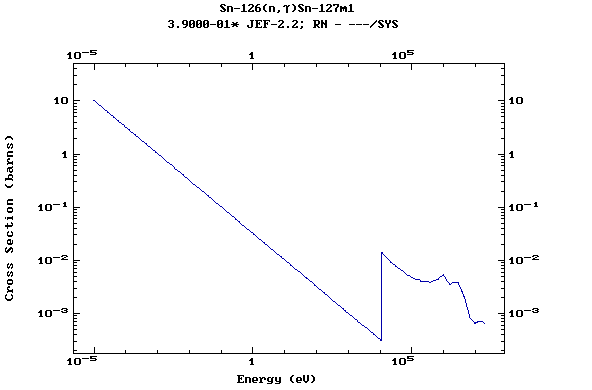
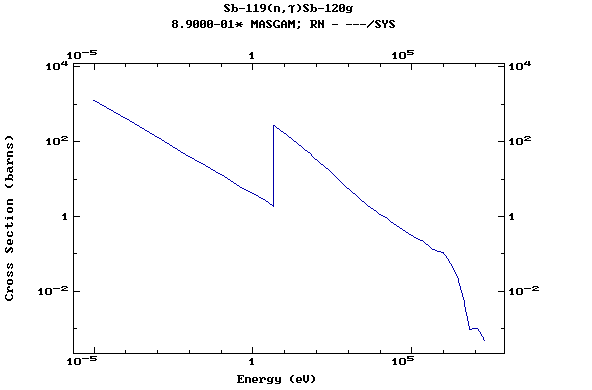
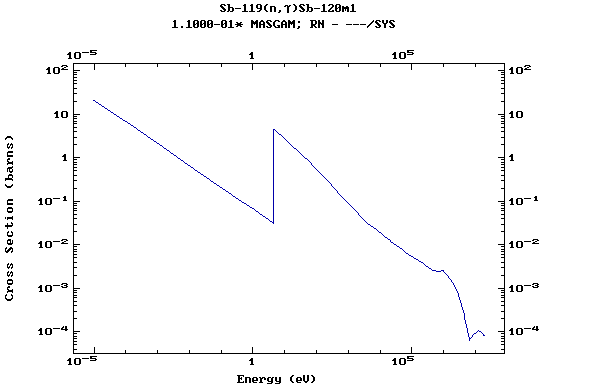
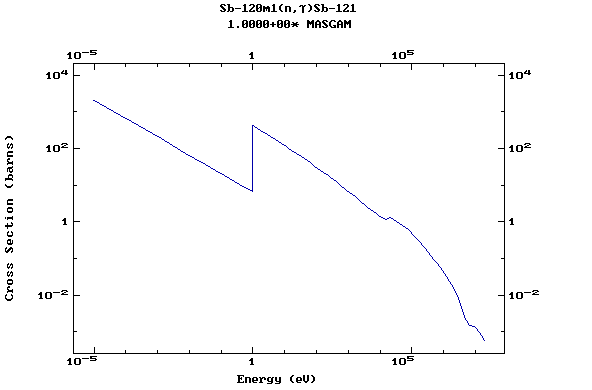
Z=51, Sb
(Antimony)
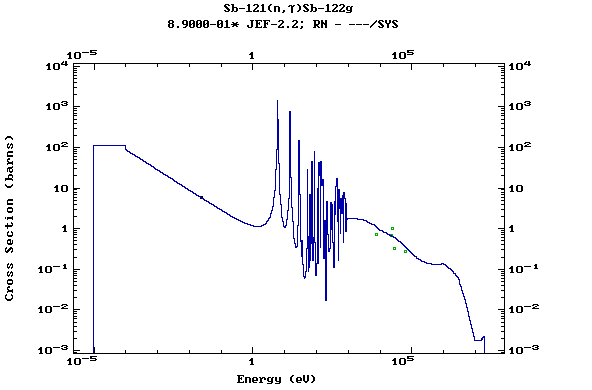
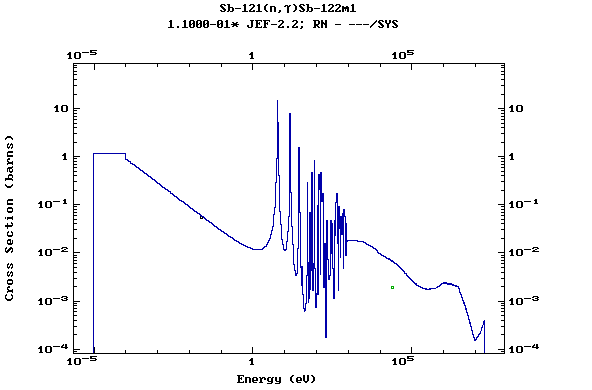
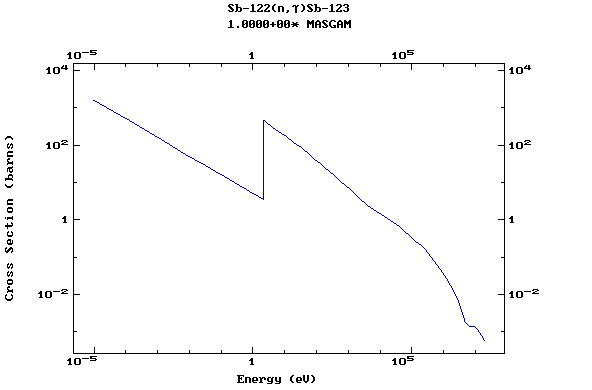
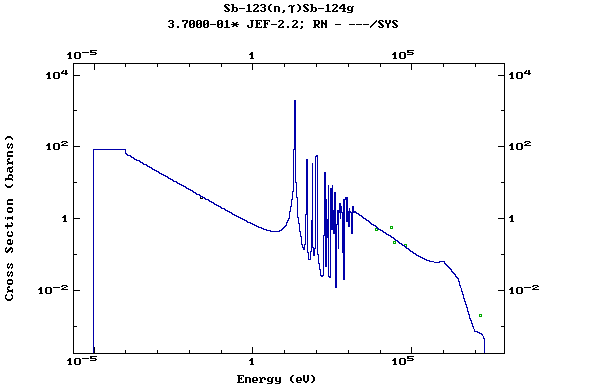
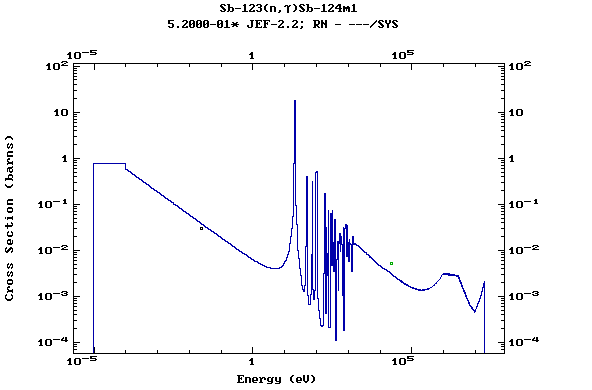
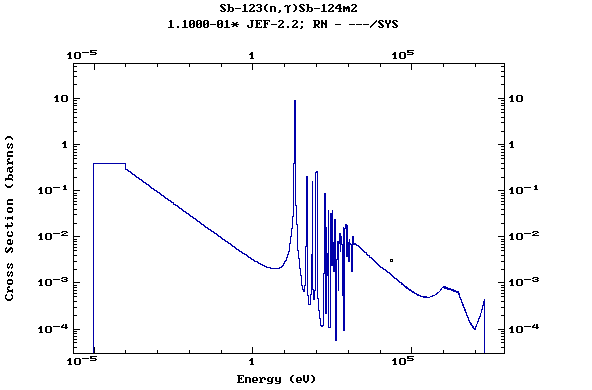
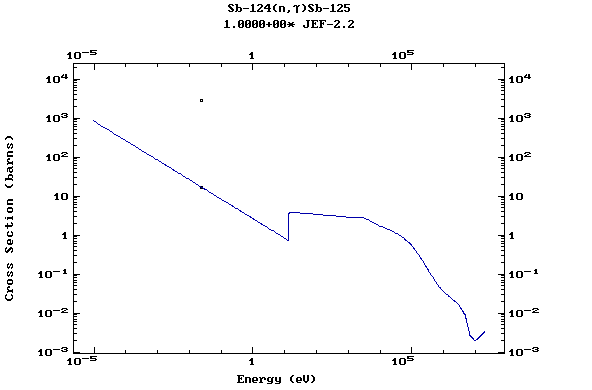
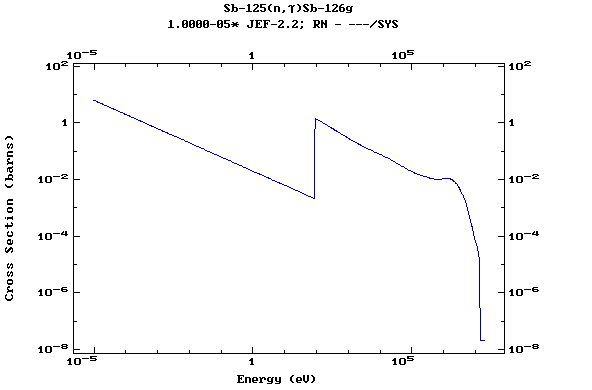
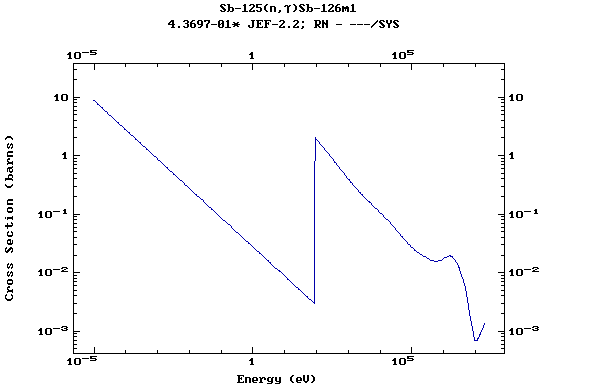
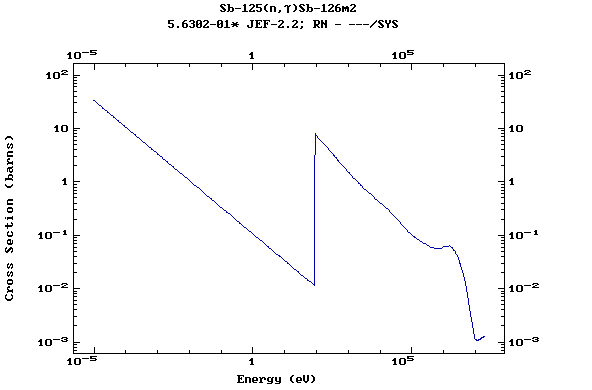
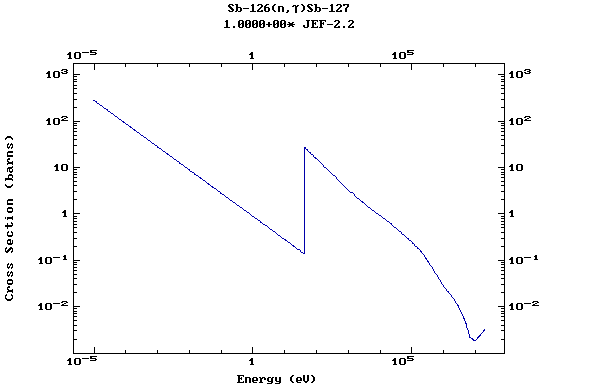
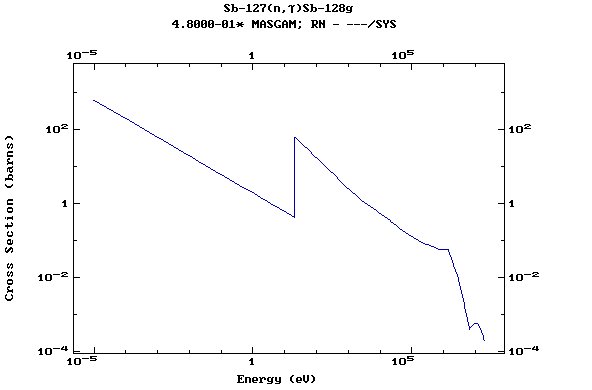
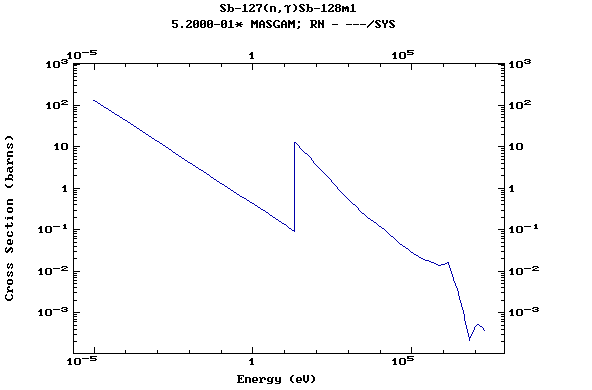
Z=52, Te
(Tellurium)
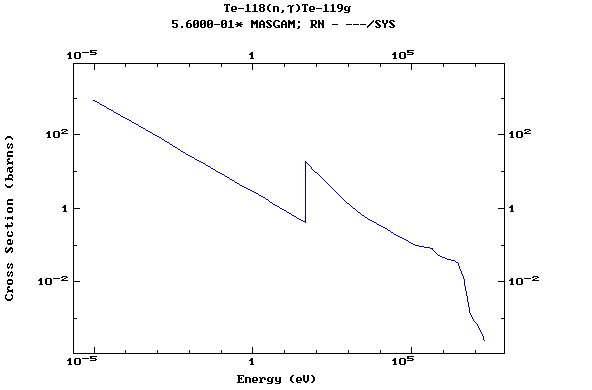
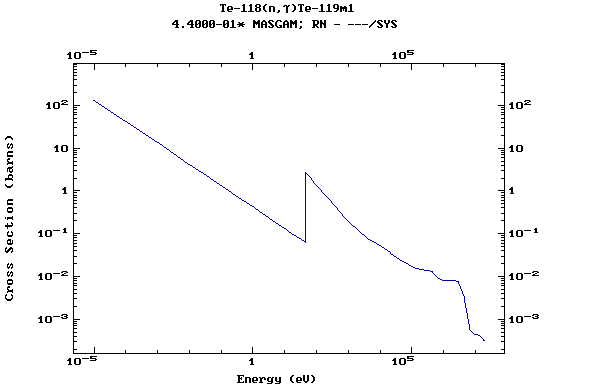
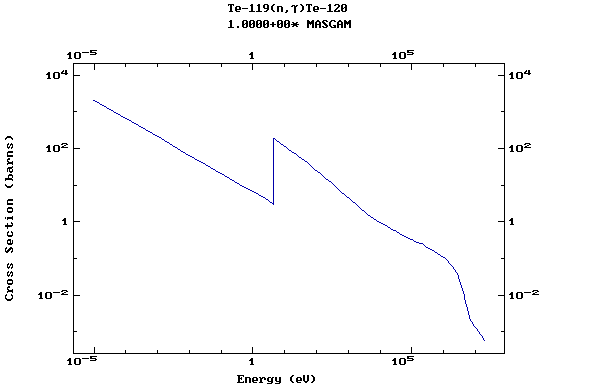
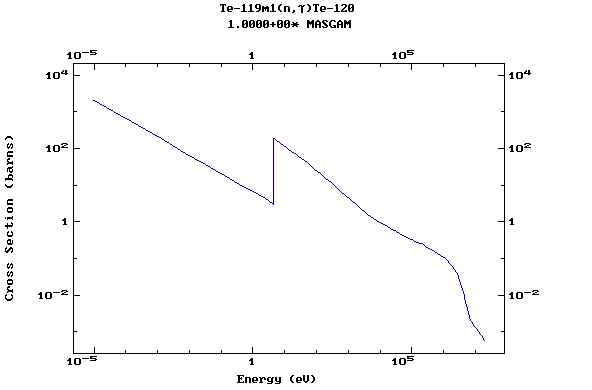
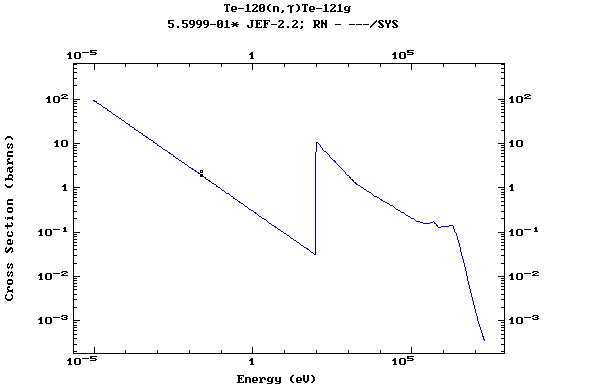
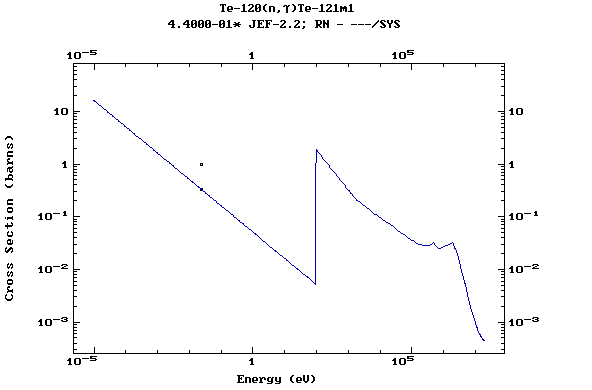
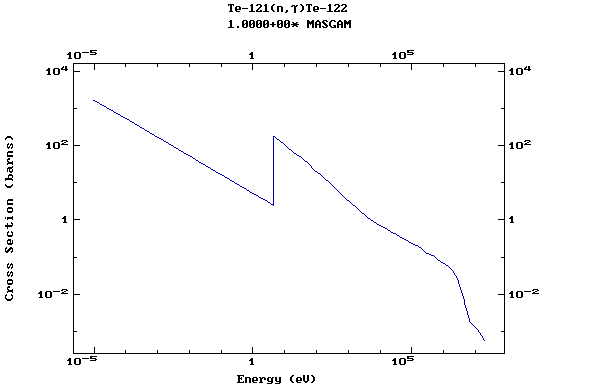
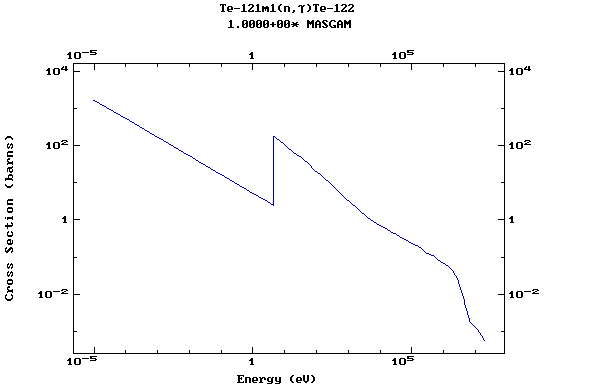
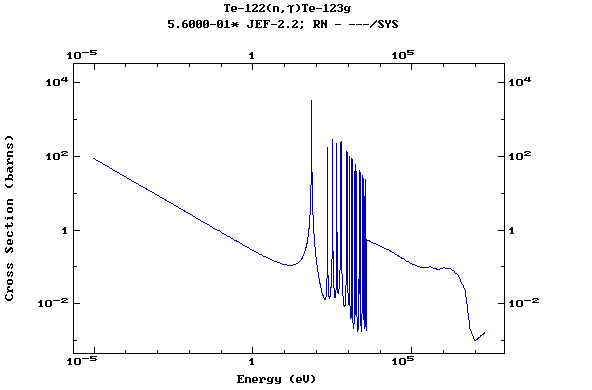
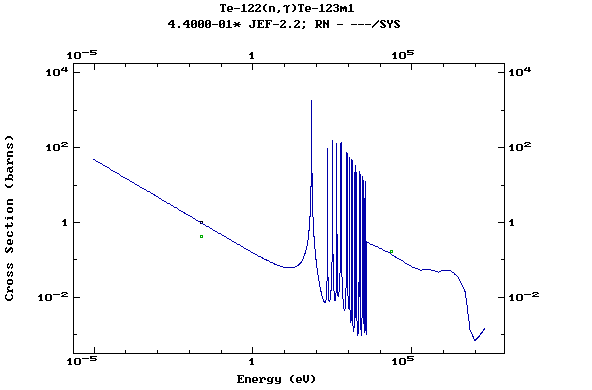
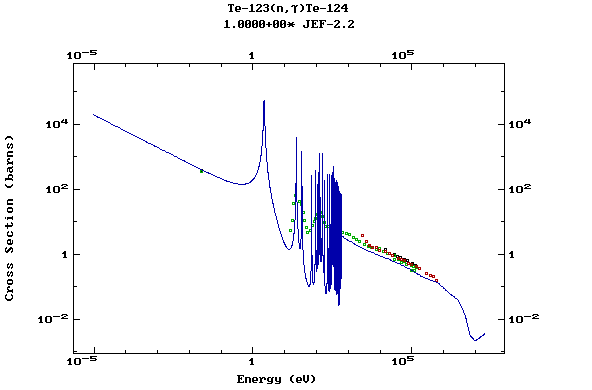
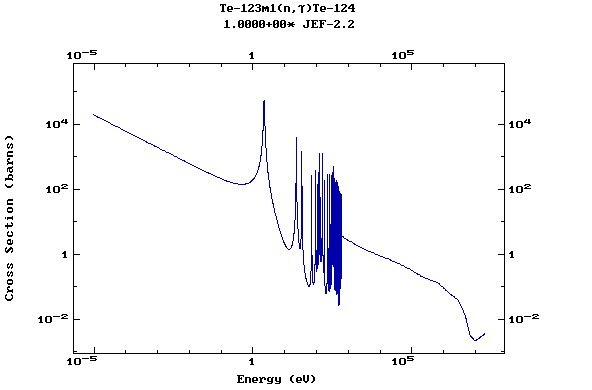
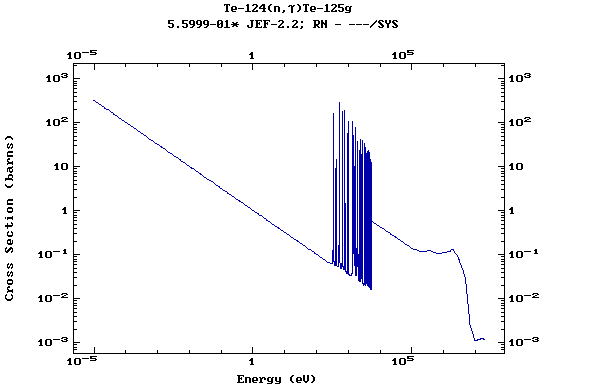
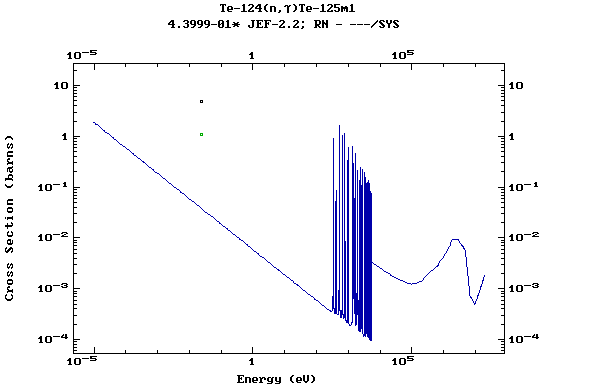
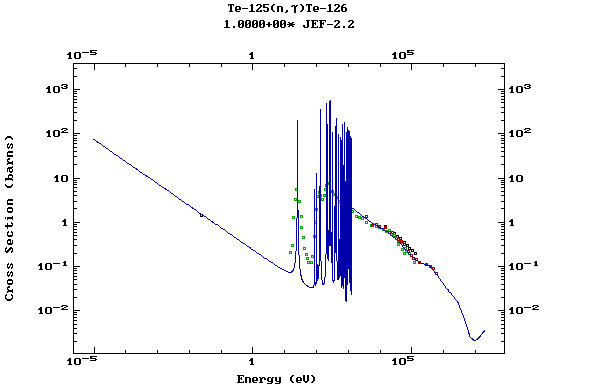
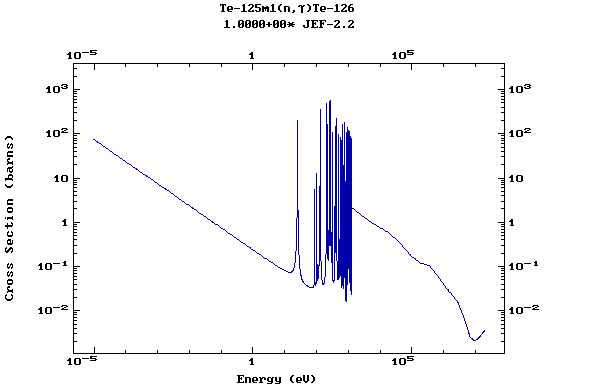
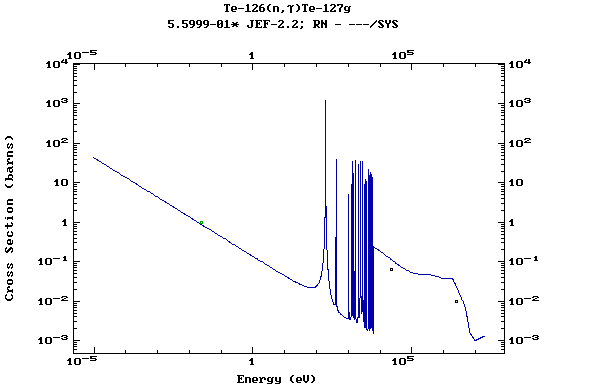
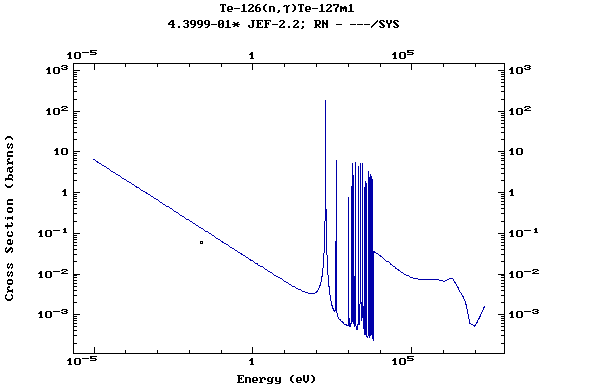
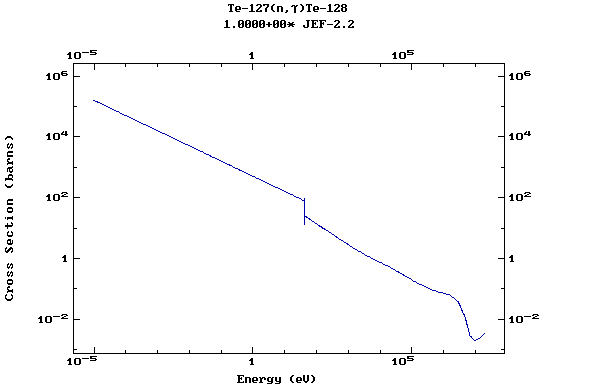
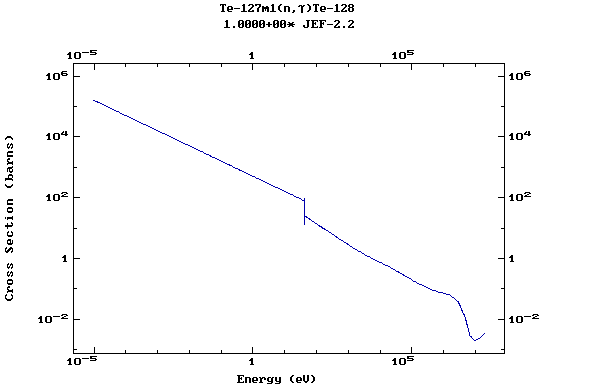
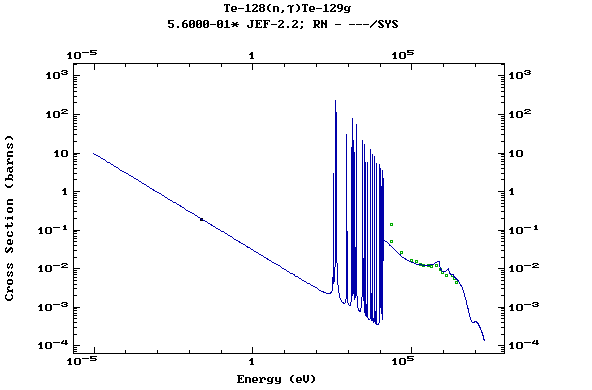
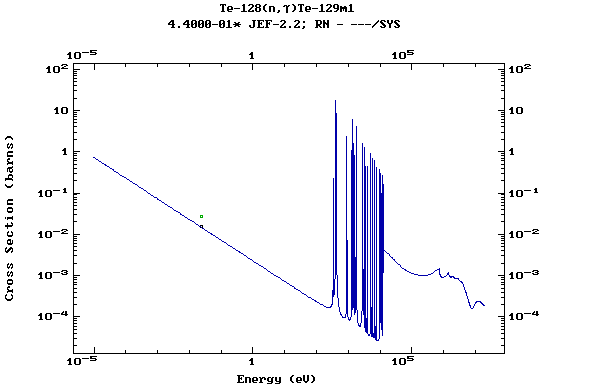
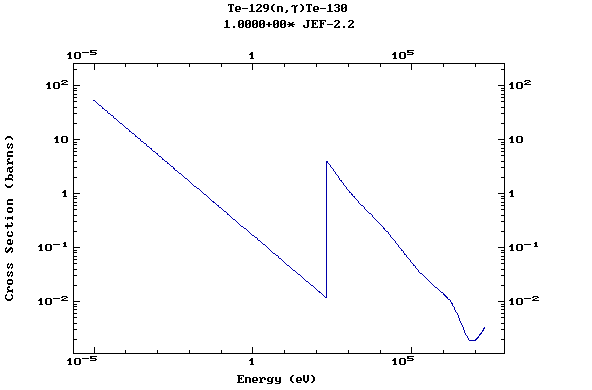
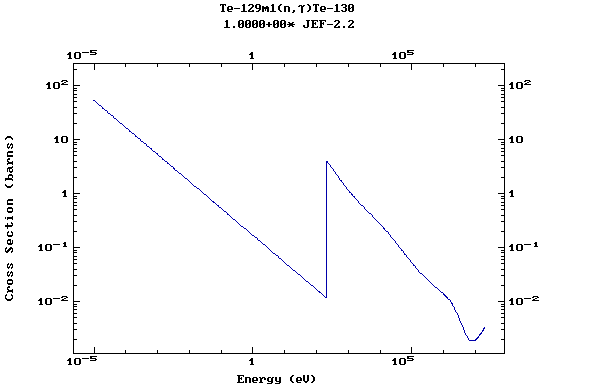
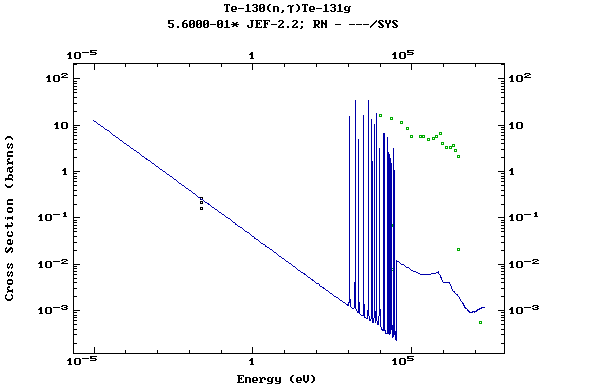
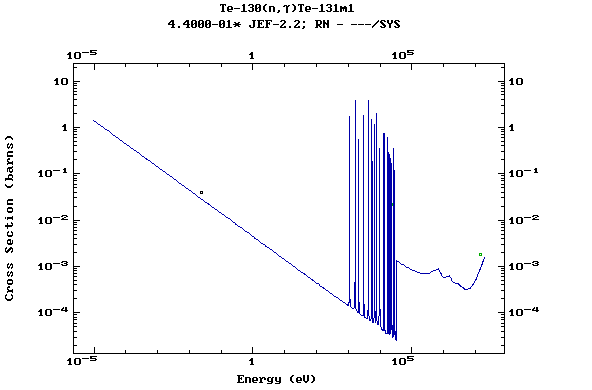
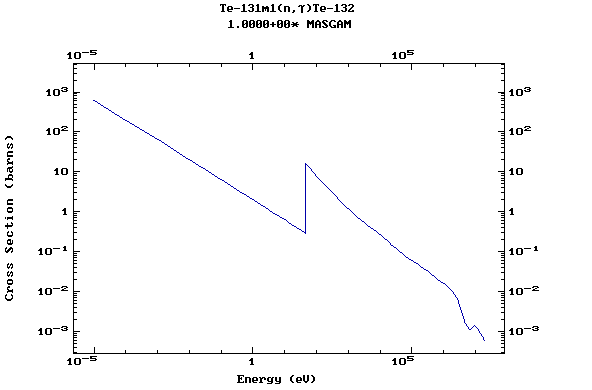
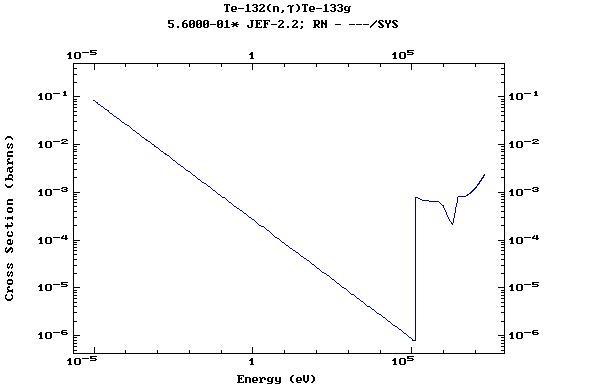
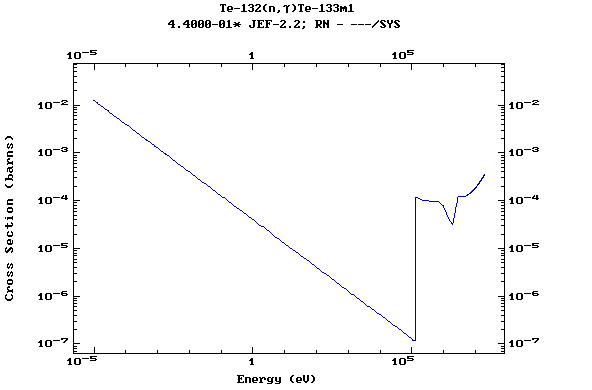
Z=53, I
(Iodine)
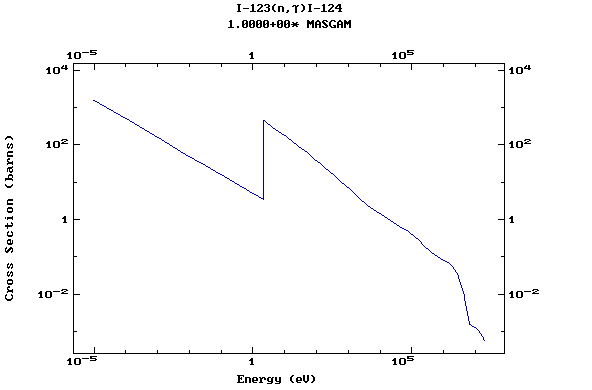
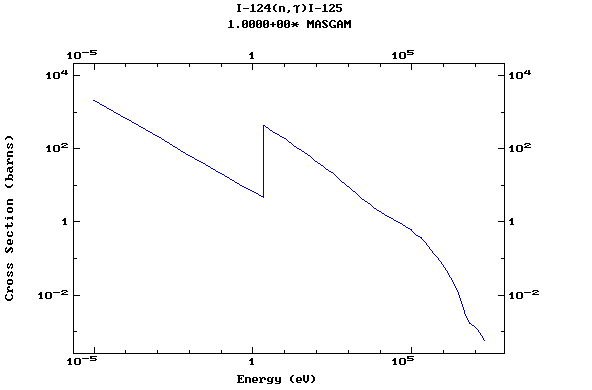
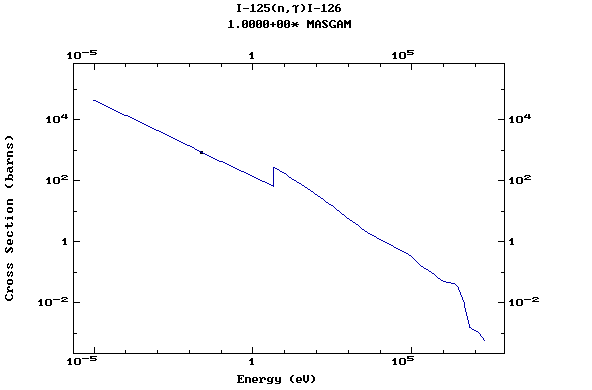
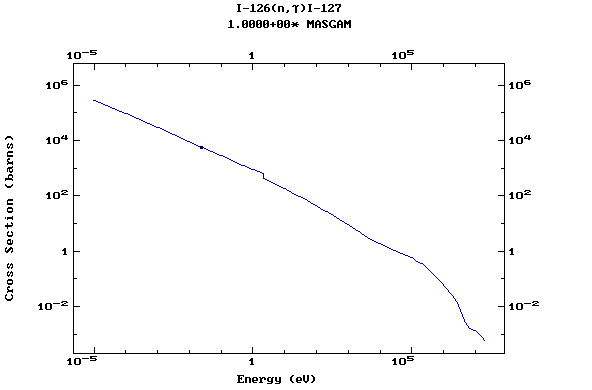
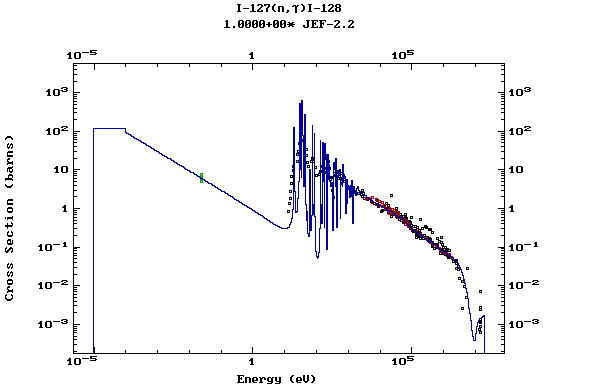
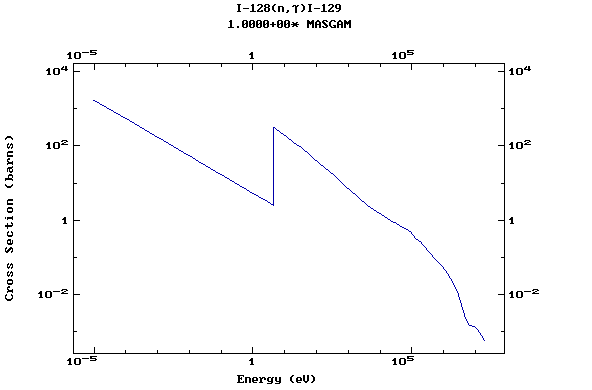
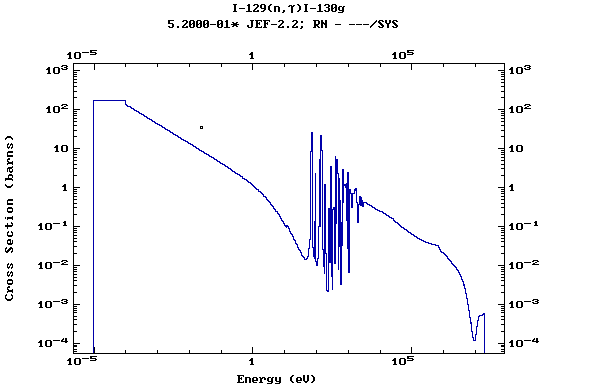
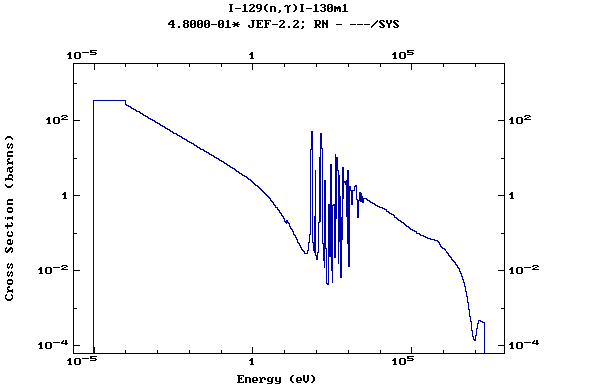
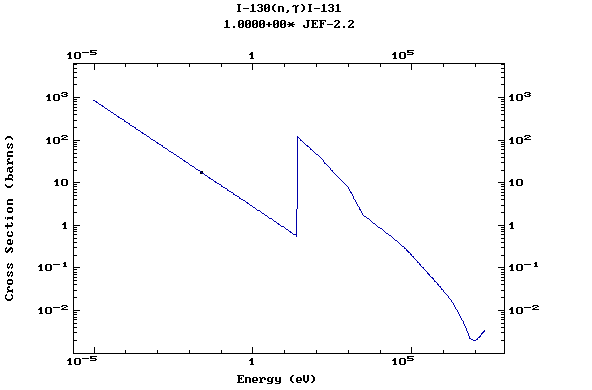
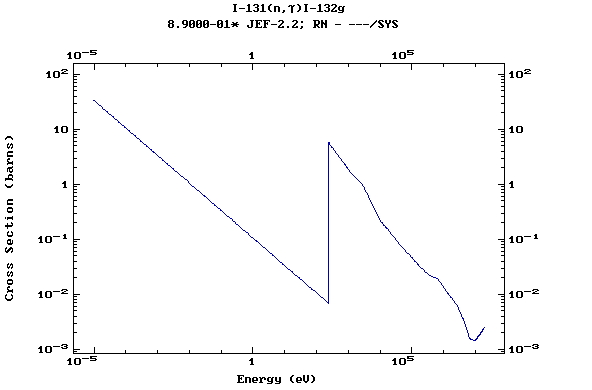
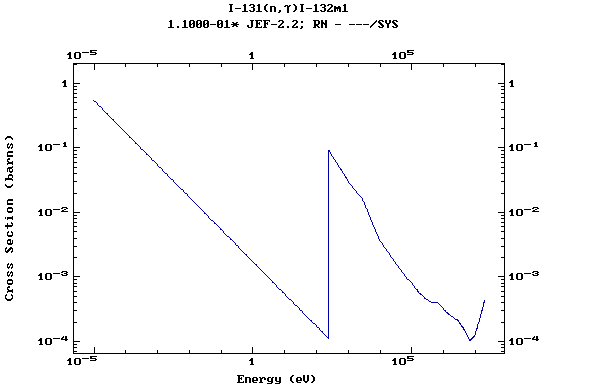
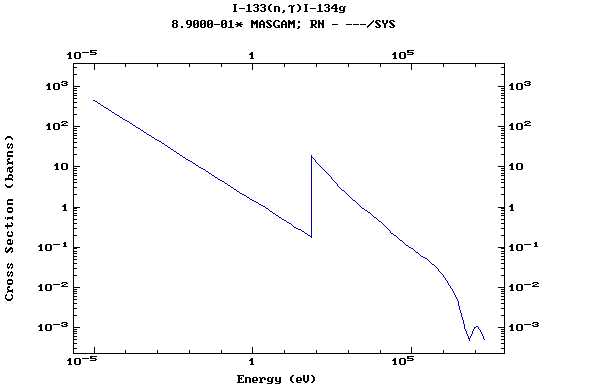
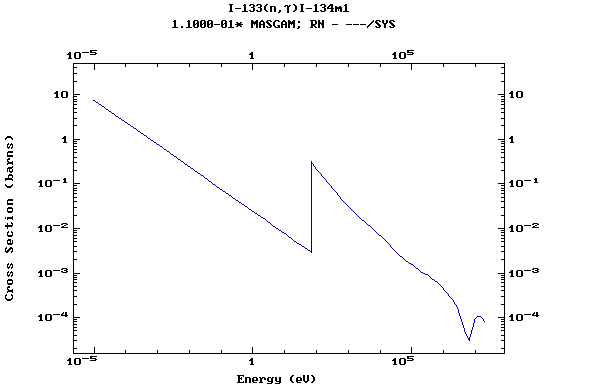
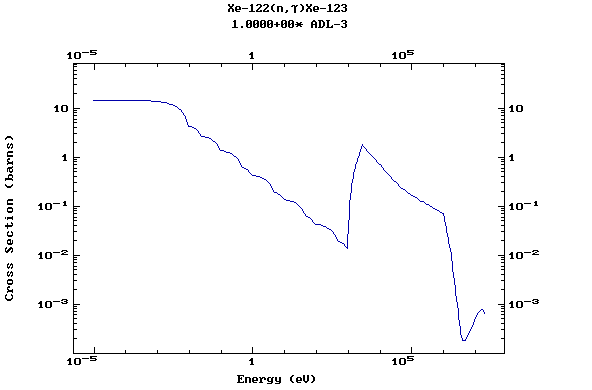
Z=54, Xe
(Xenon)
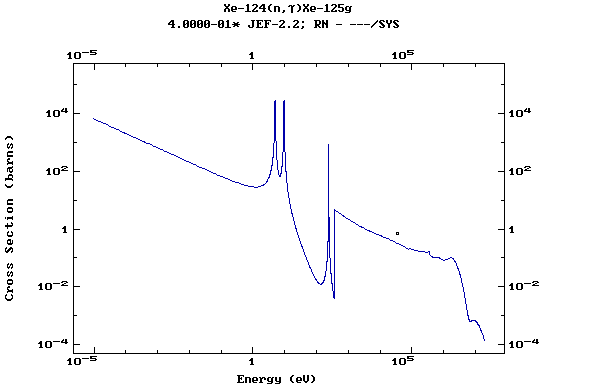
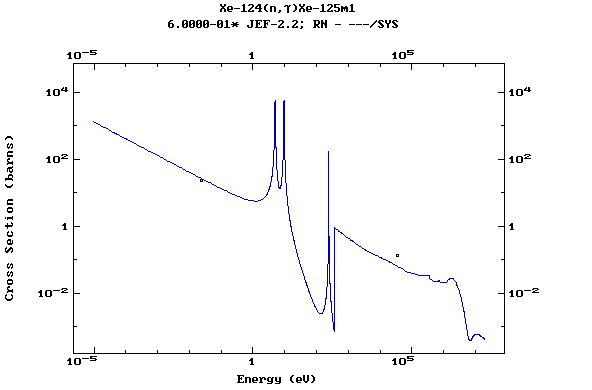
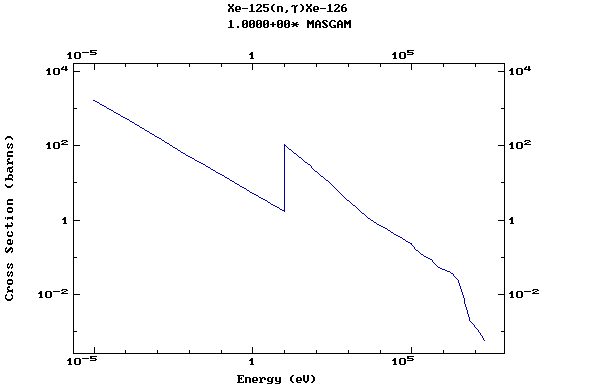
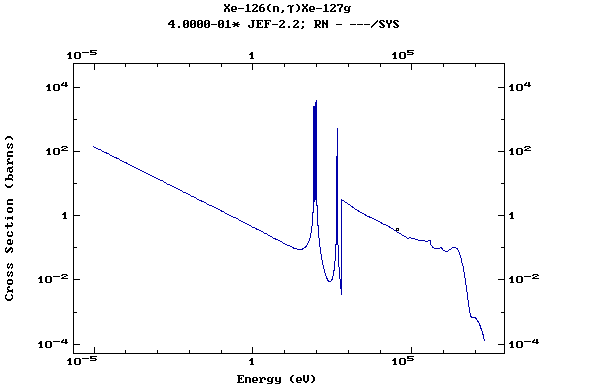
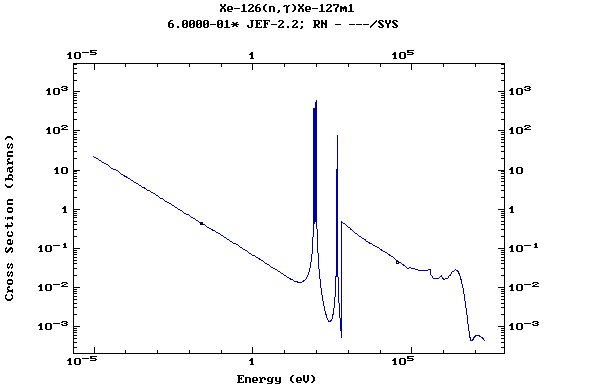
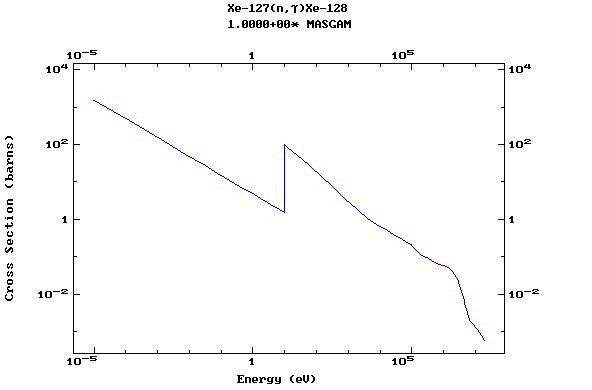
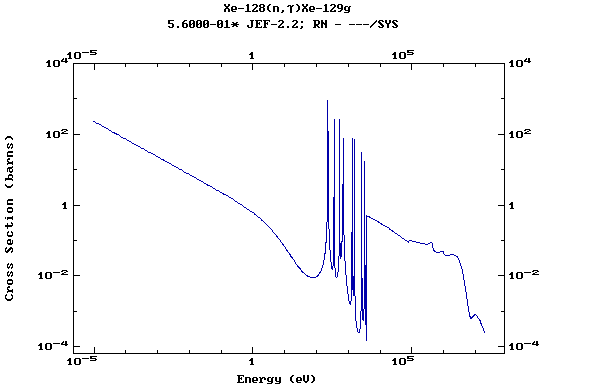
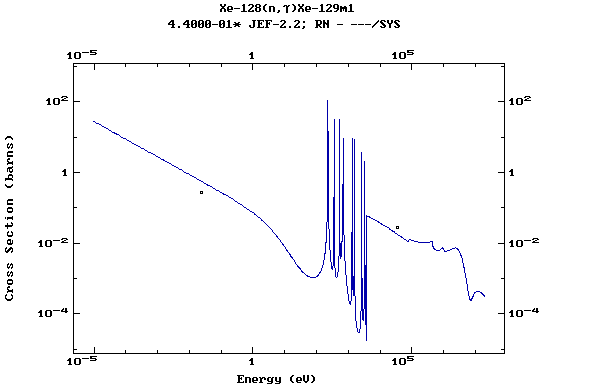
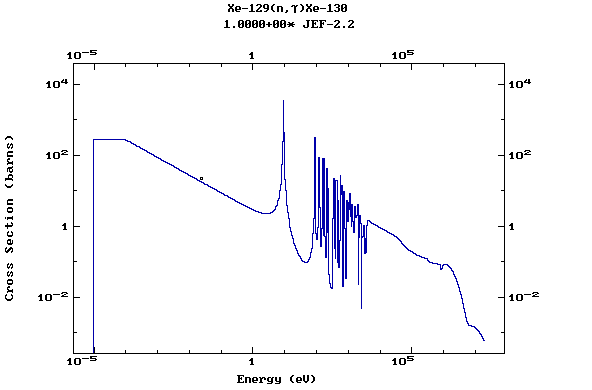
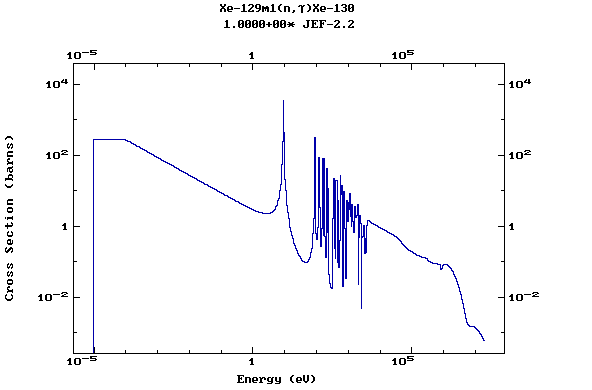
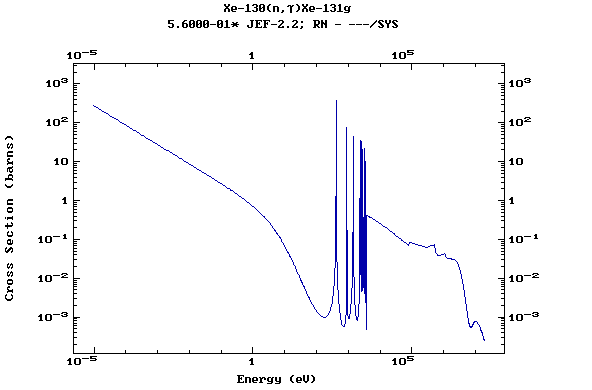
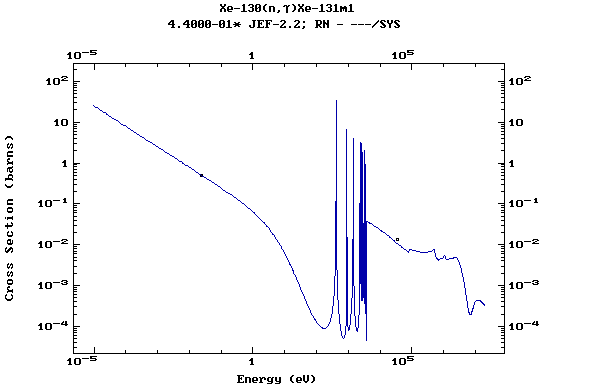
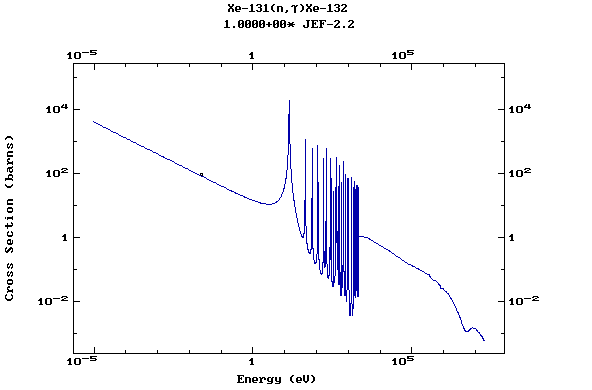
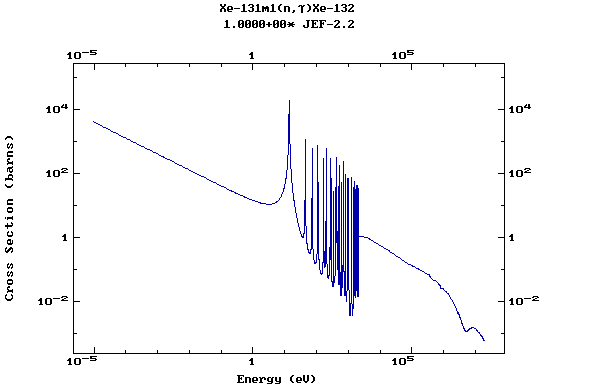
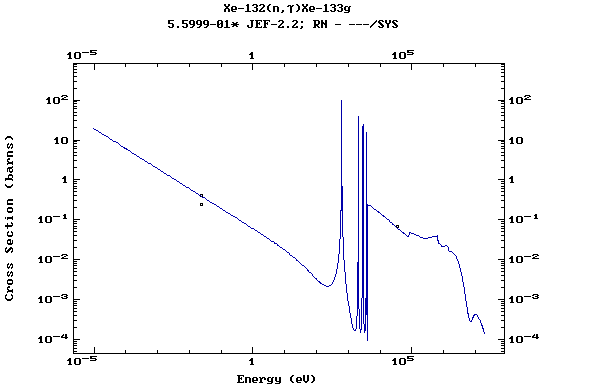
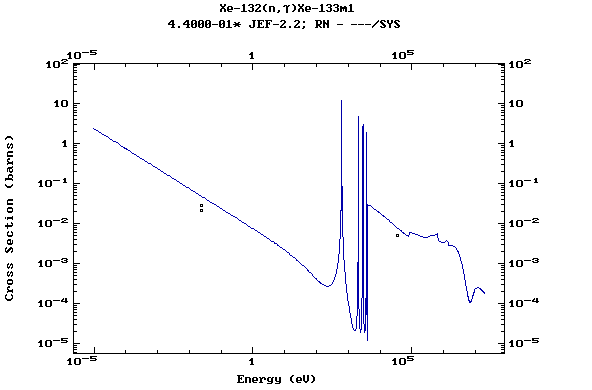
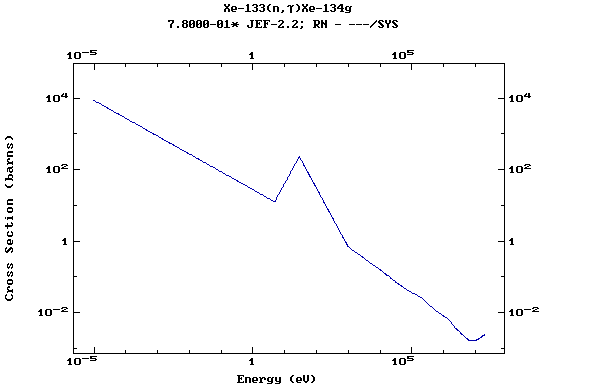
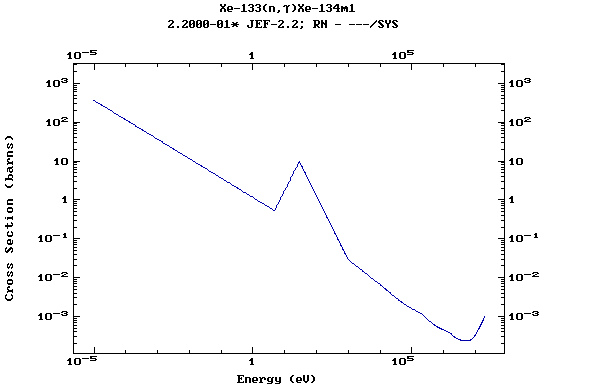
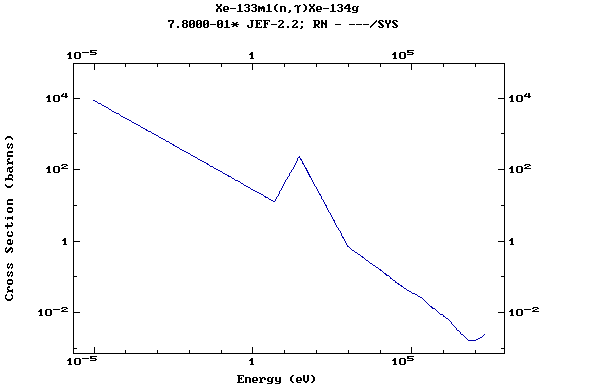
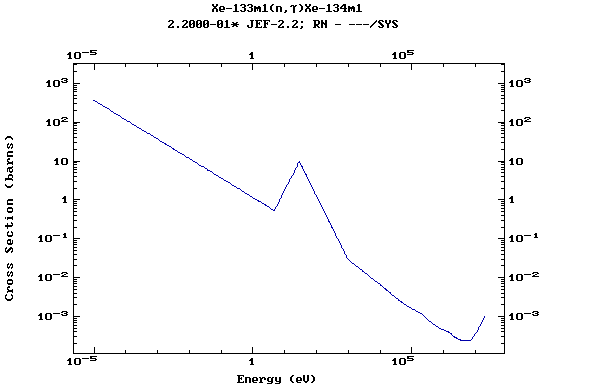
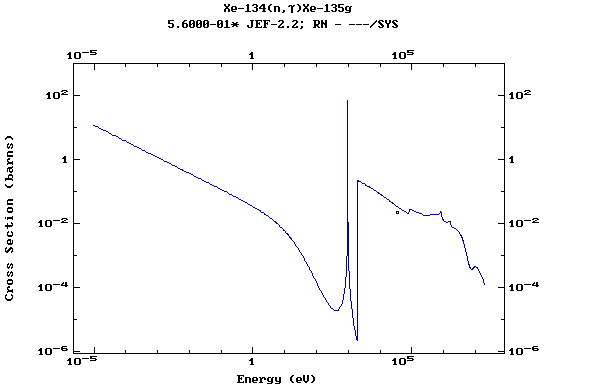
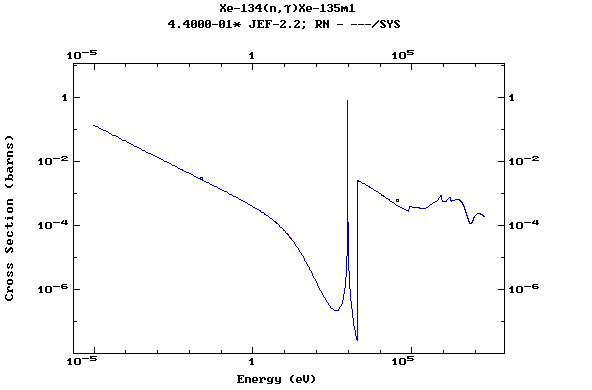
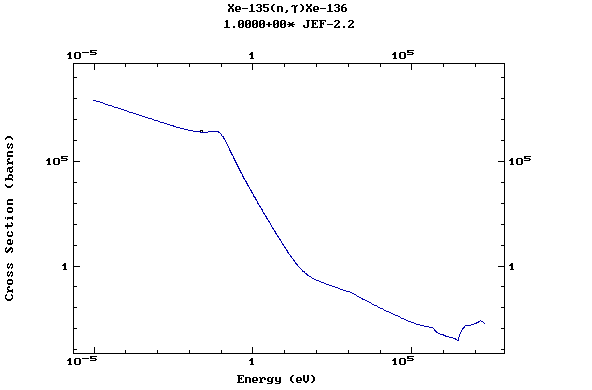
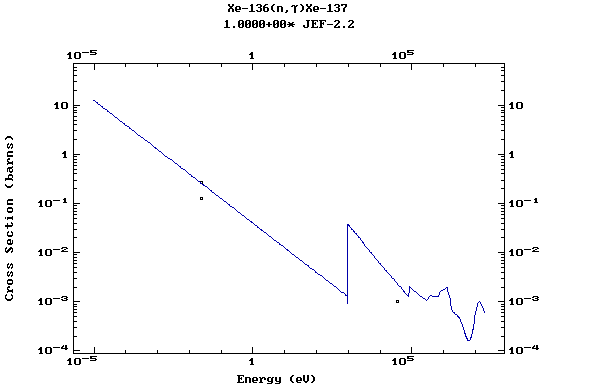
Z=55, Cs
(Cesium)
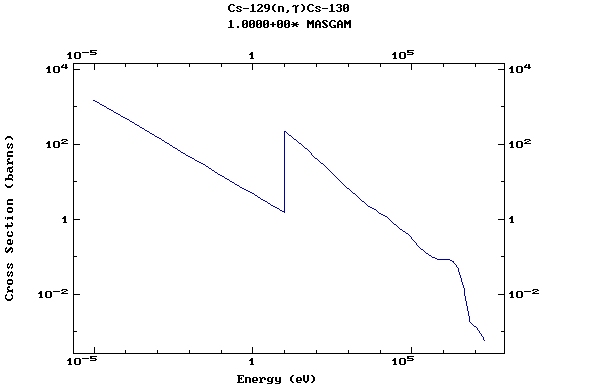
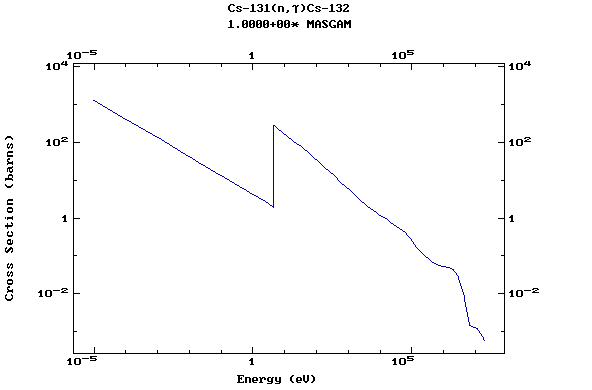
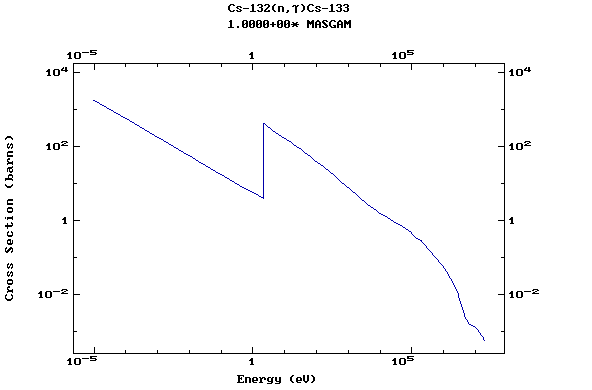
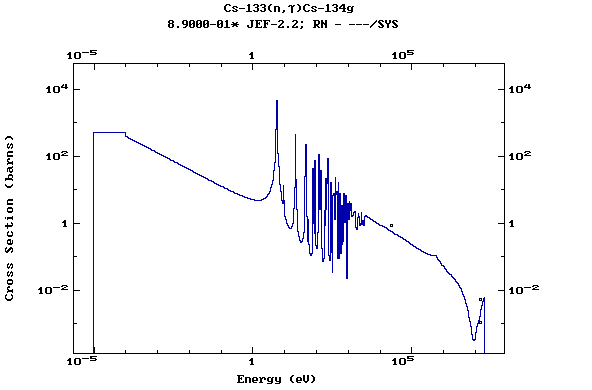
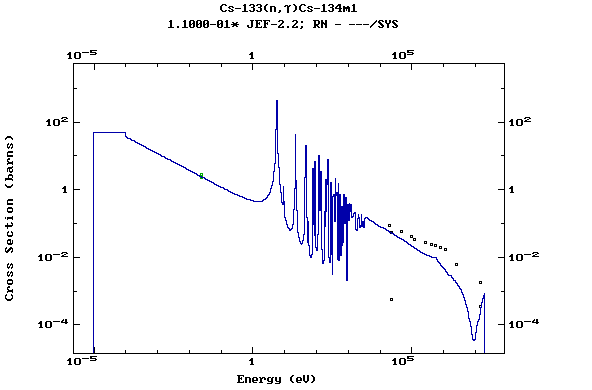
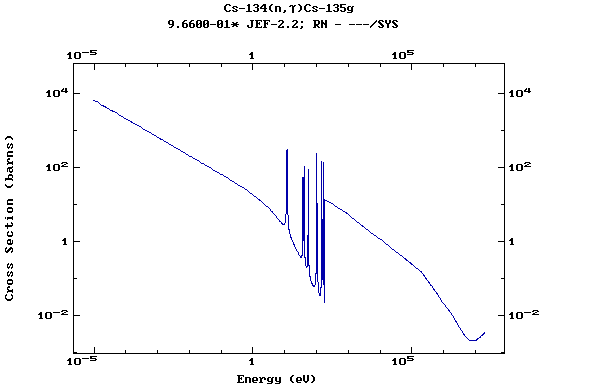
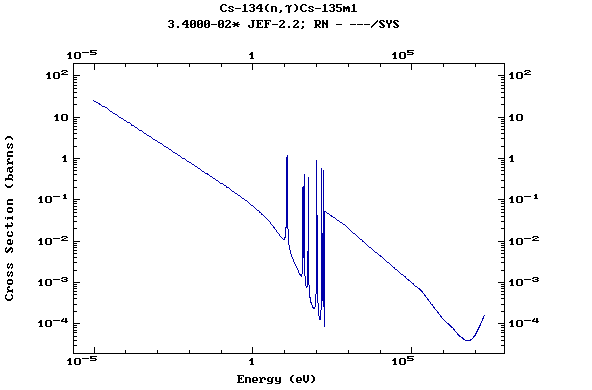
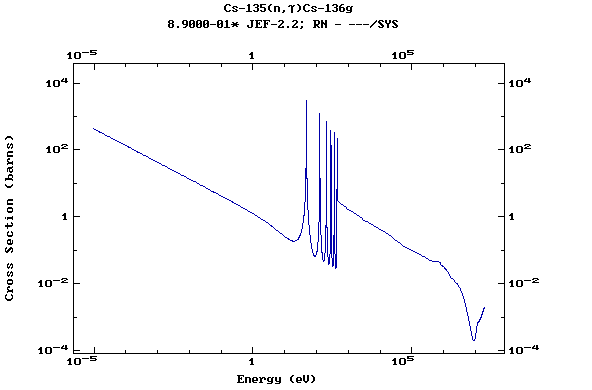
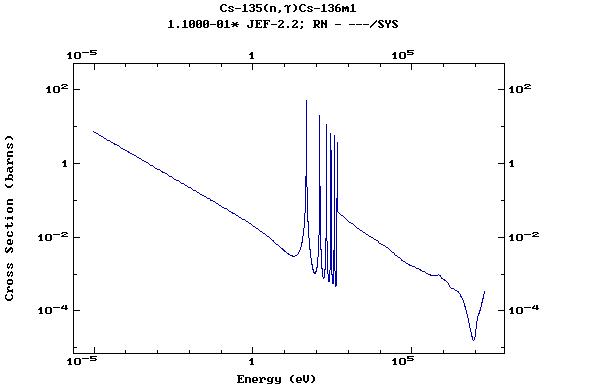
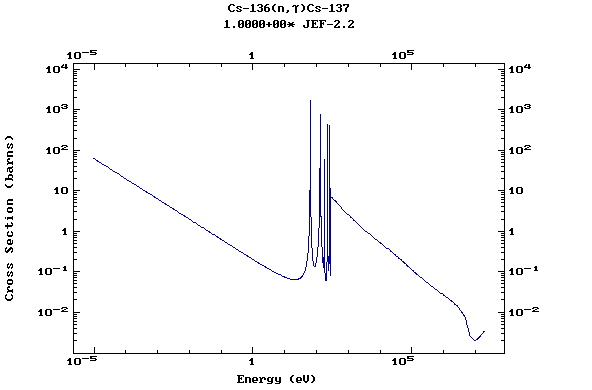
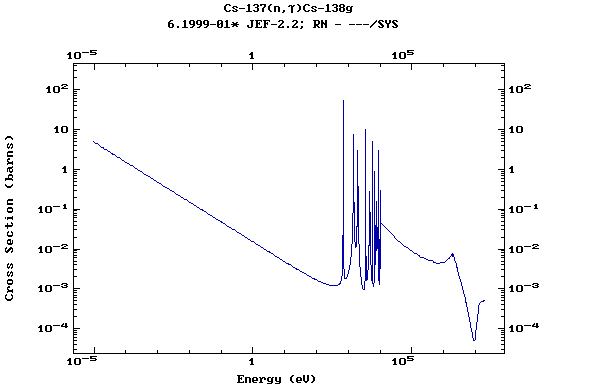
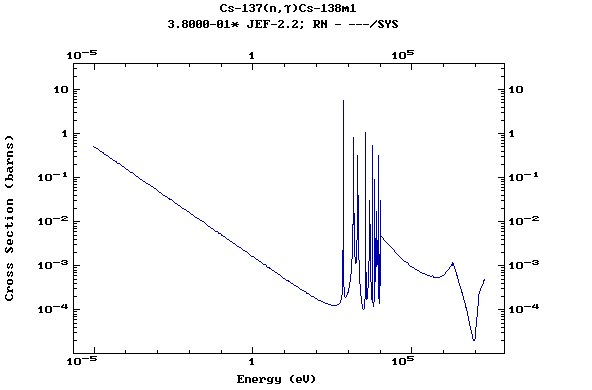
Z=56, Ba
(Barium)
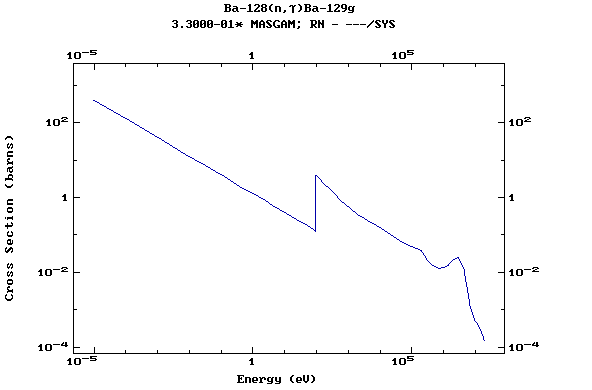
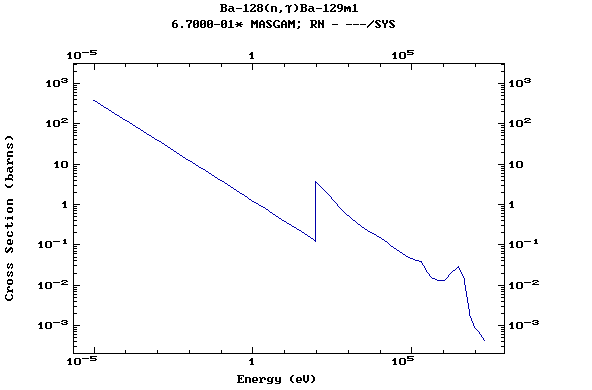
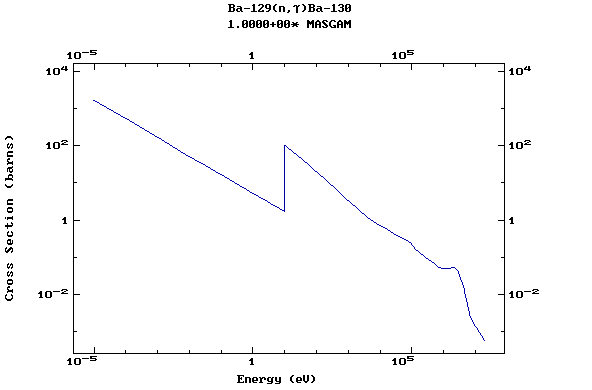
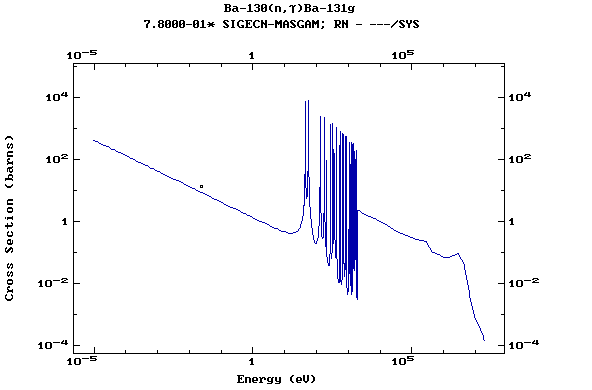
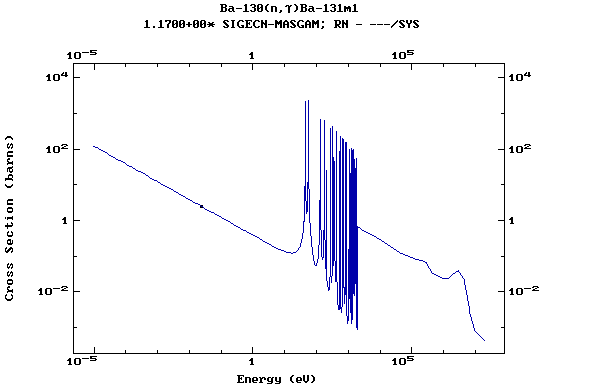
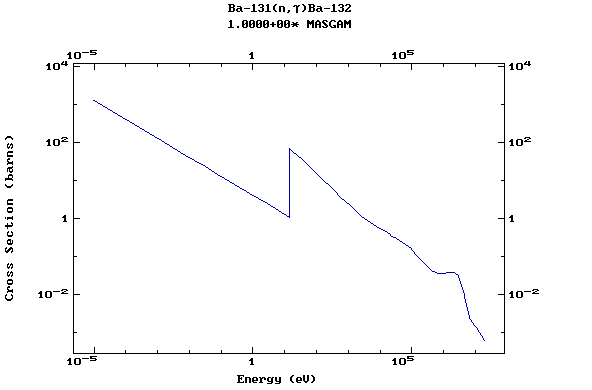
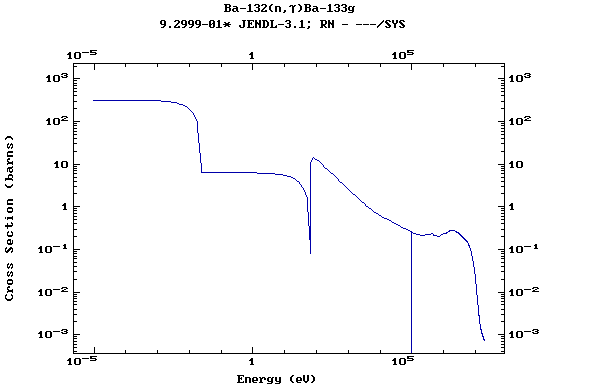
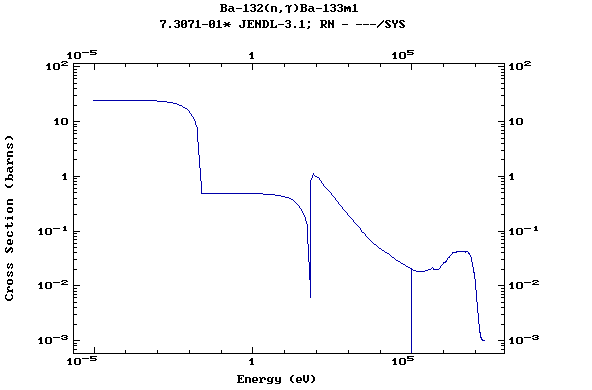
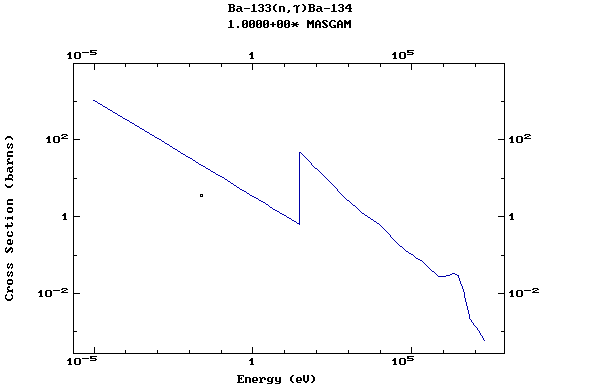
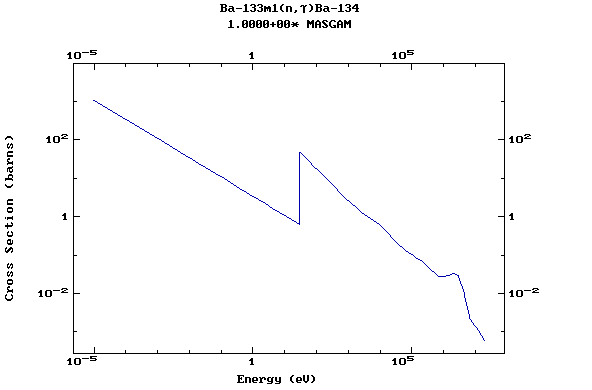
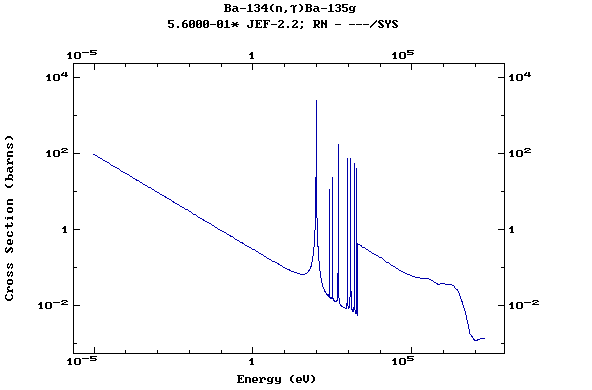
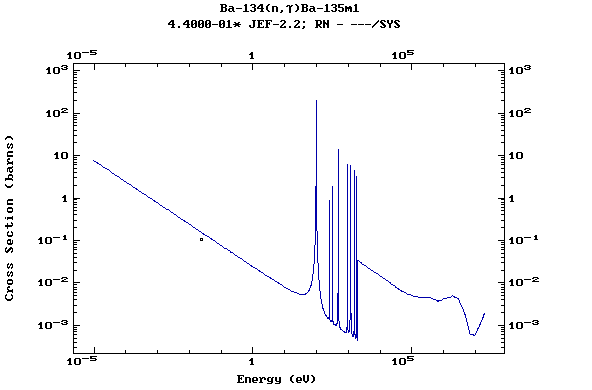
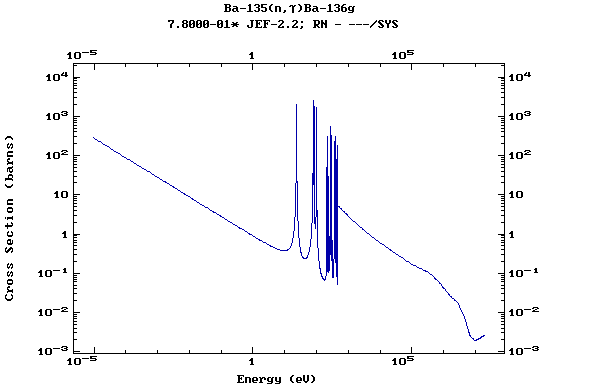
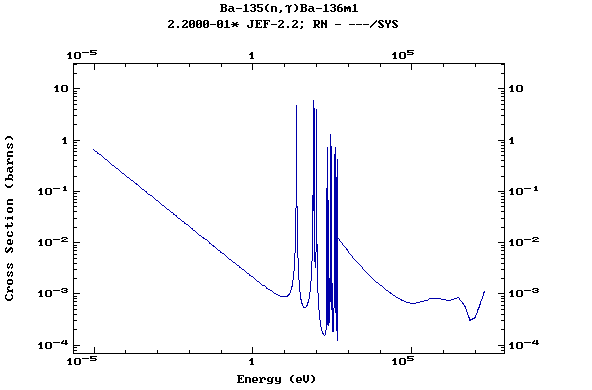
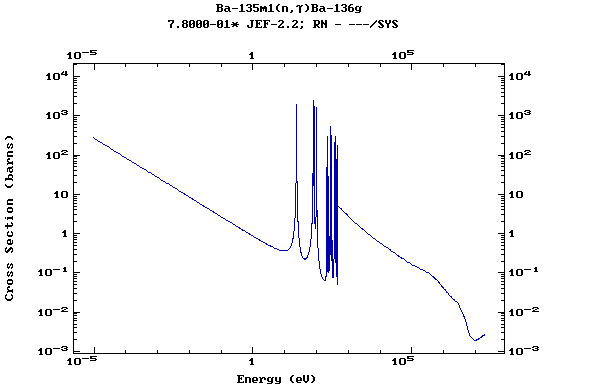
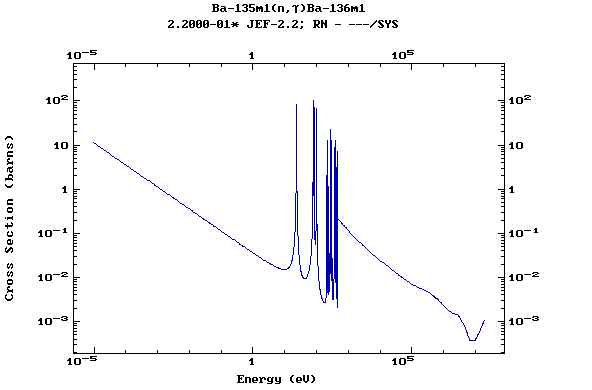
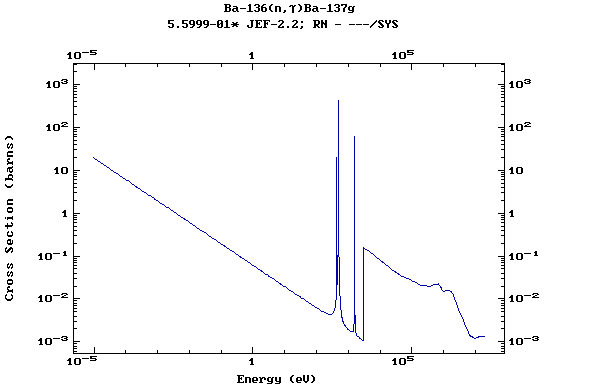
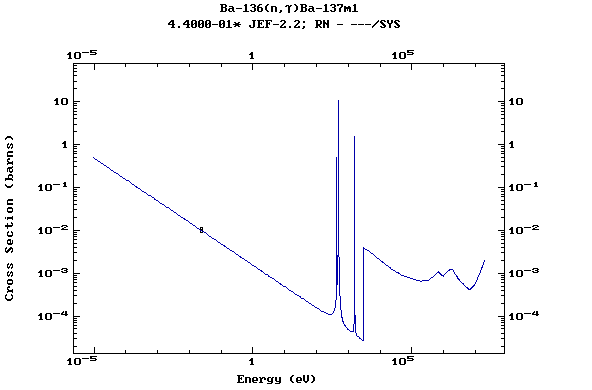
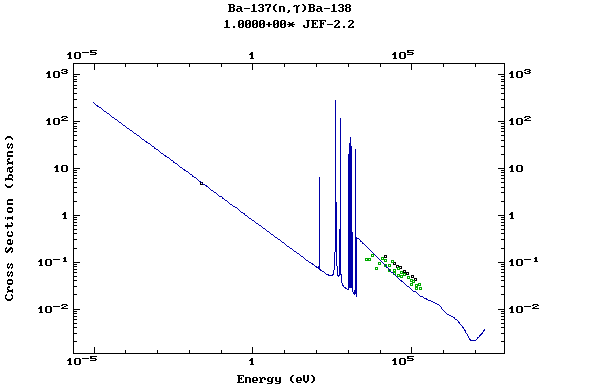
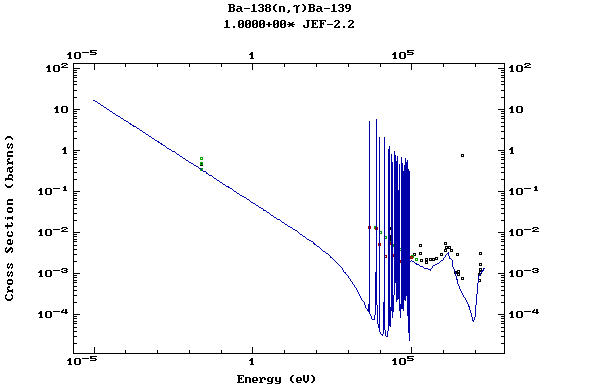
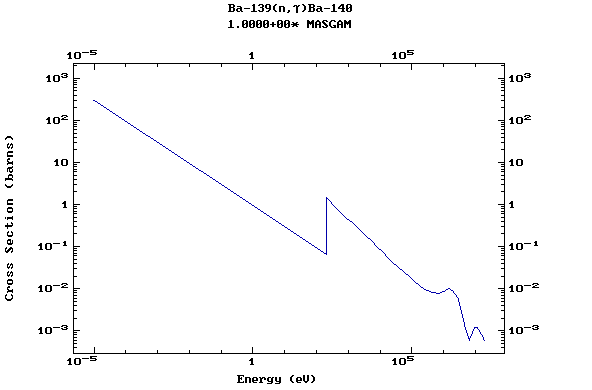
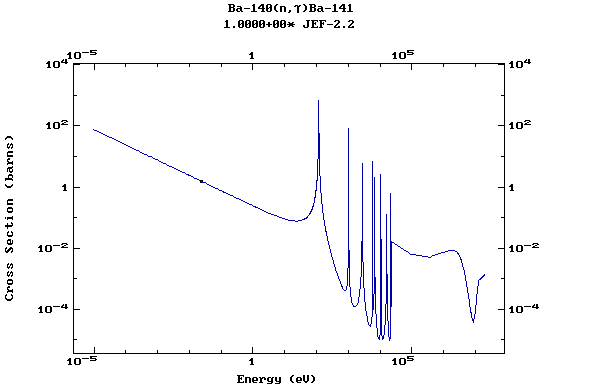
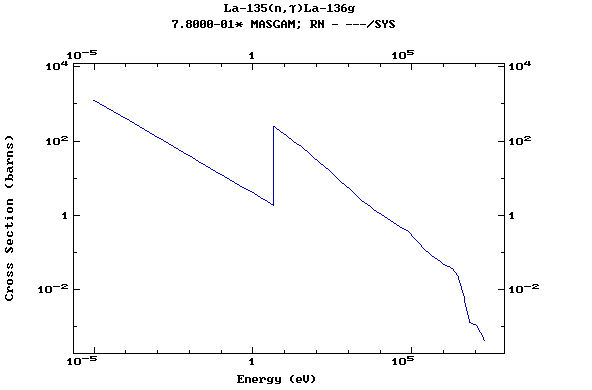
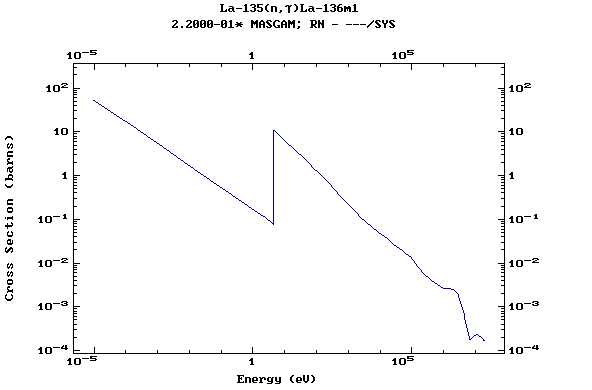
Z=57, La
(Lanthanum)
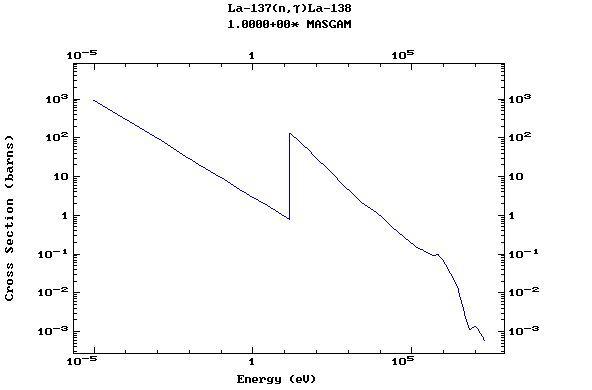
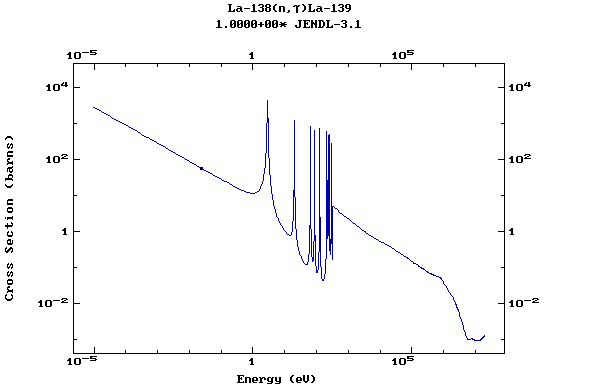
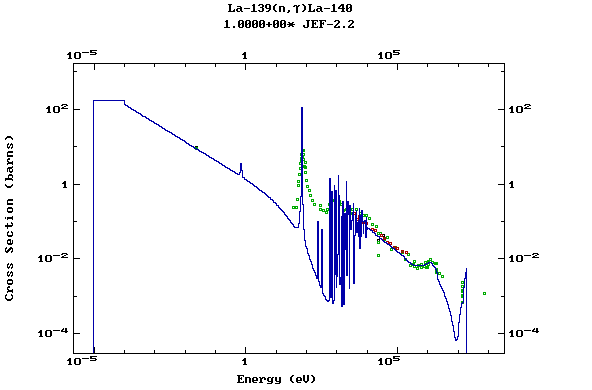
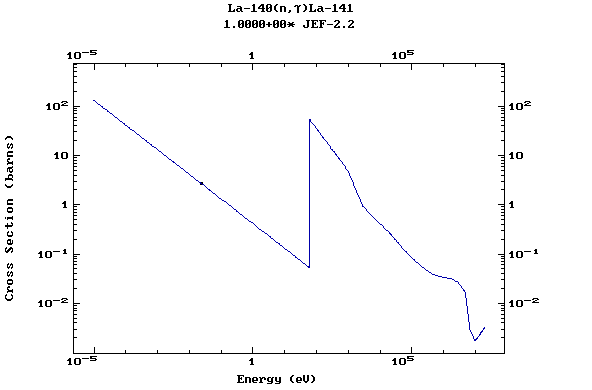
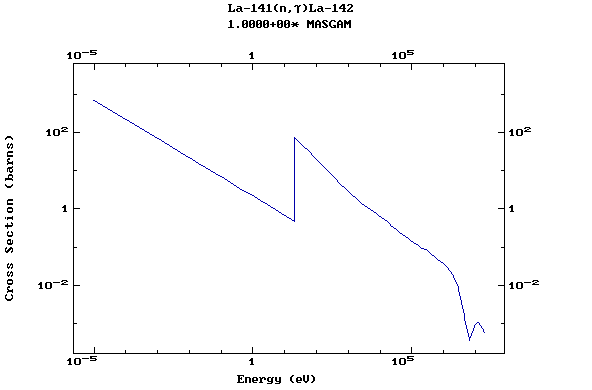
Z=58, Ce
(Cerium)
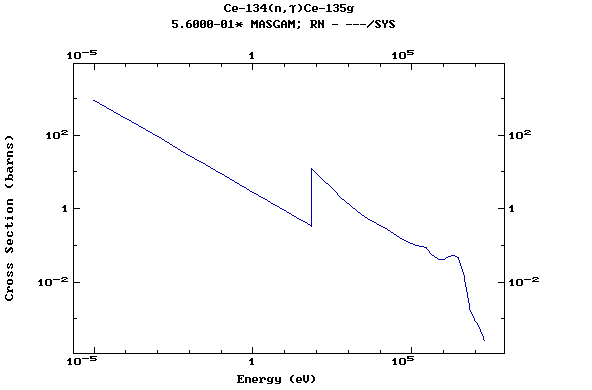
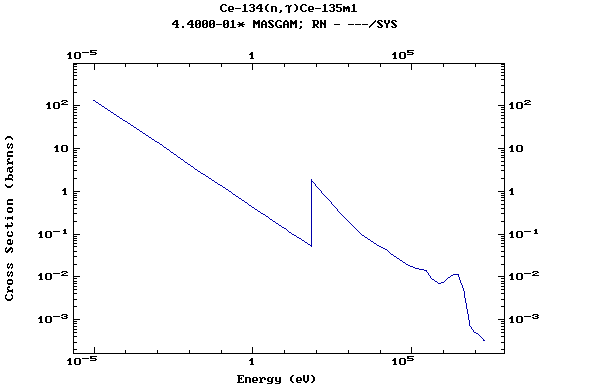
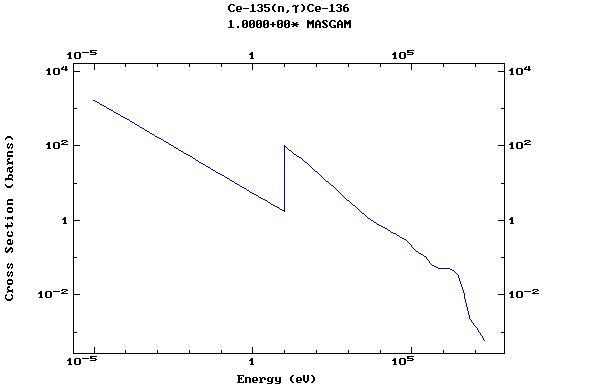
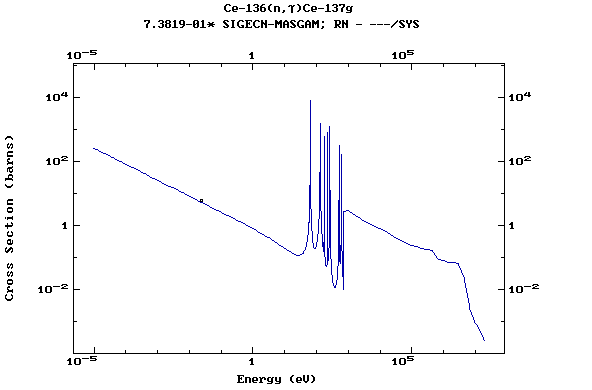
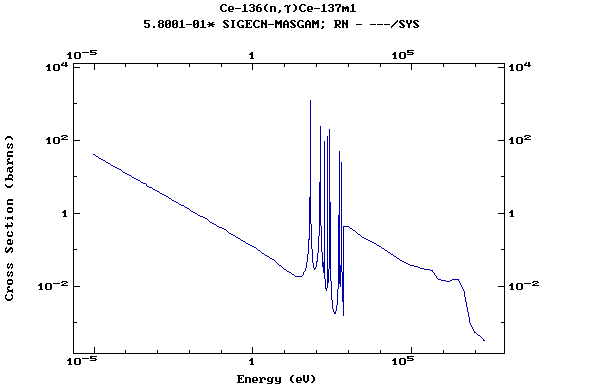
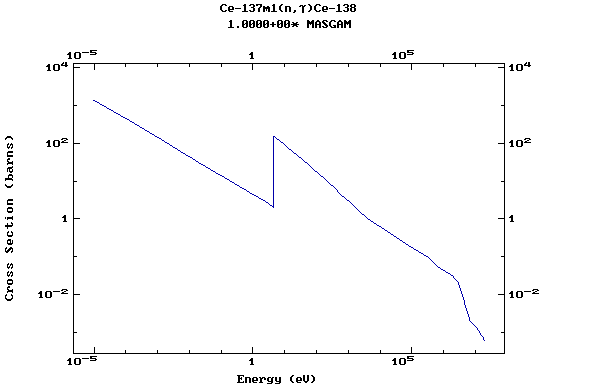
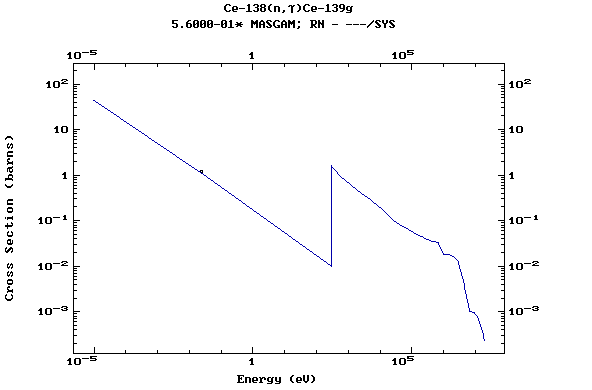
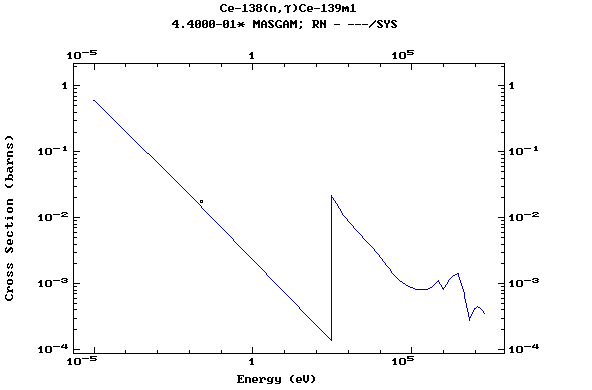
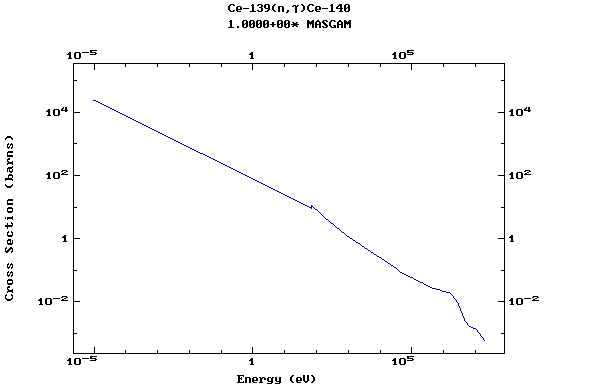
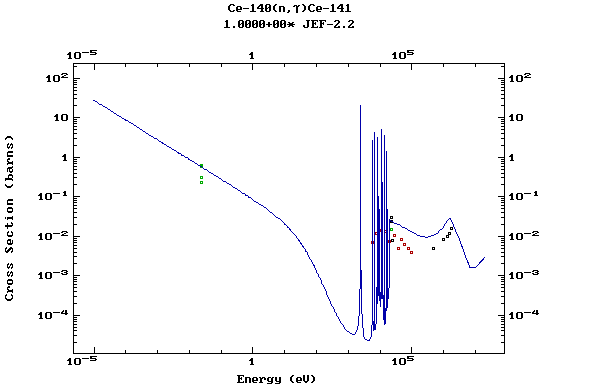
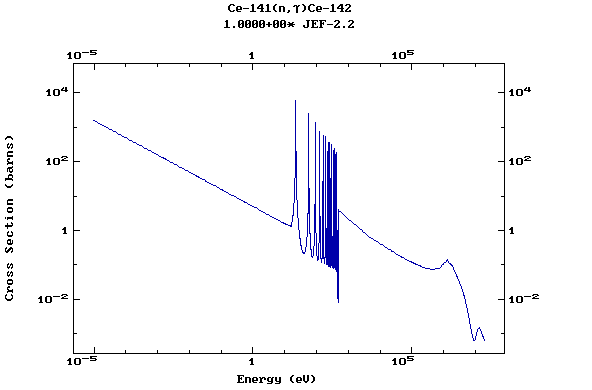
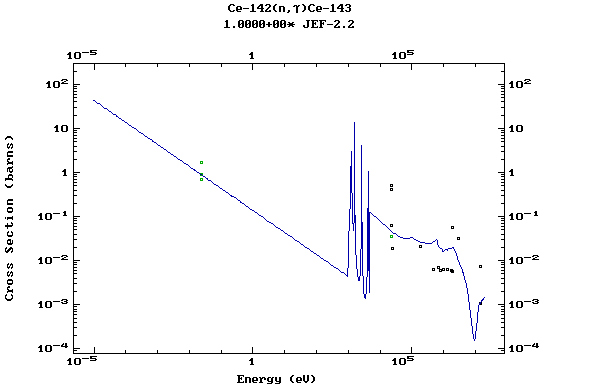
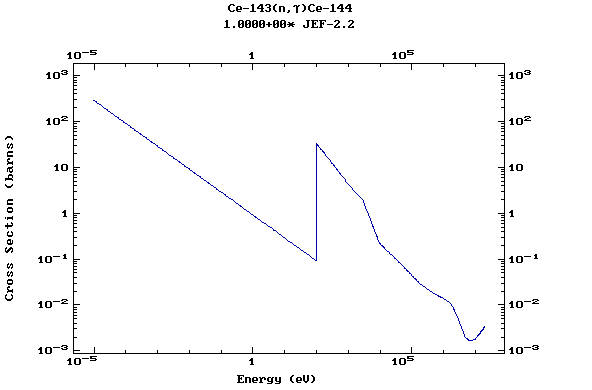
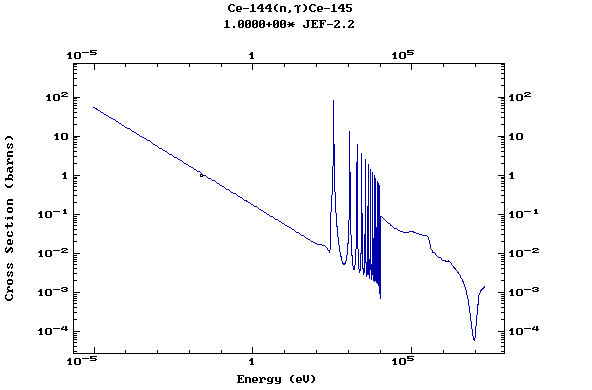
Z=59, Pr
(Praesodymium)
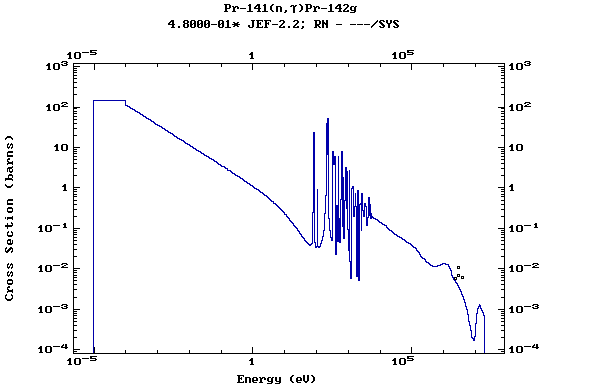
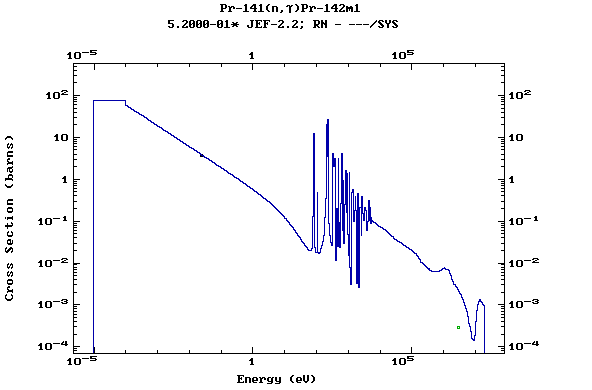
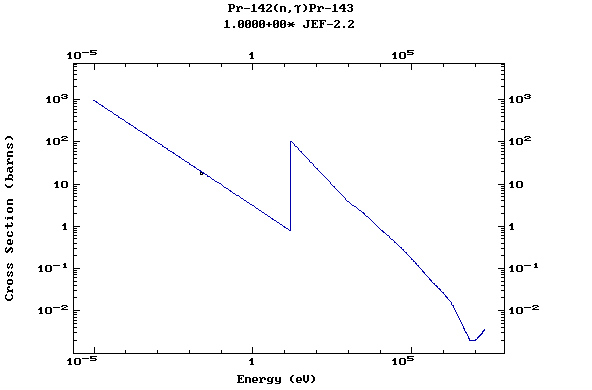
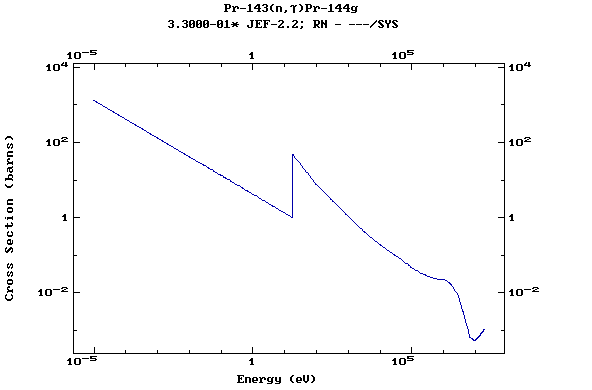
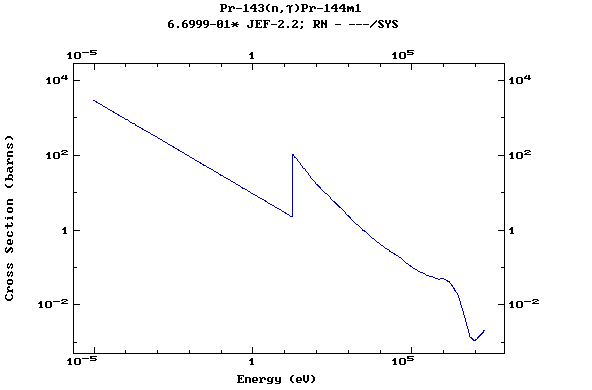
Z=60, Nd
(Neodymium)
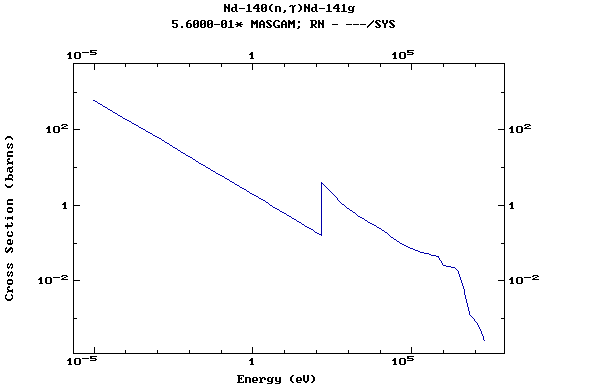
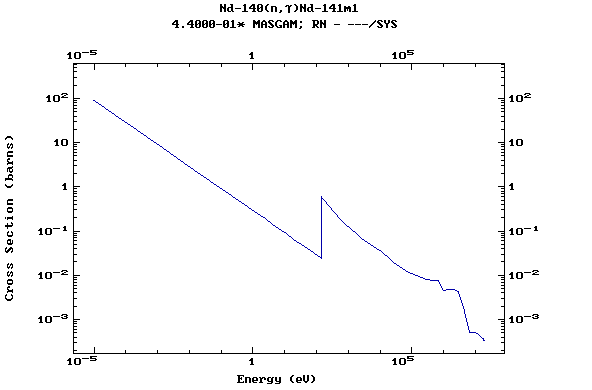
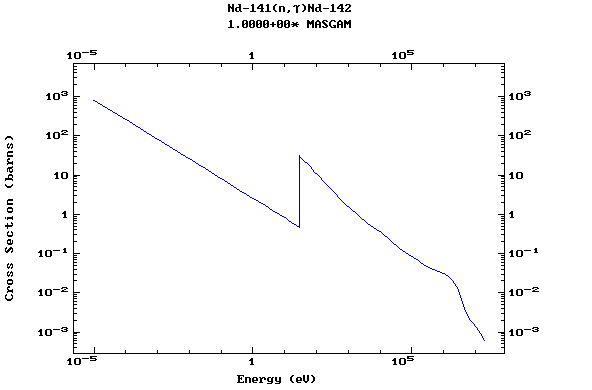
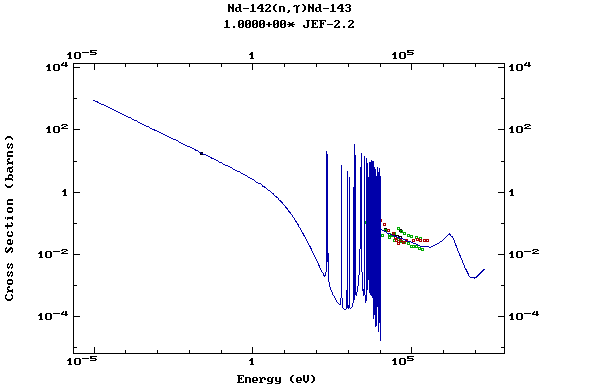
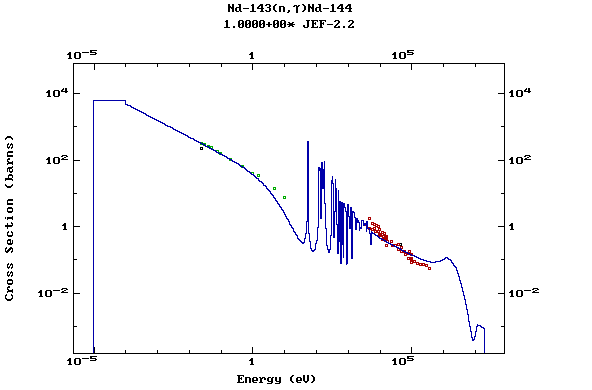
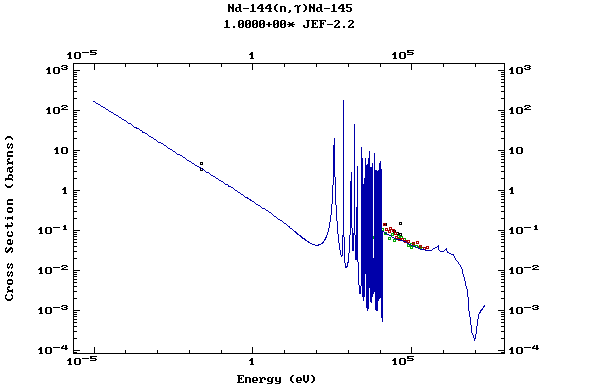
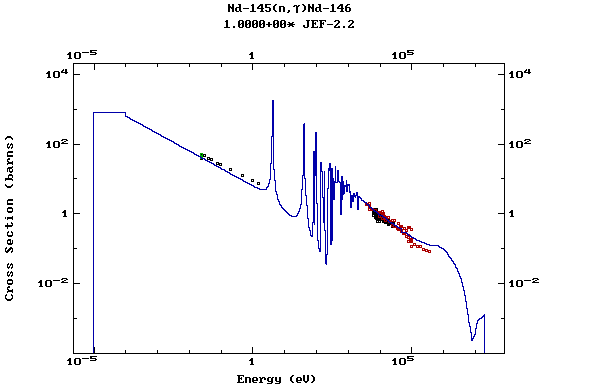
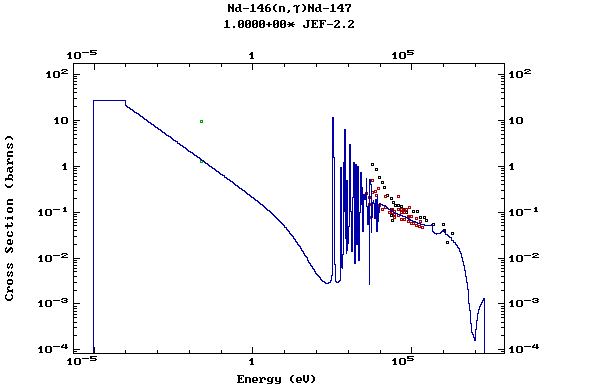
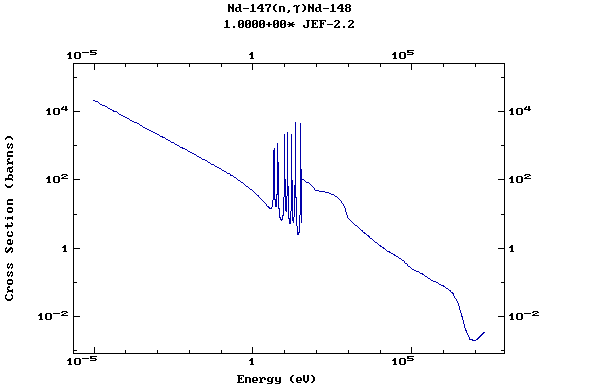
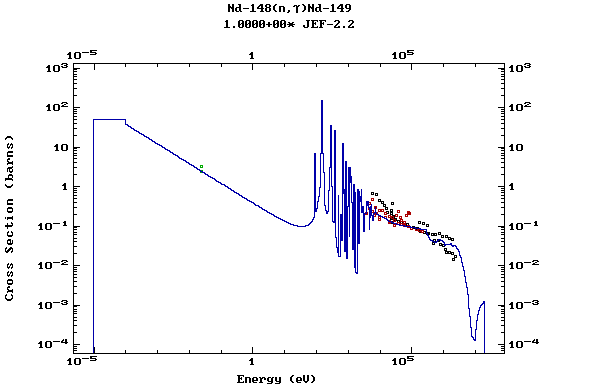
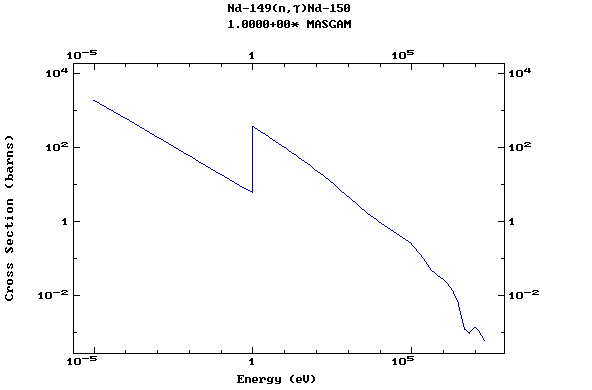
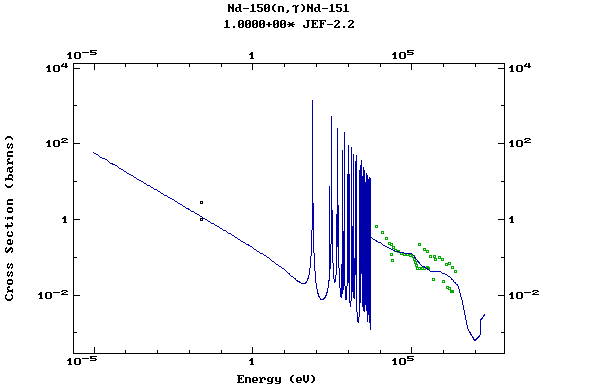
Z=61, Pm
(Promethium)
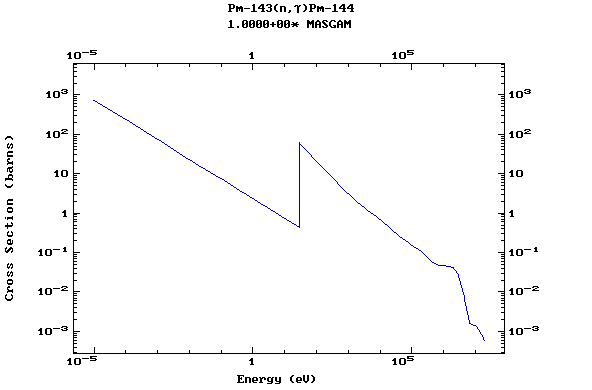
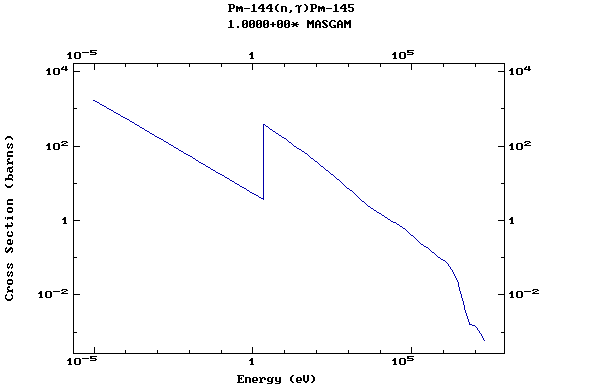
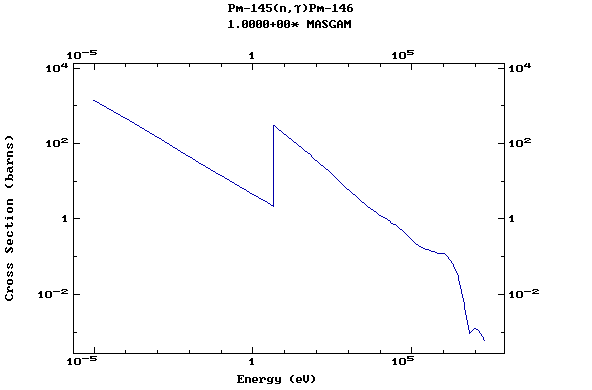
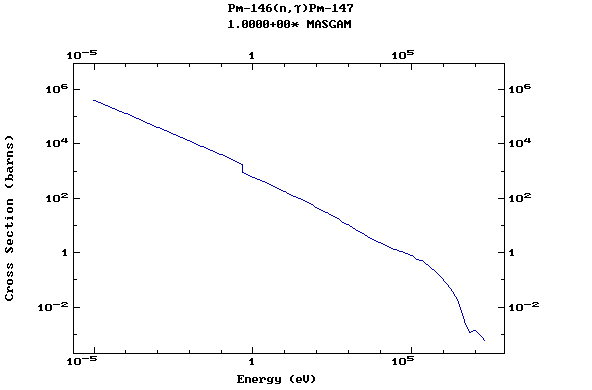
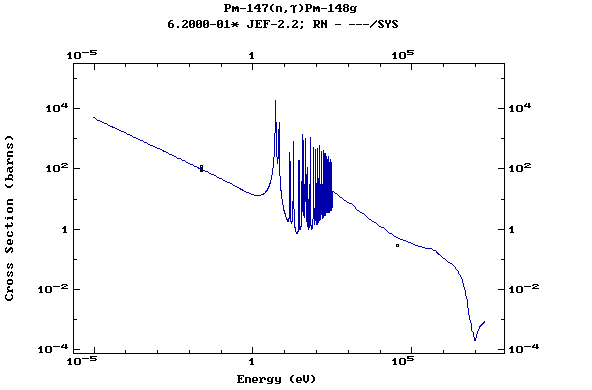
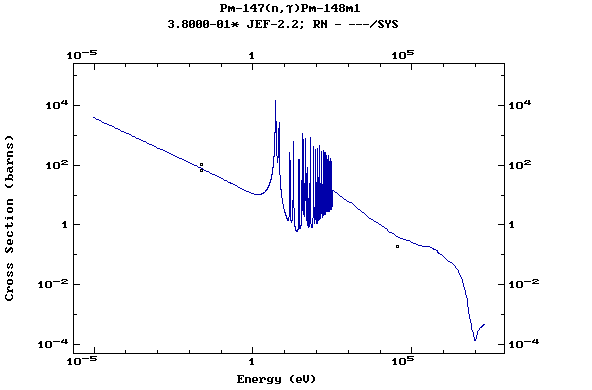
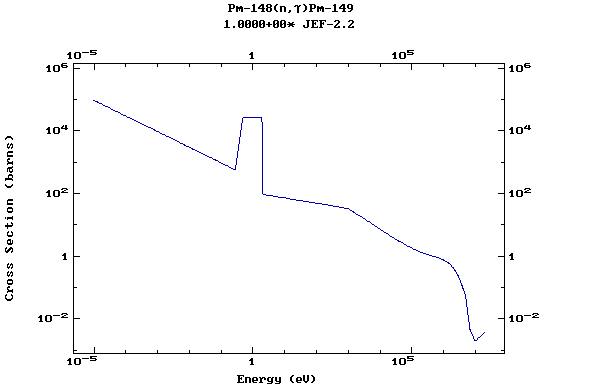
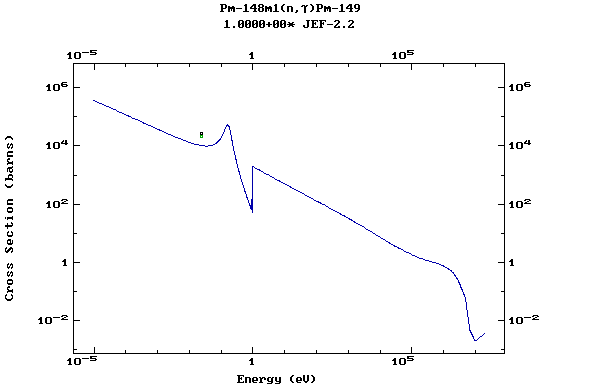
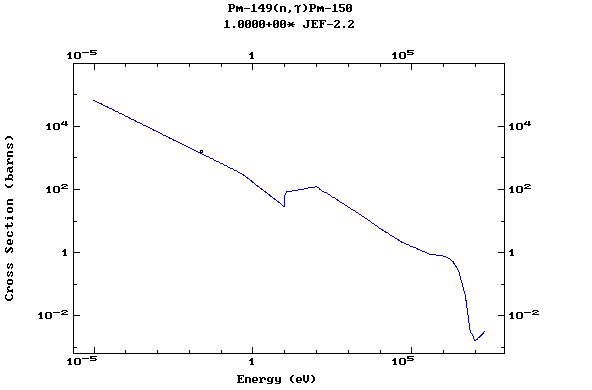
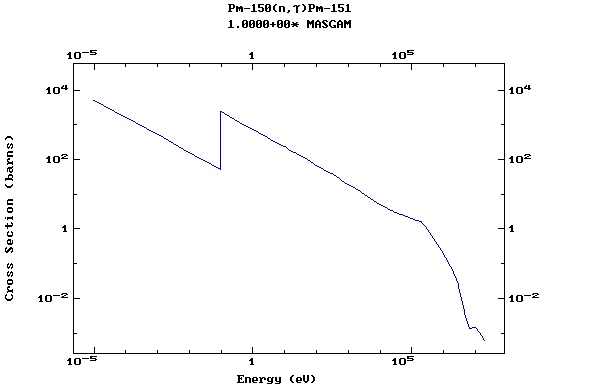
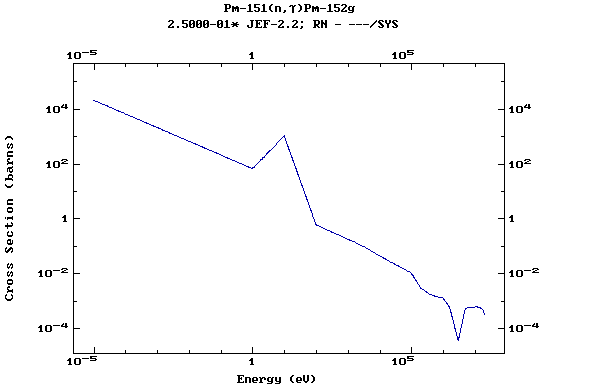
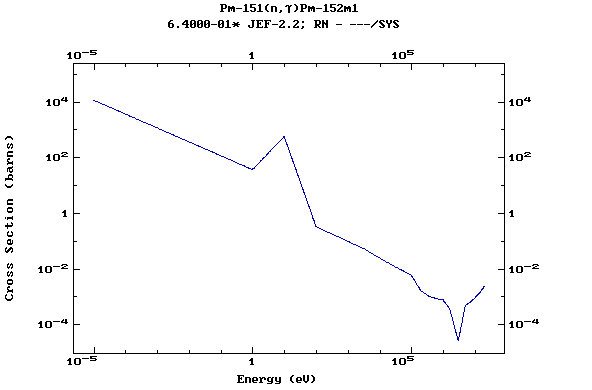
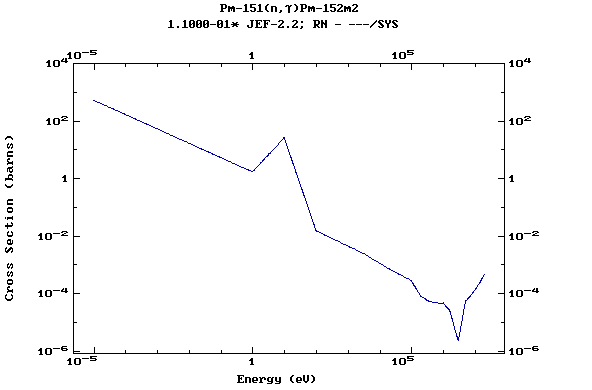
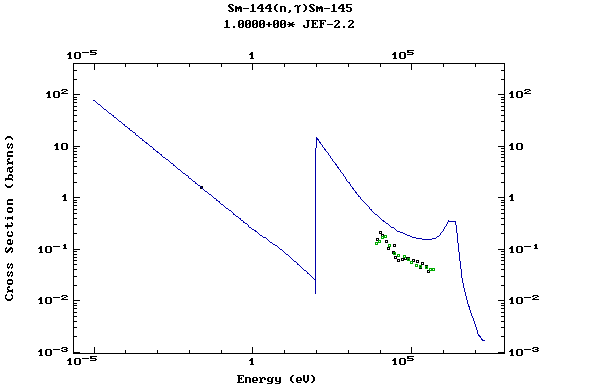
Z=62, Sm
(Samarium)
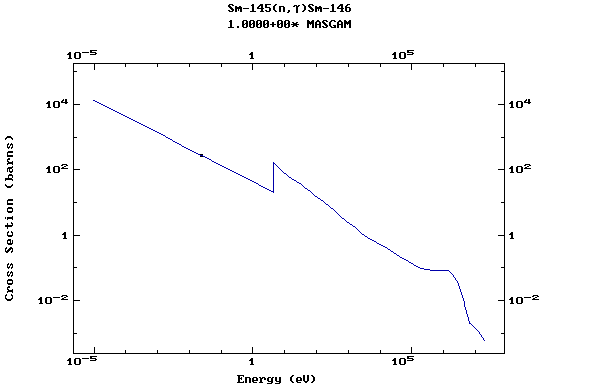
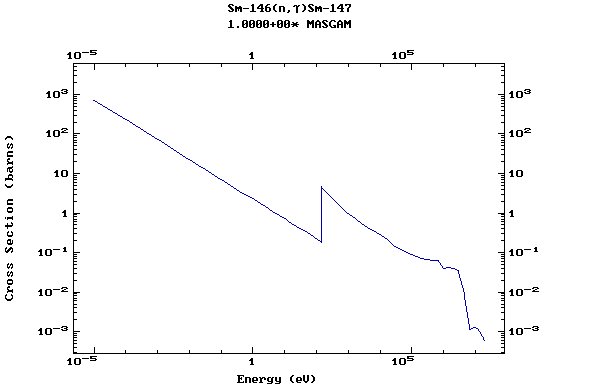
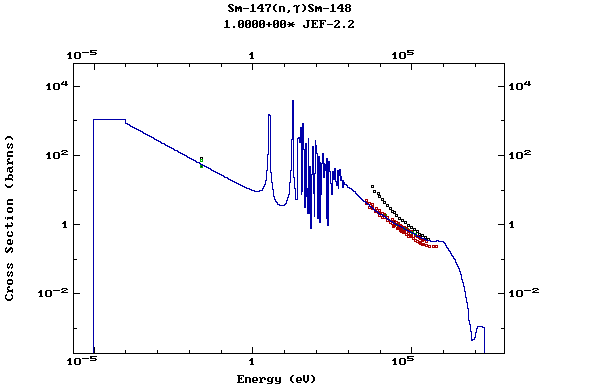
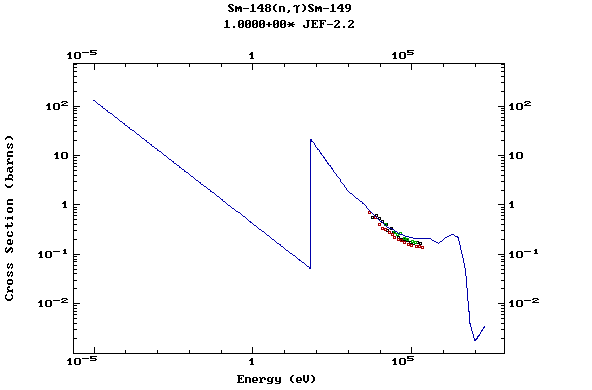
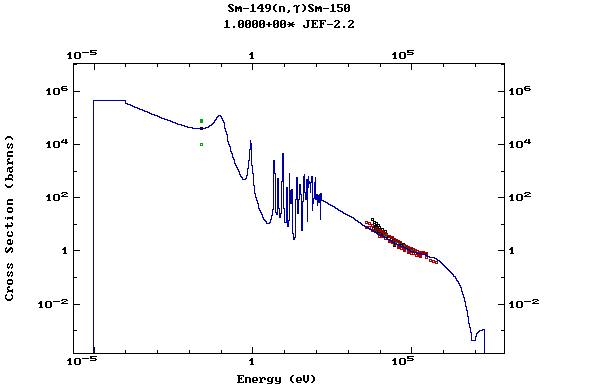
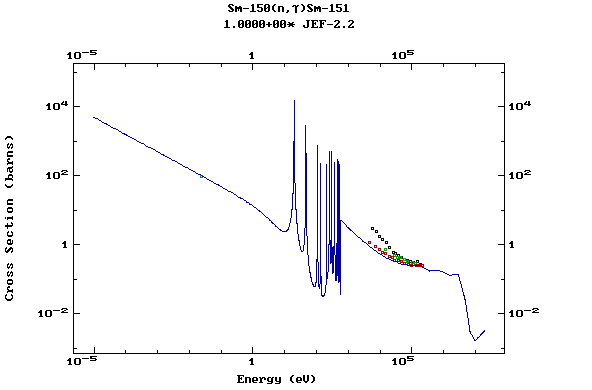
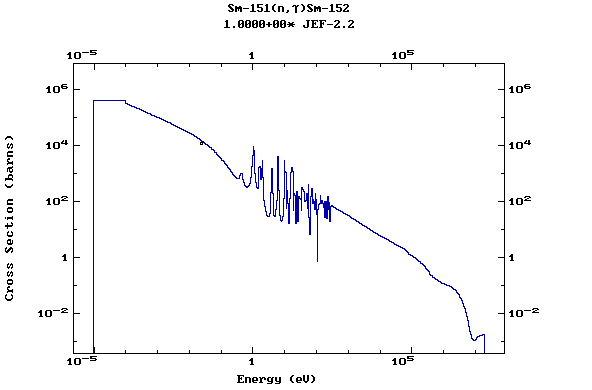
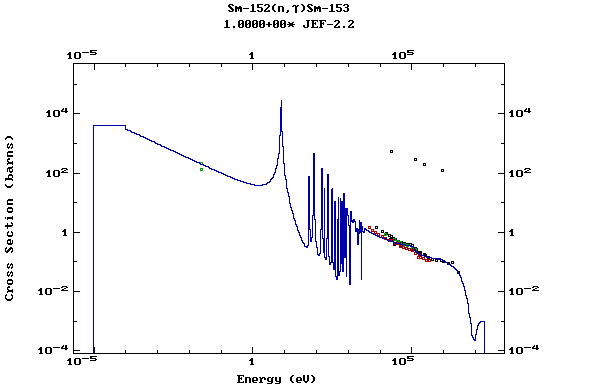
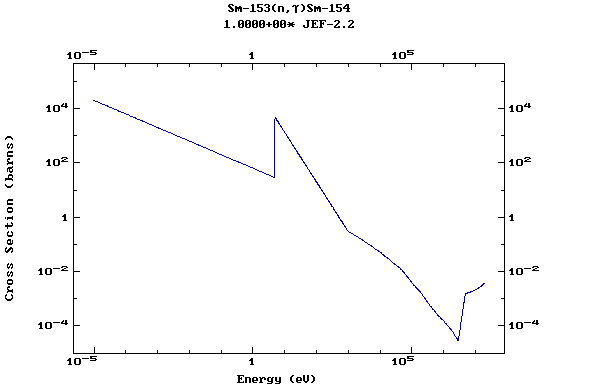
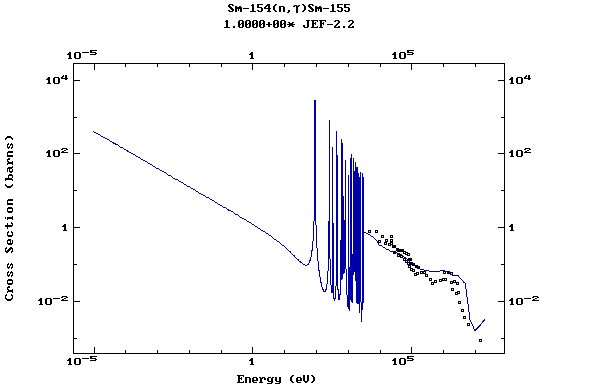
Z=63, Eu
(Europium)
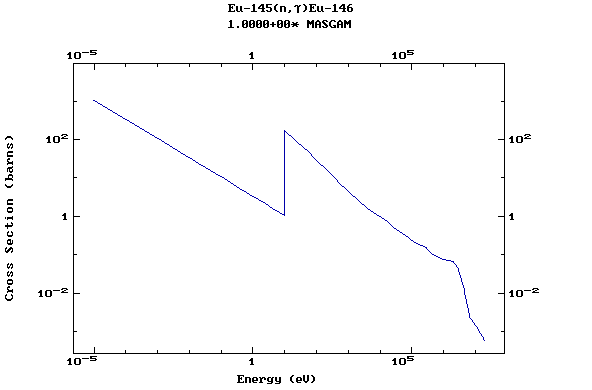
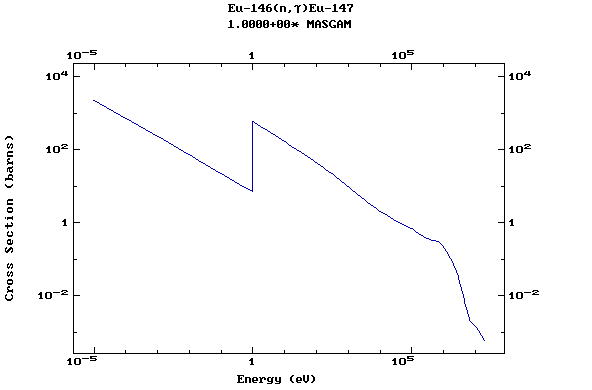
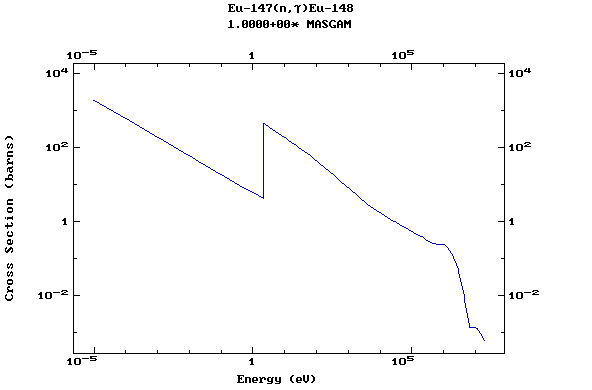
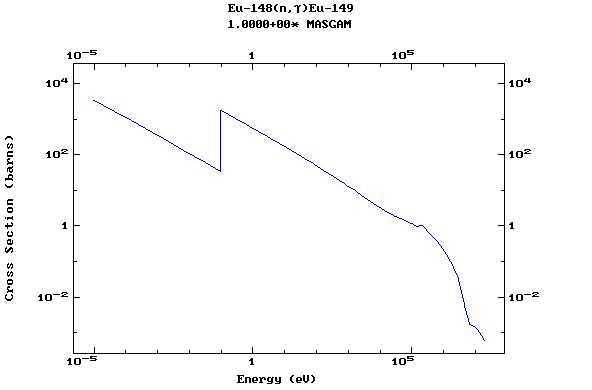
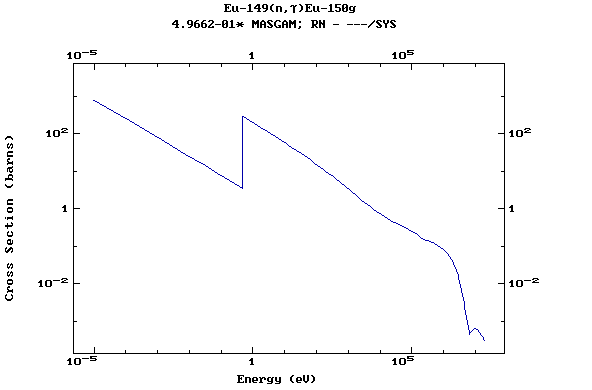
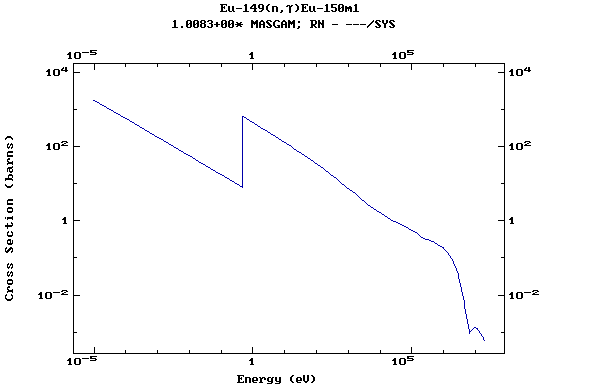
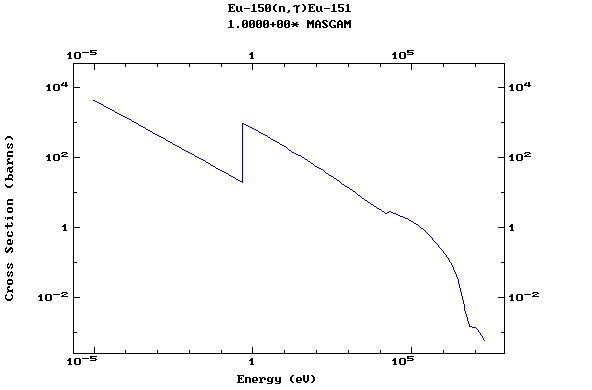
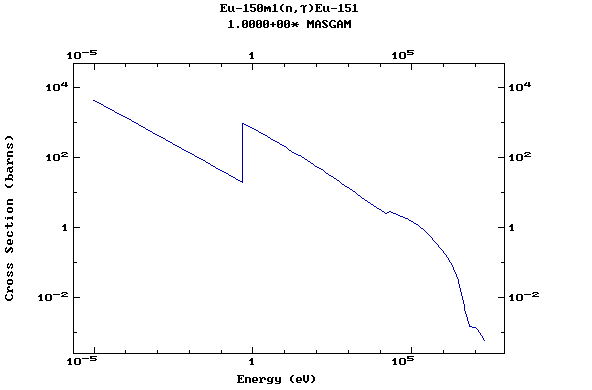
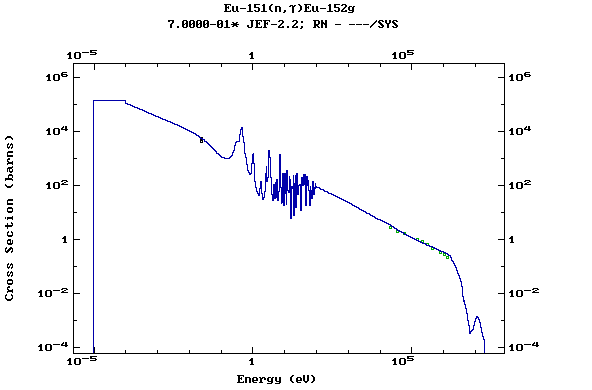
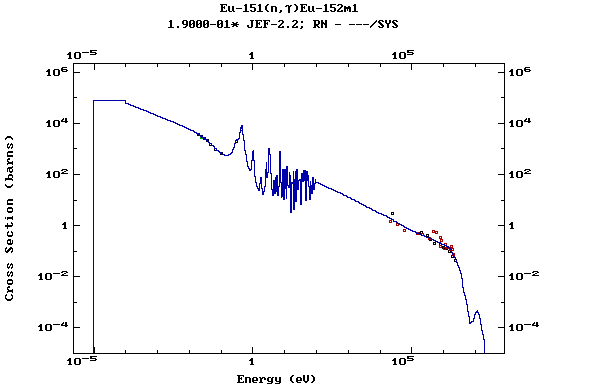
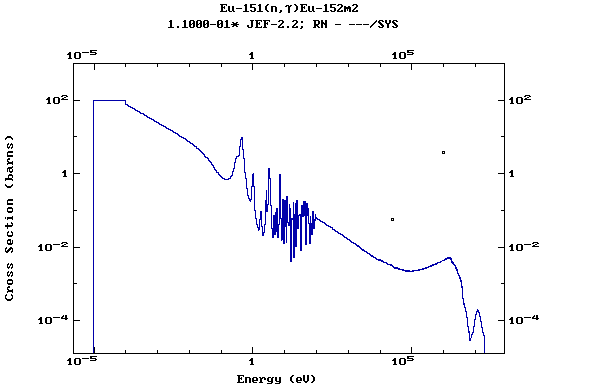
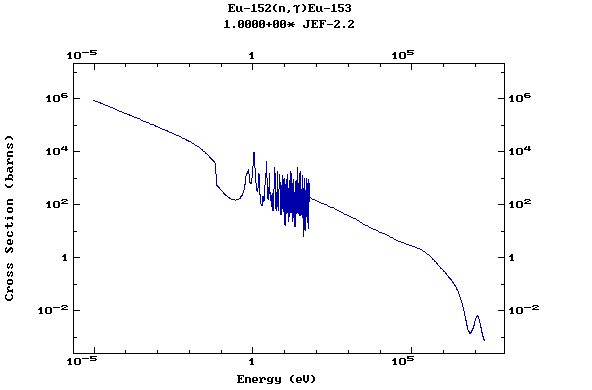
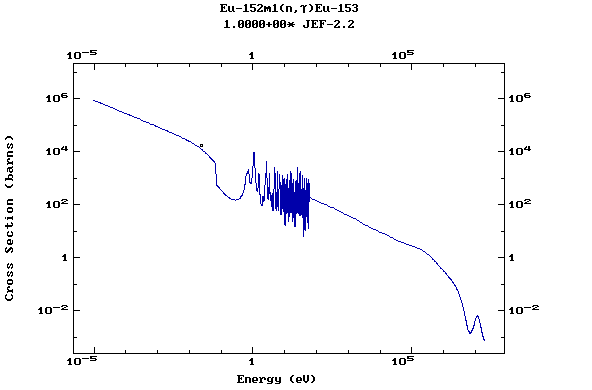
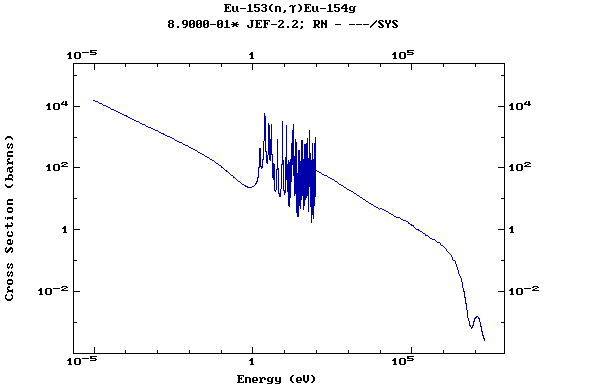
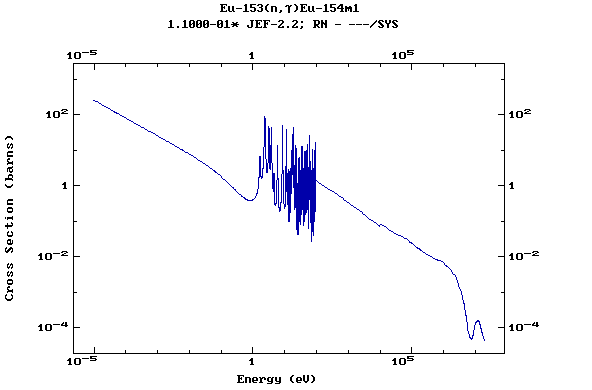
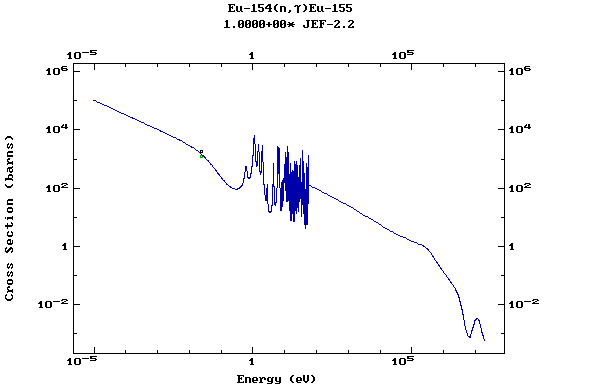
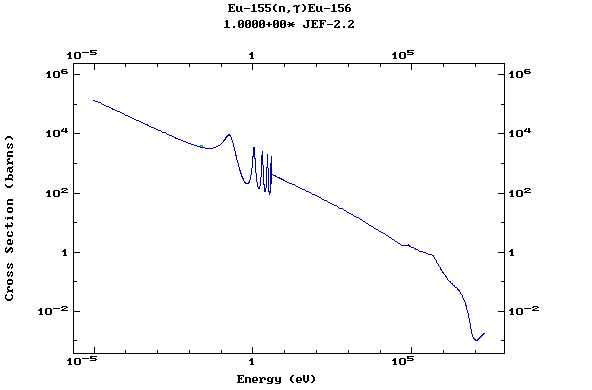
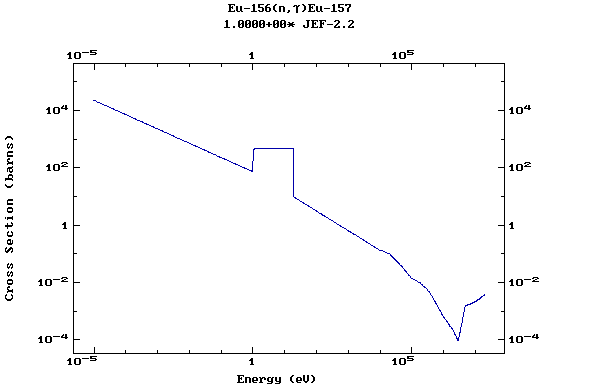
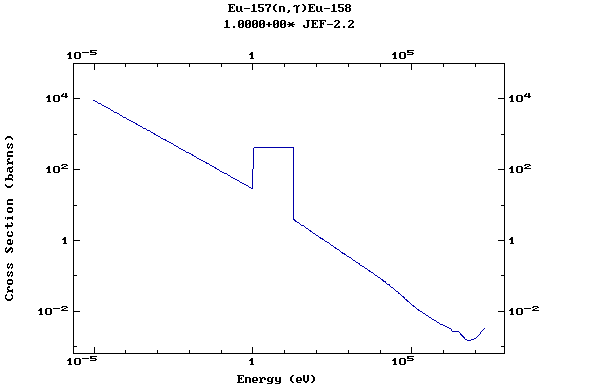
Z=64, Gd
(Gadolinium)
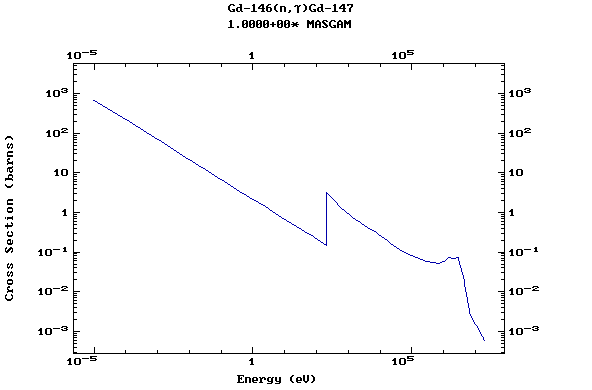
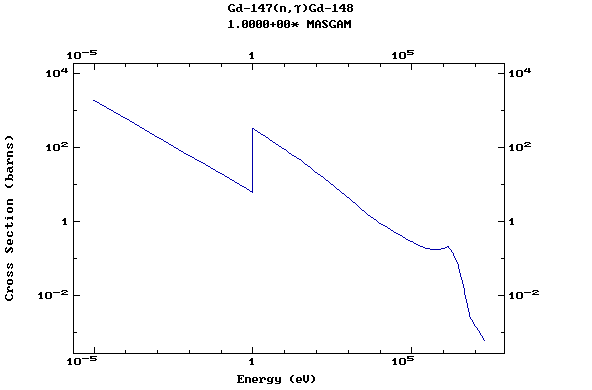
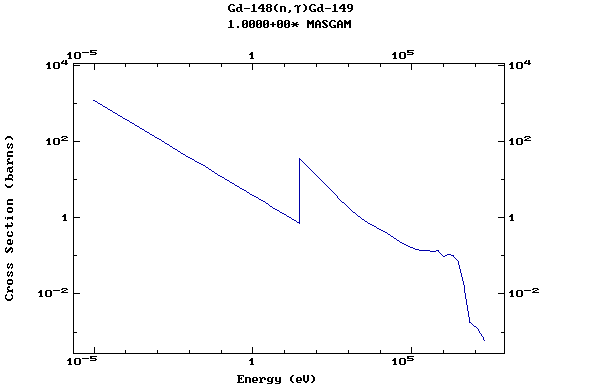
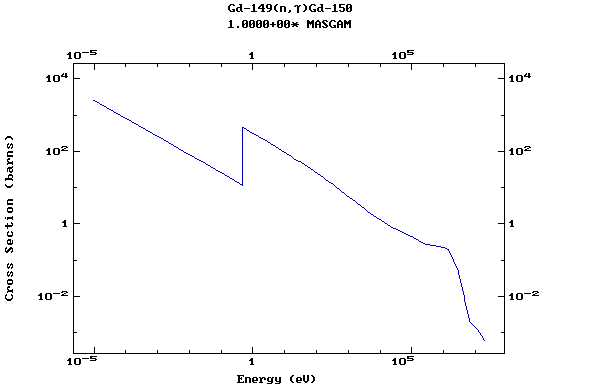
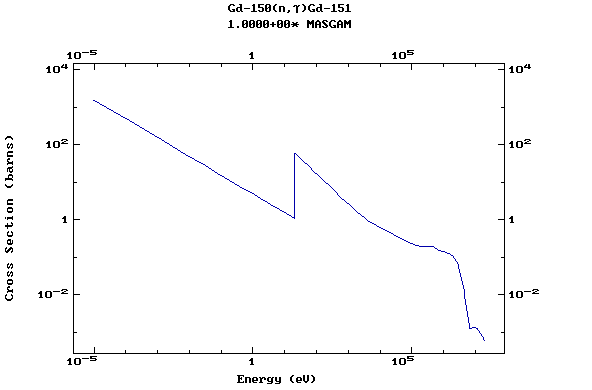
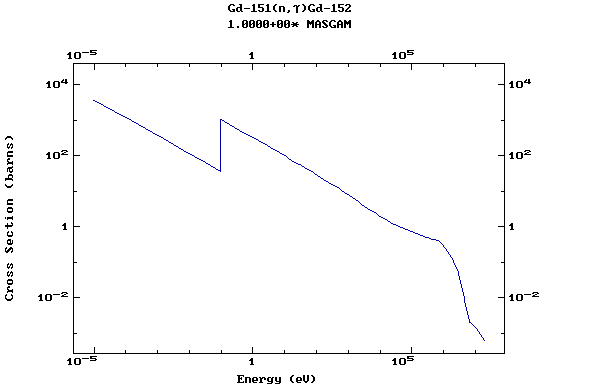
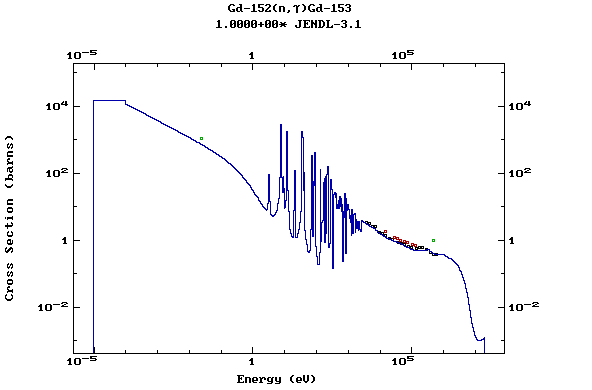
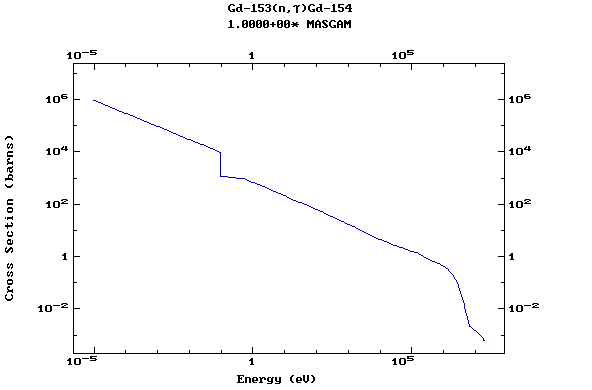
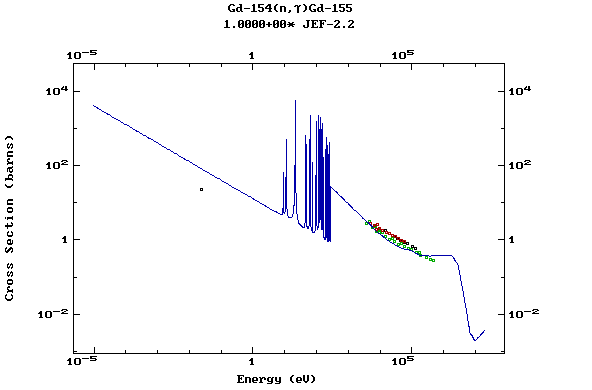
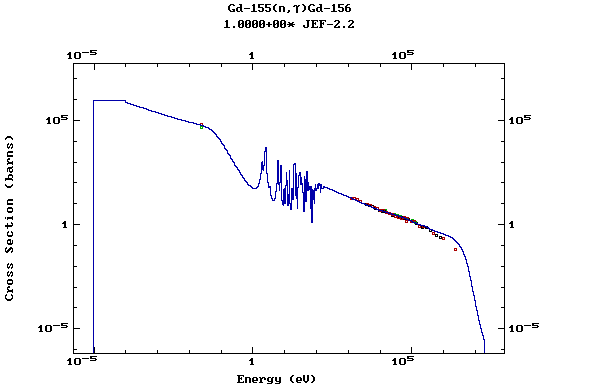
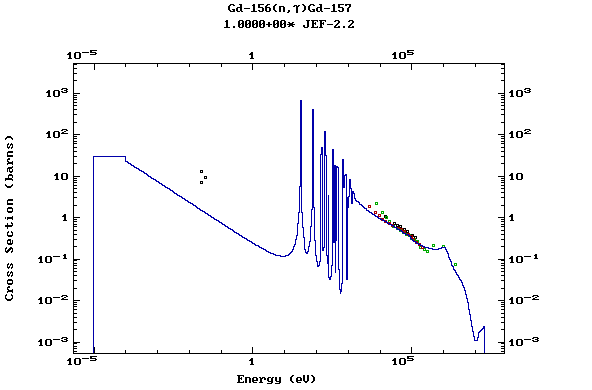
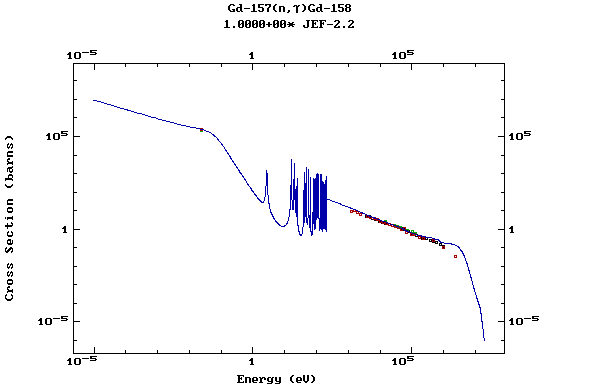
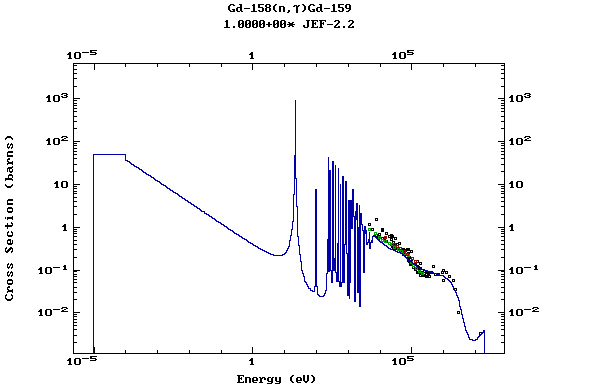
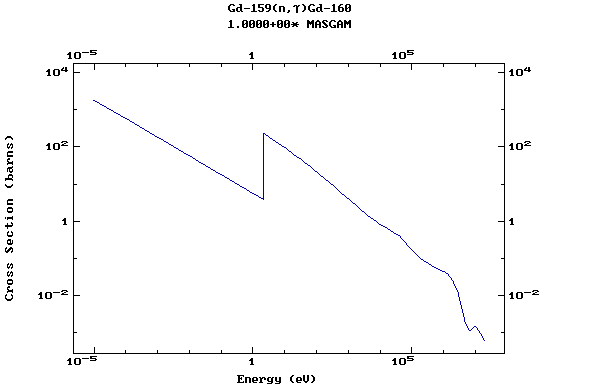
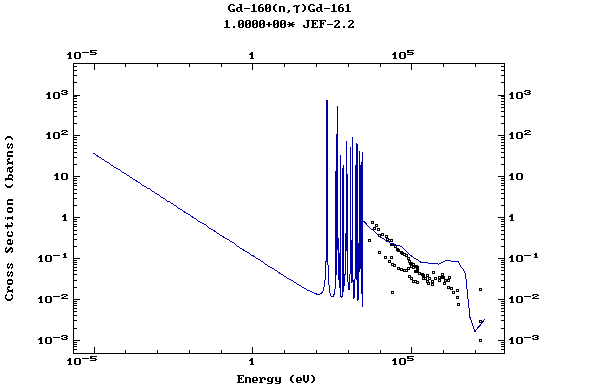
Z=65, Tb
(Terbium)
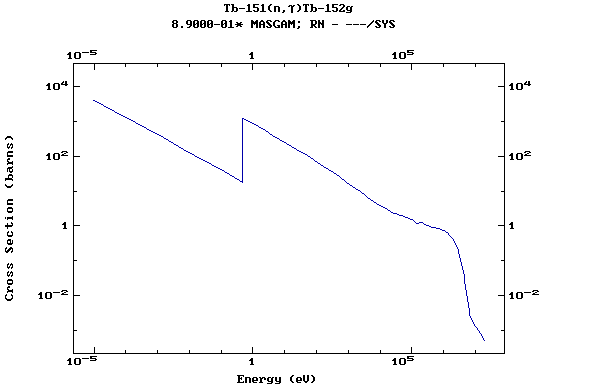
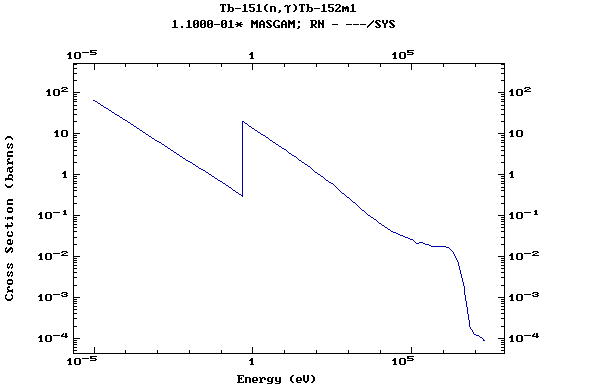
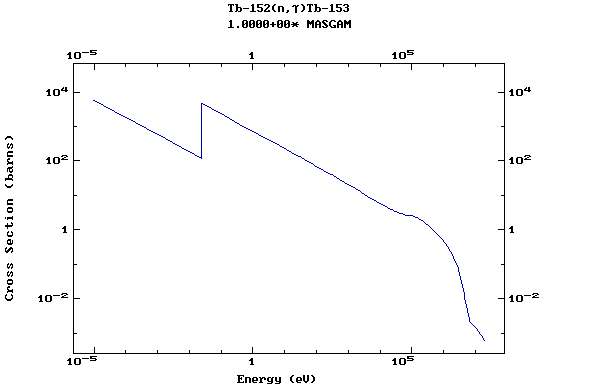
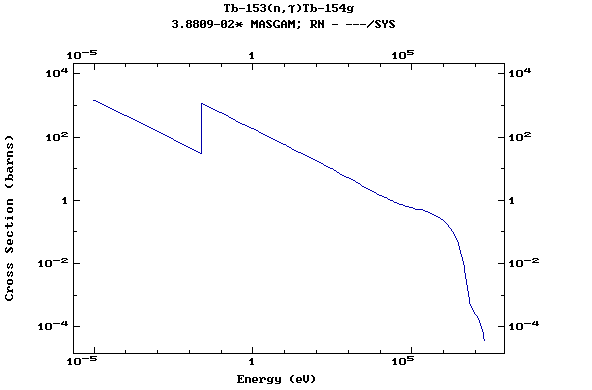
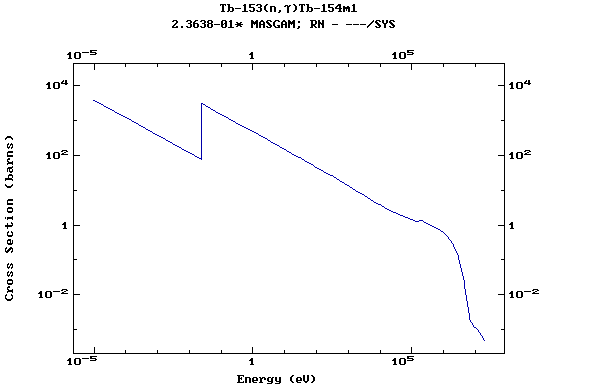
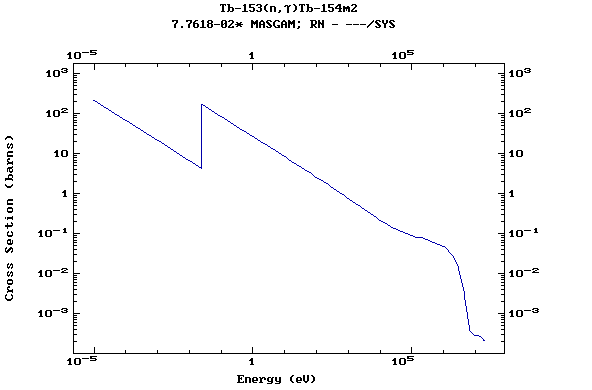
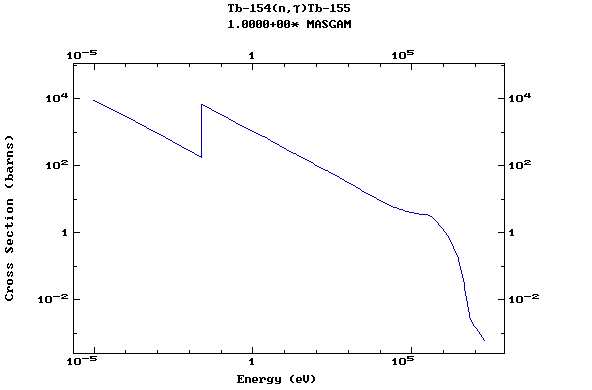
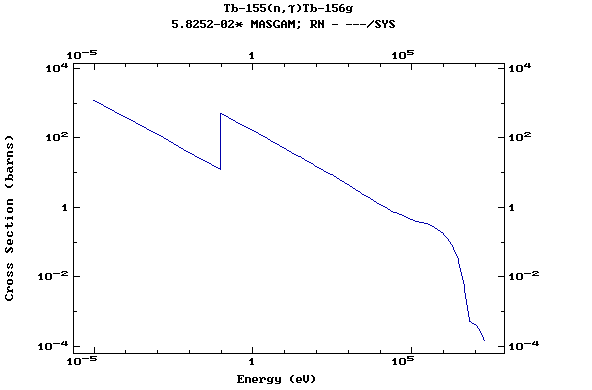
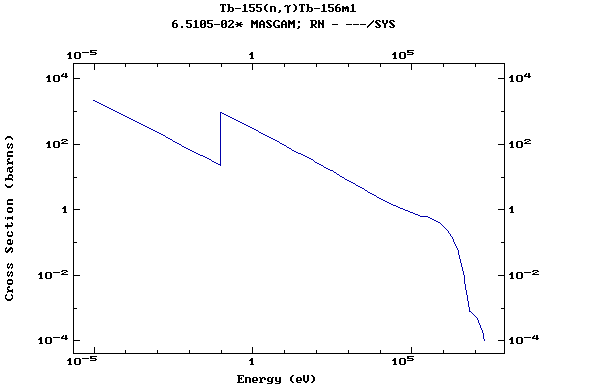
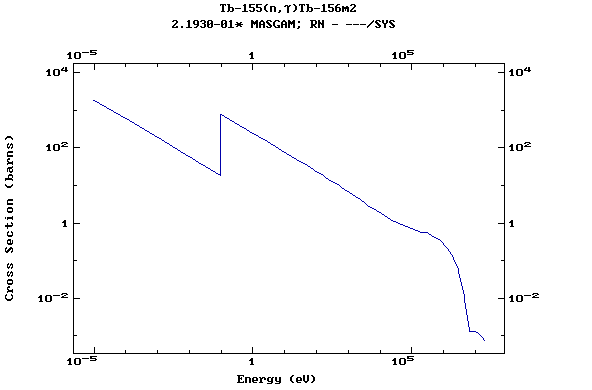
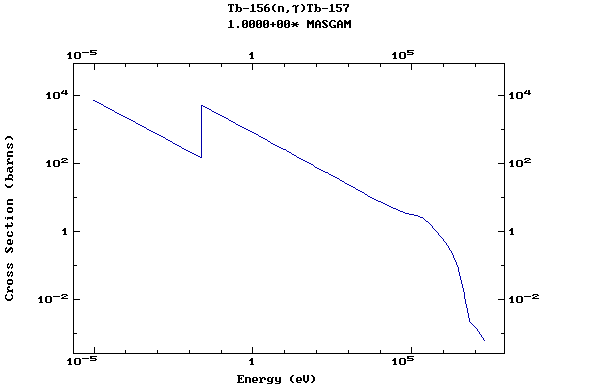
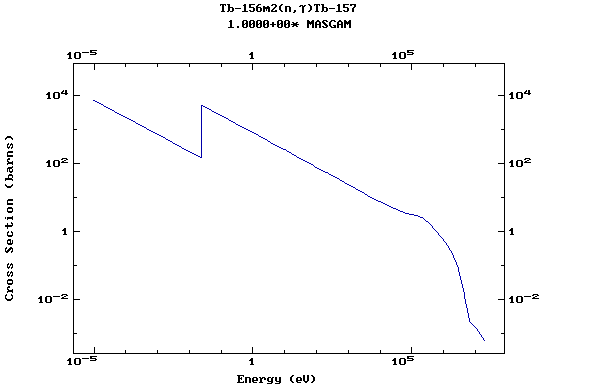
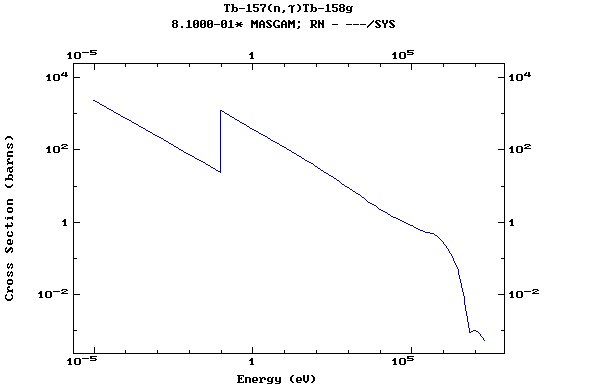
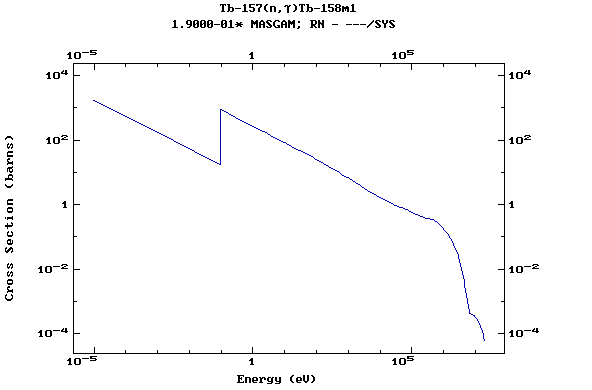
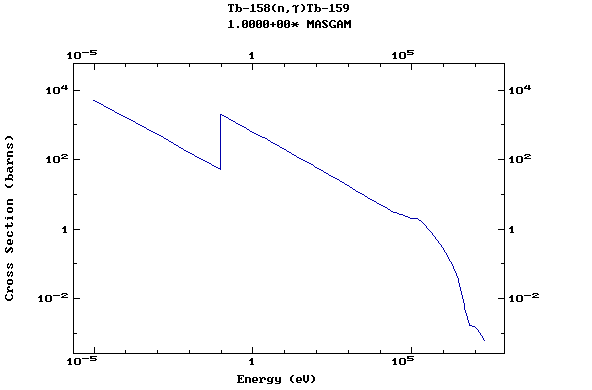
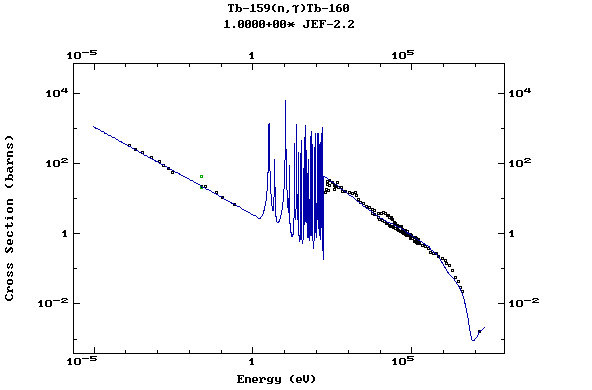
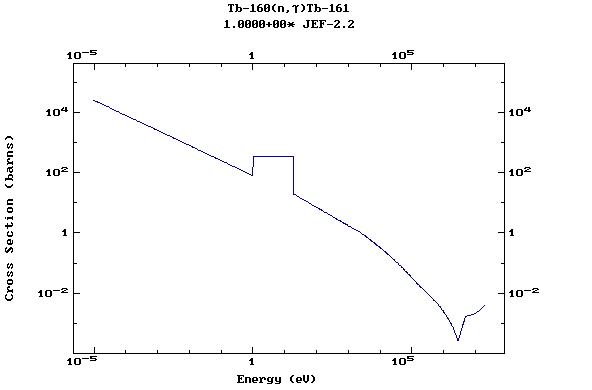
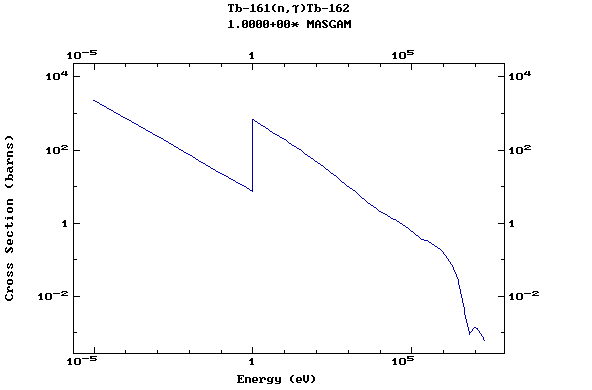
Z=66, Dy
(Dysprosium)
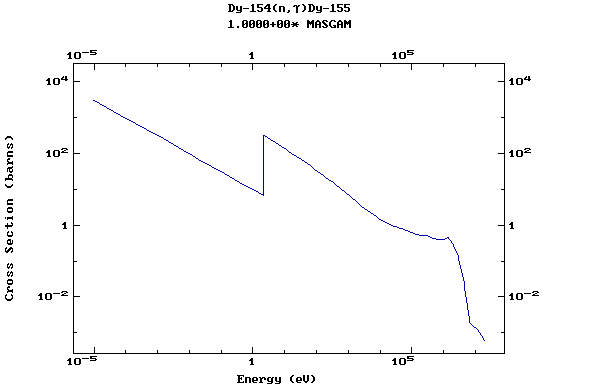
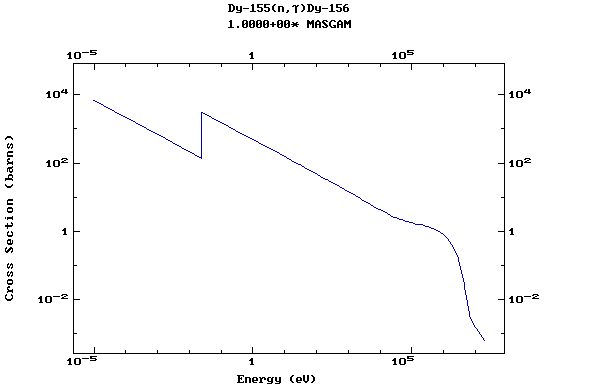
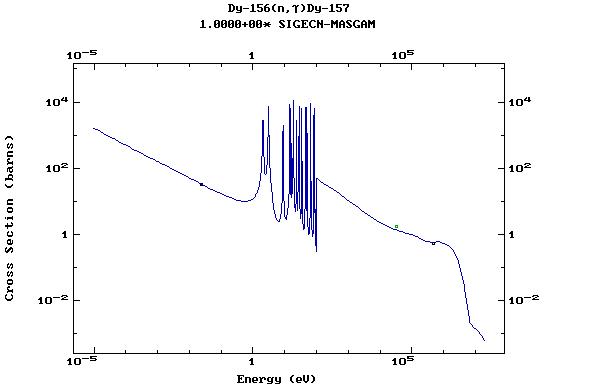
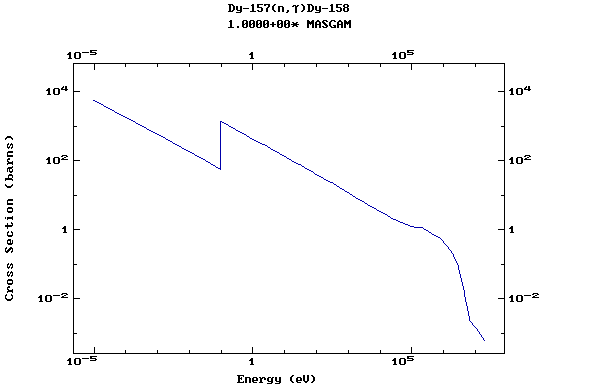
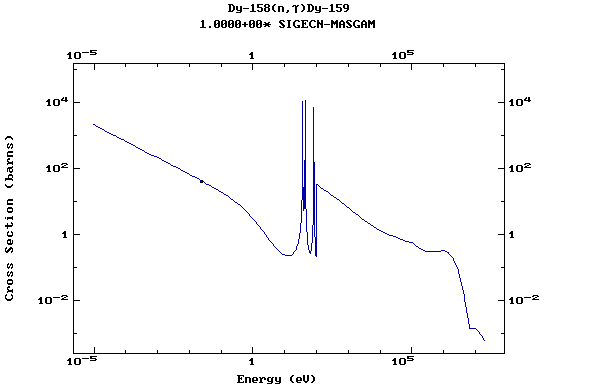
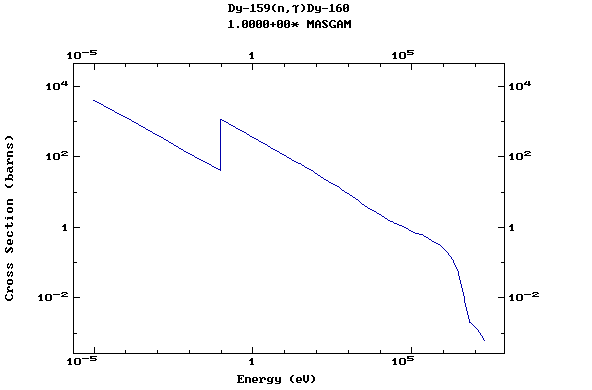
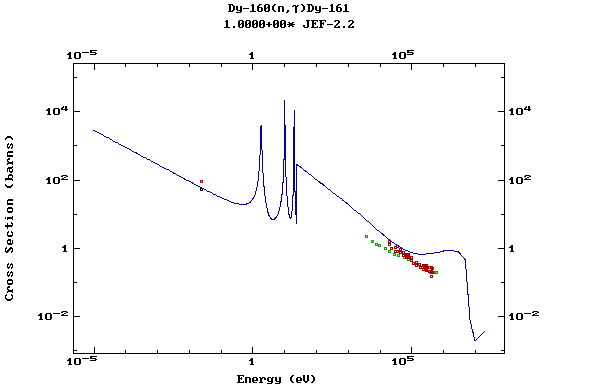
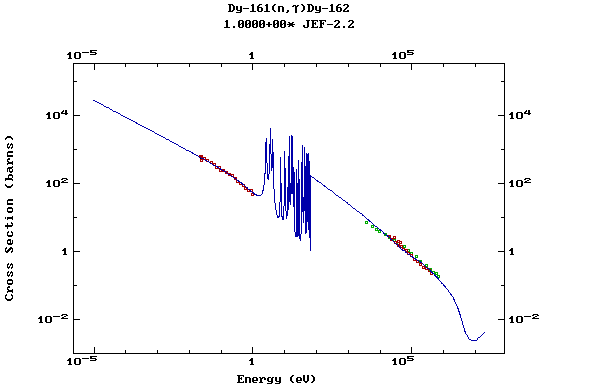
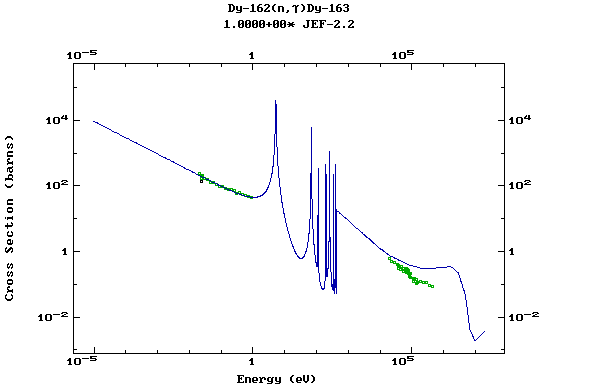
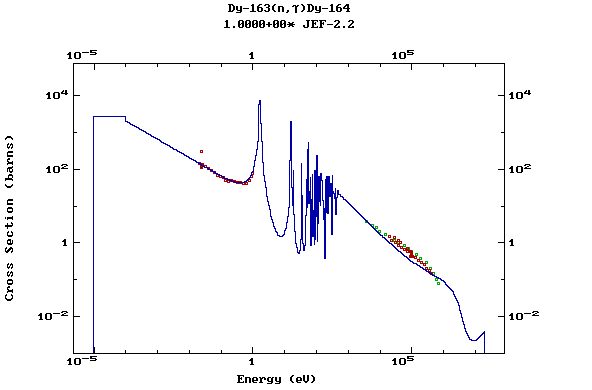
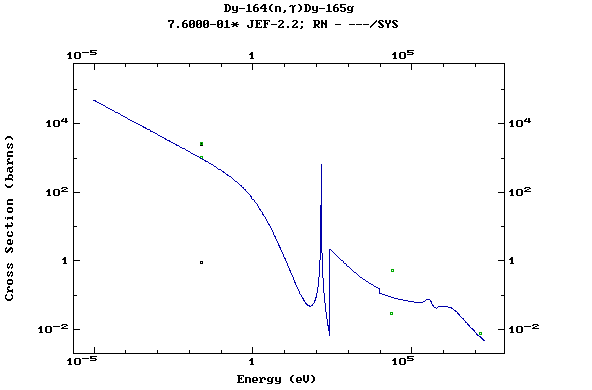
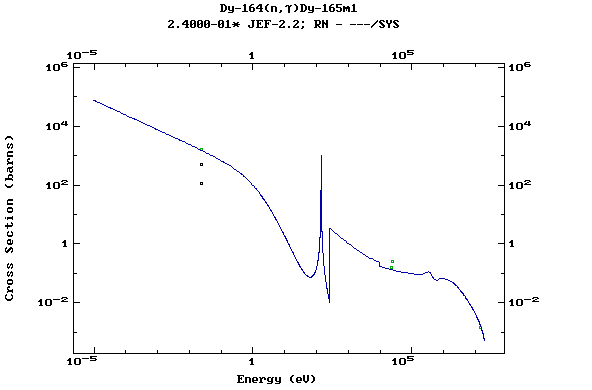
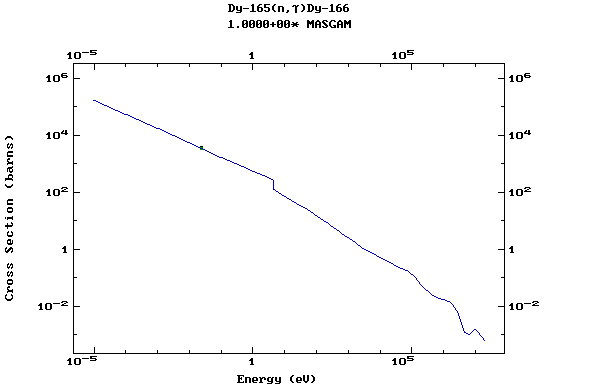
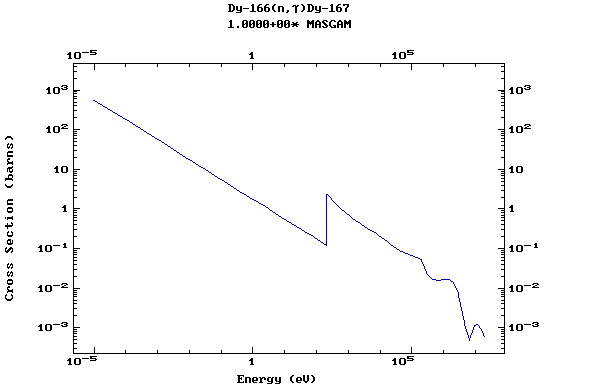
Z=67, Ho
(Holmium)
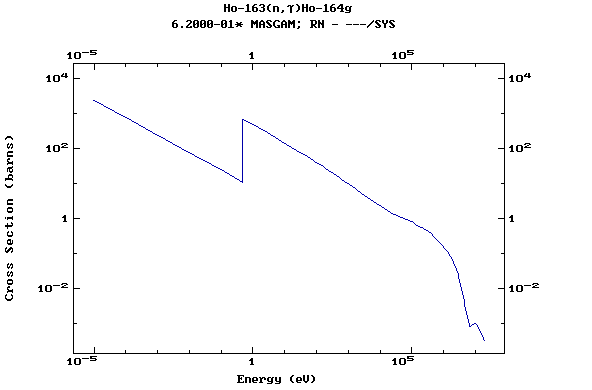
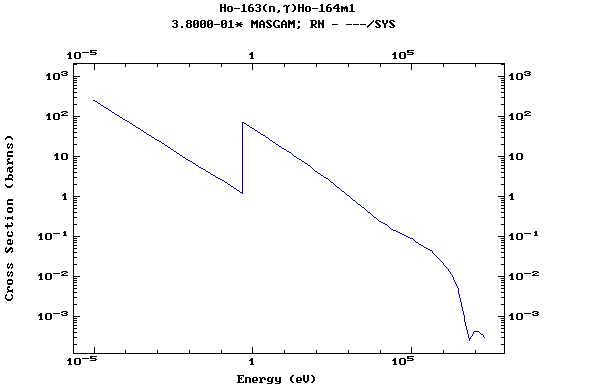
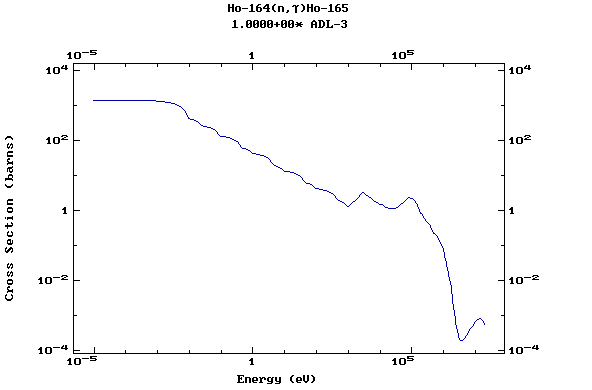
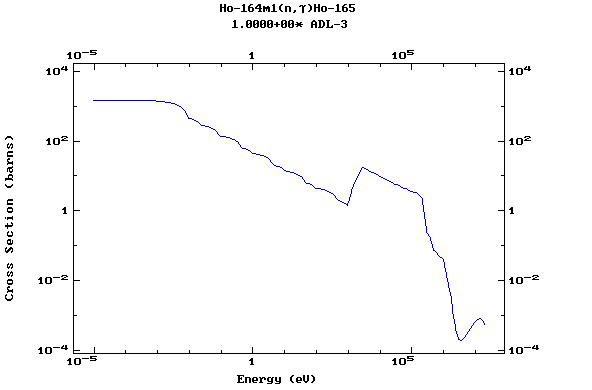
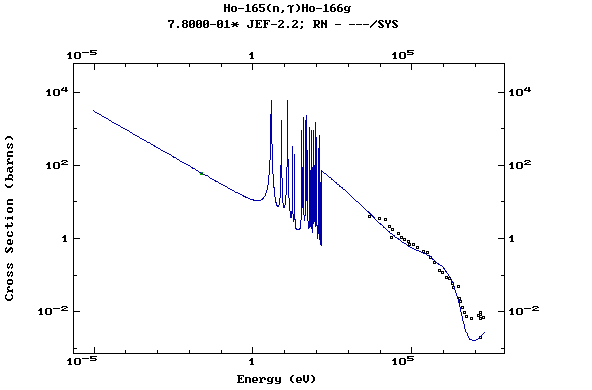
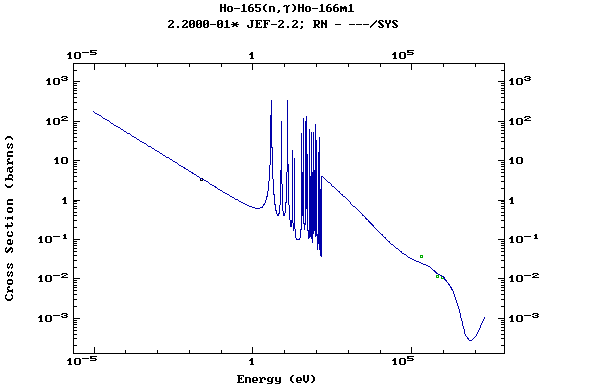
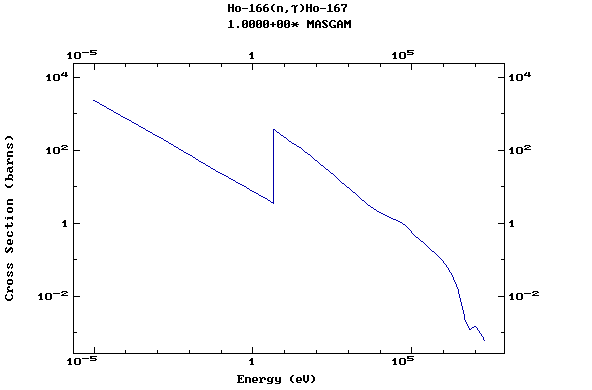
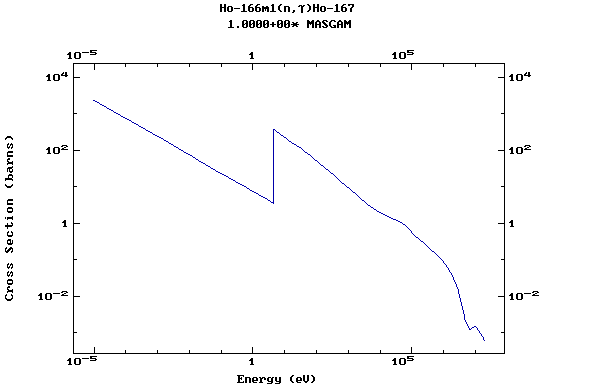
Z=68, Er
(Erbium)
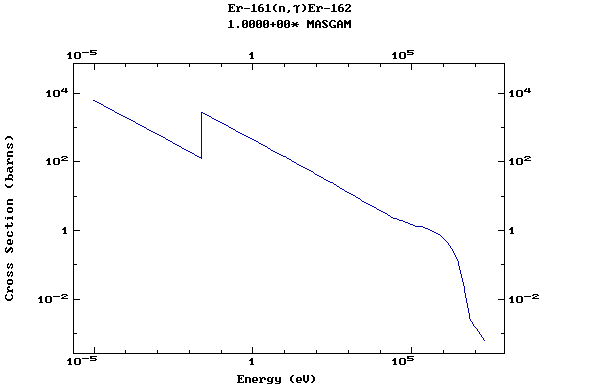
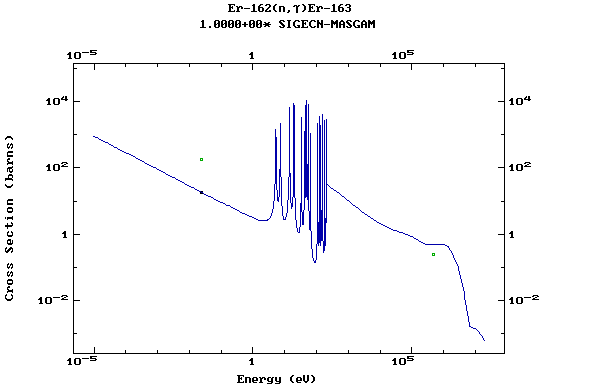
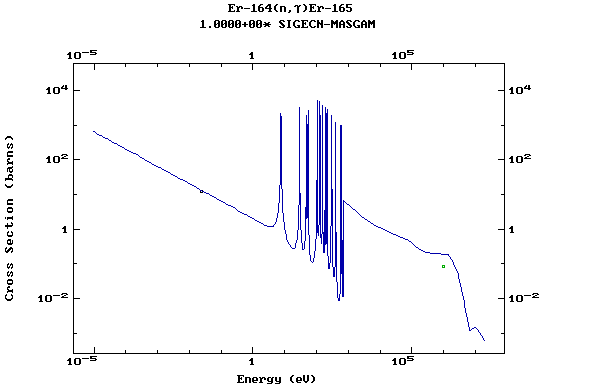
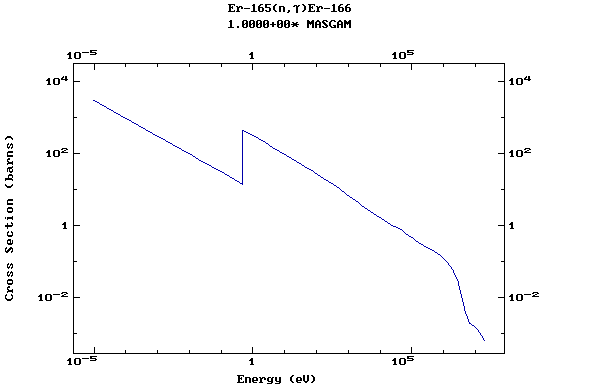
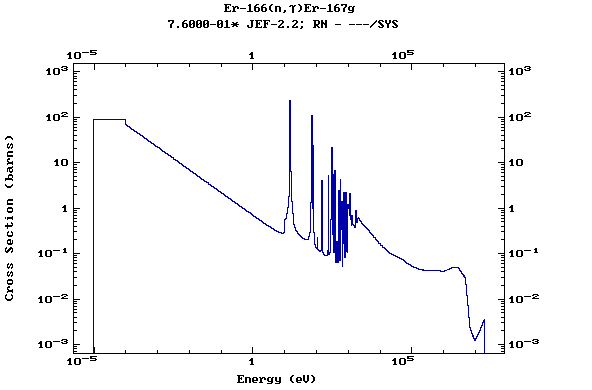
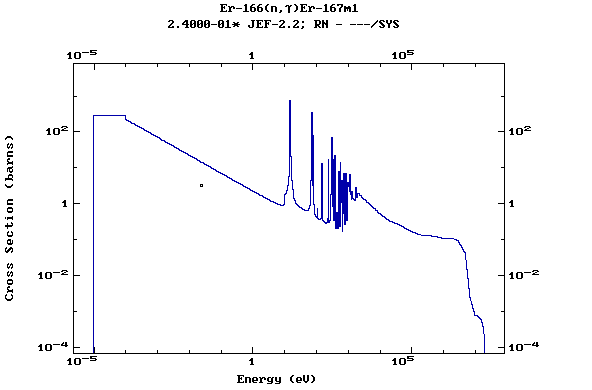
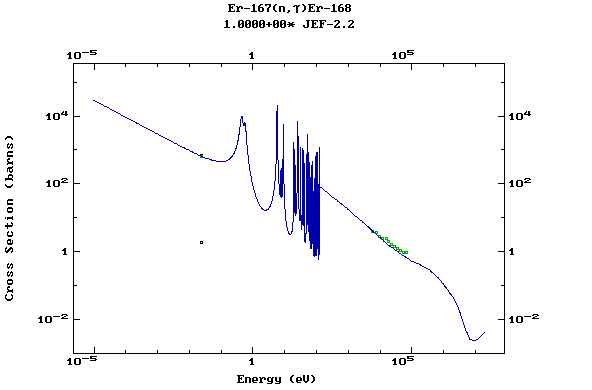
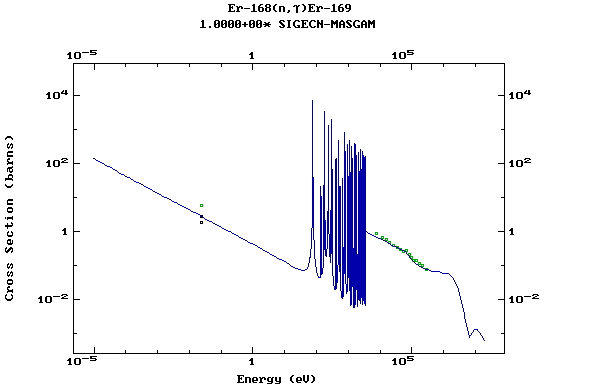
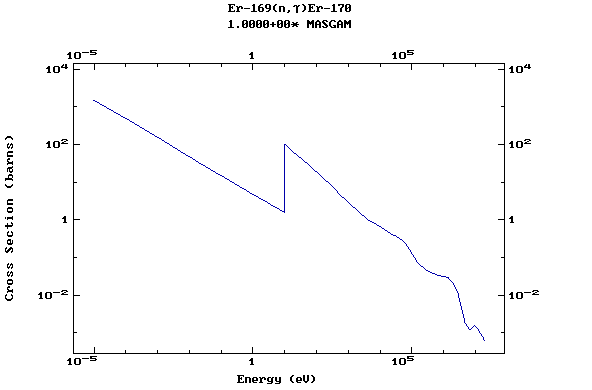
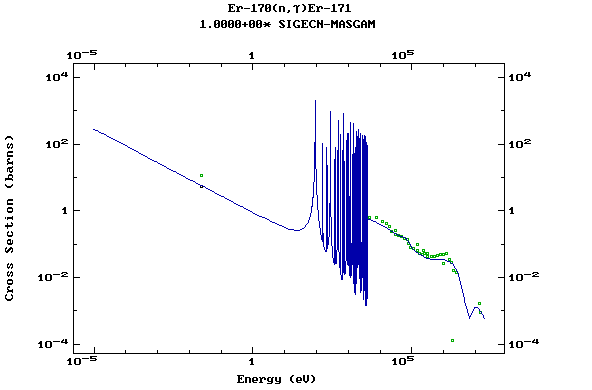
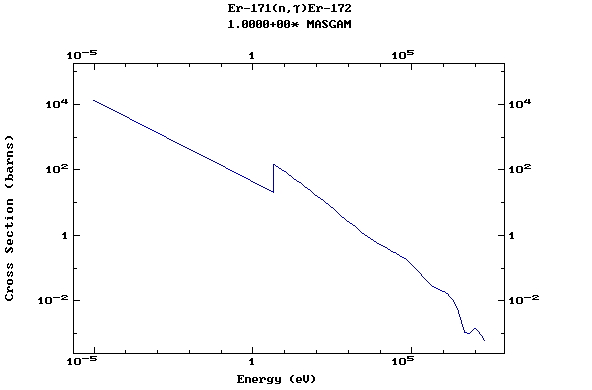
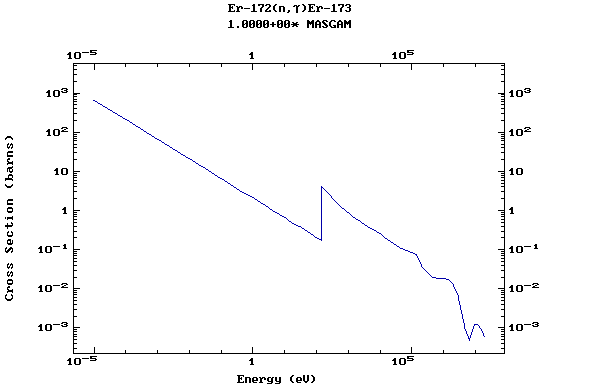
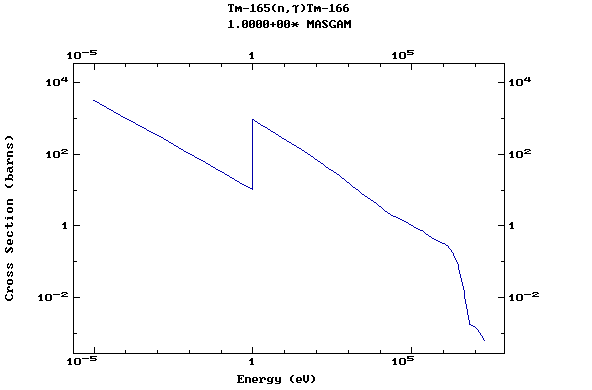
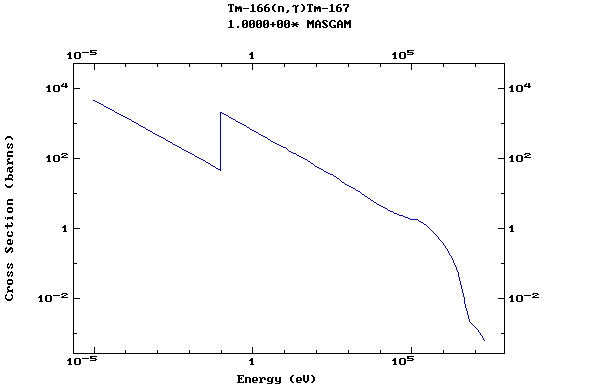
Z=69, Tm
(Thulium)
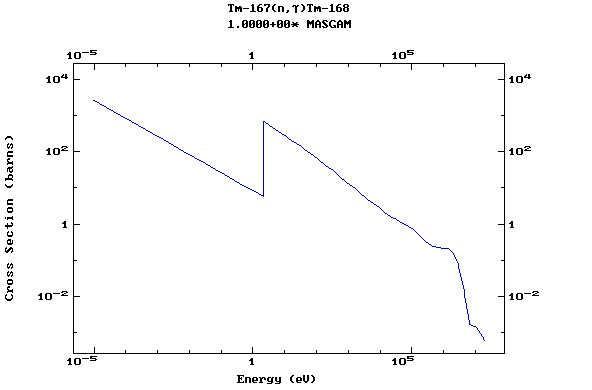
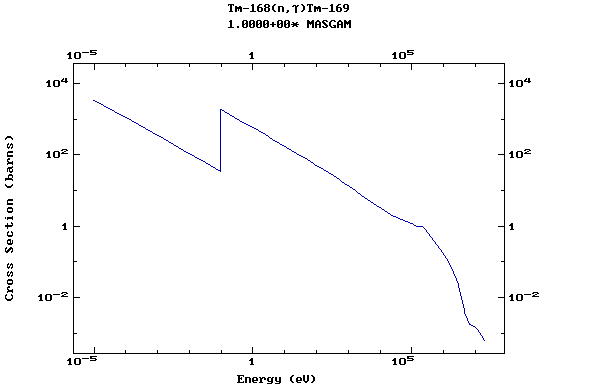
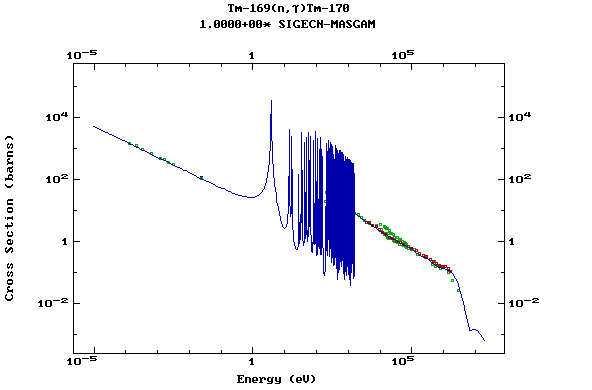
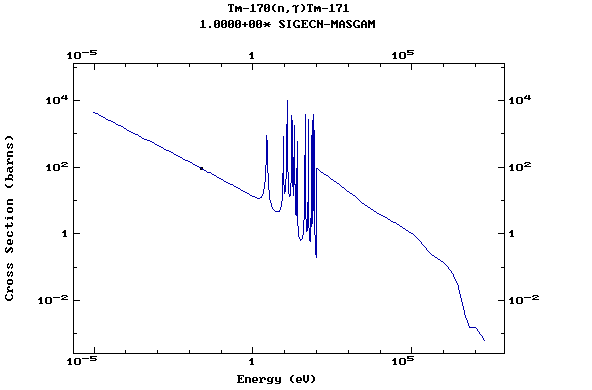
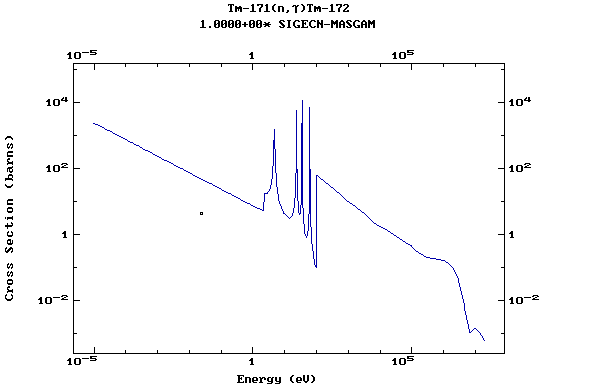
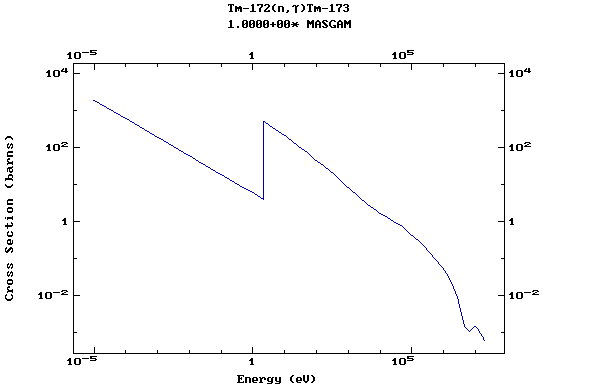
Z=70, Yb
(Ytterbium)
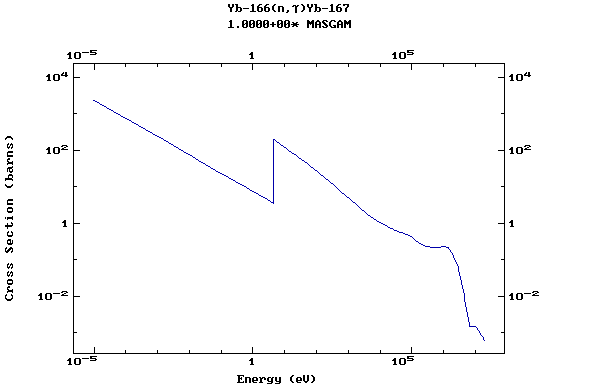
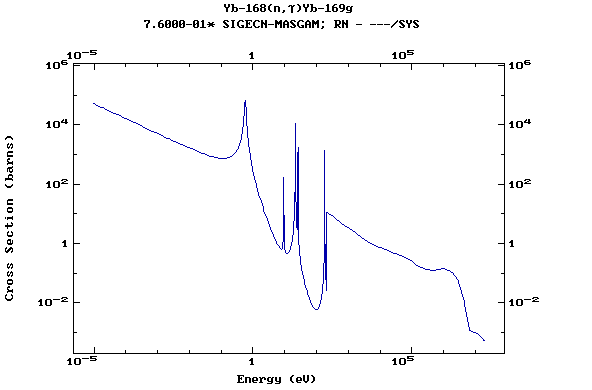
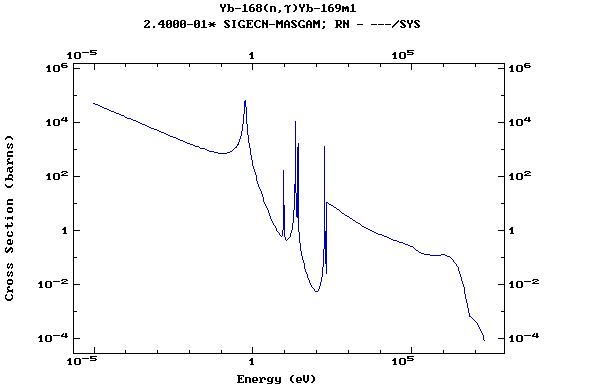
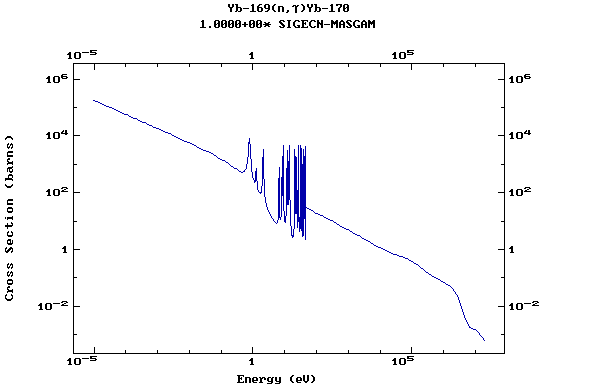
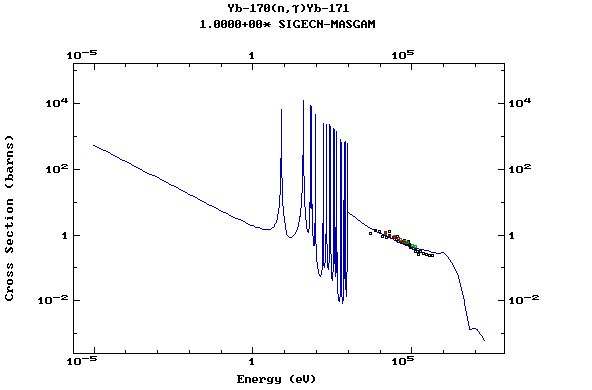
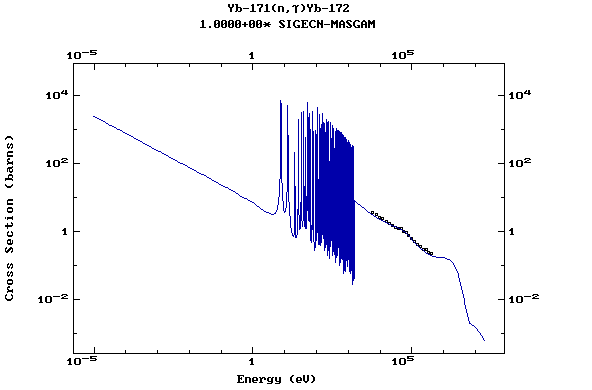
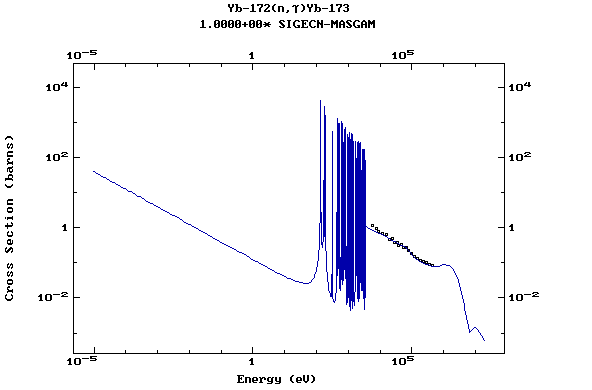
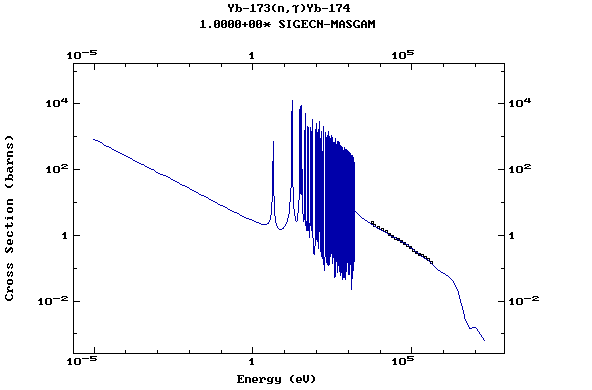
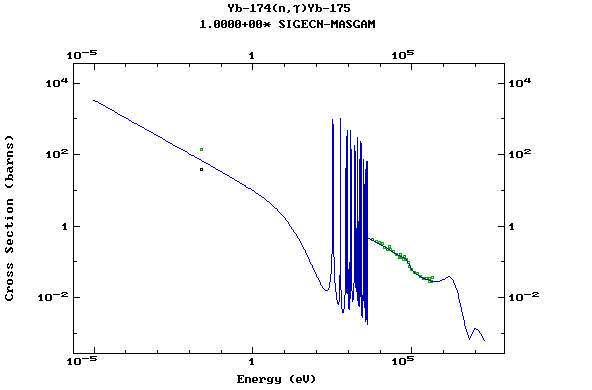
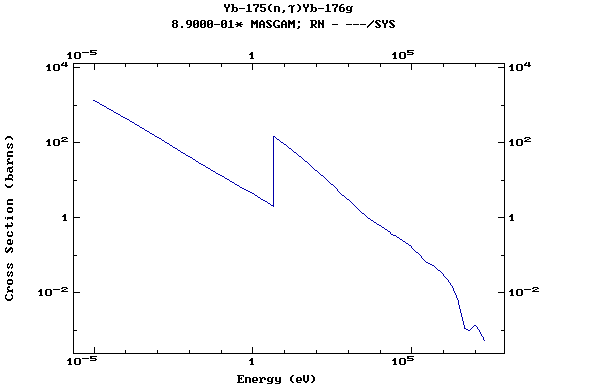
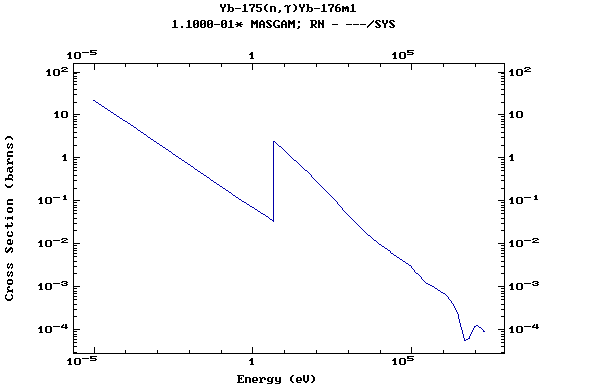
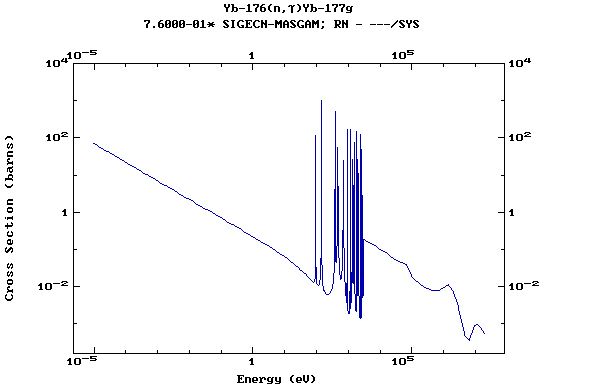
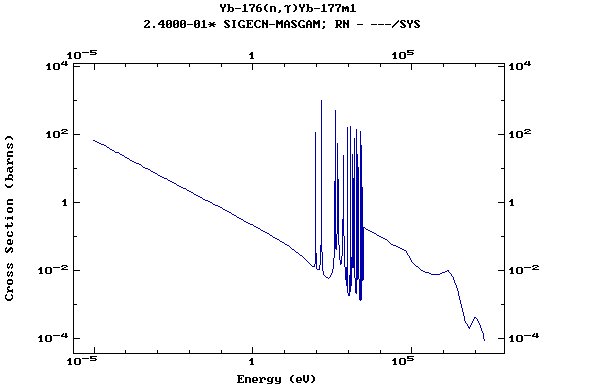
Z=71, Lu
(Lutetium)
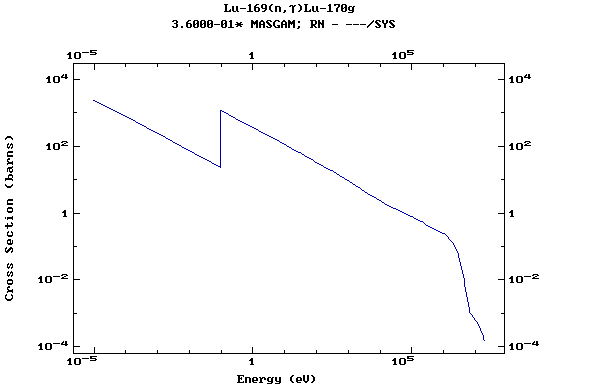
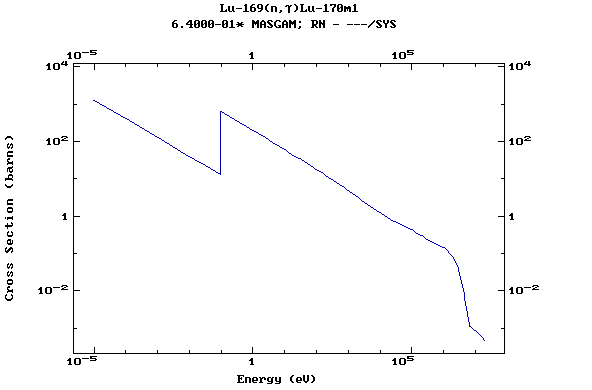
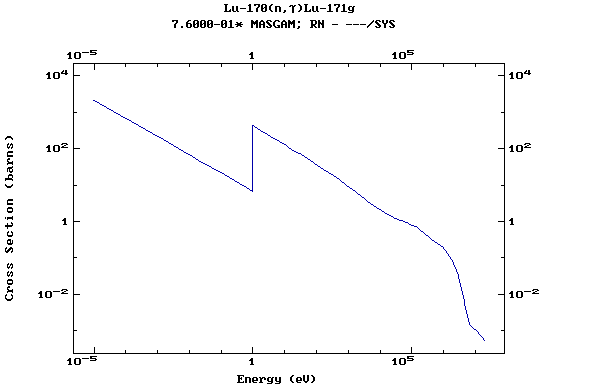
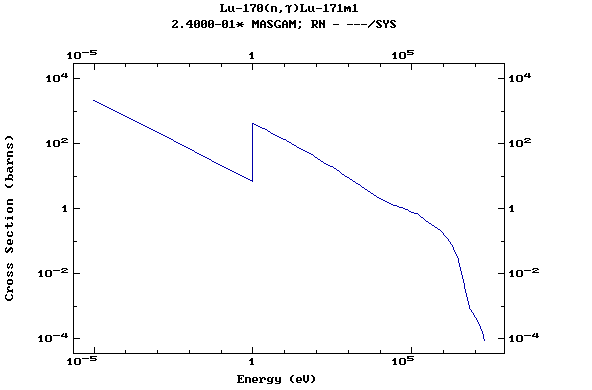
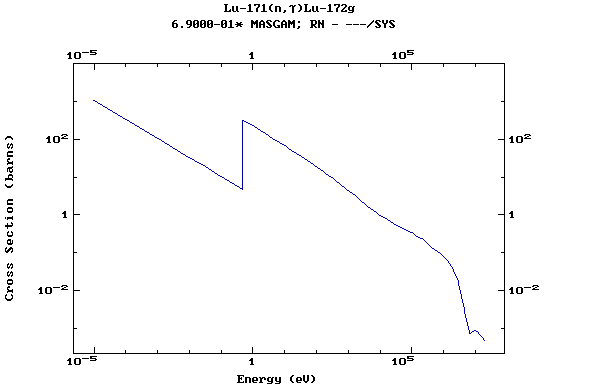
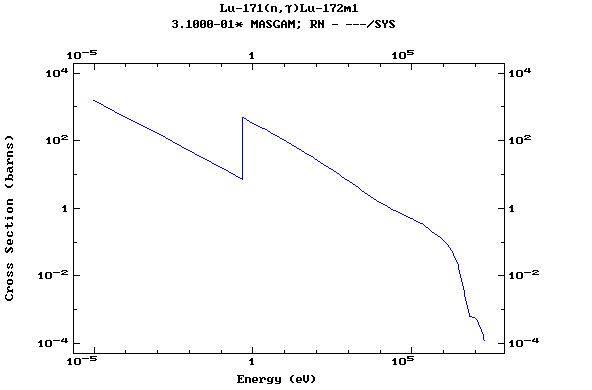
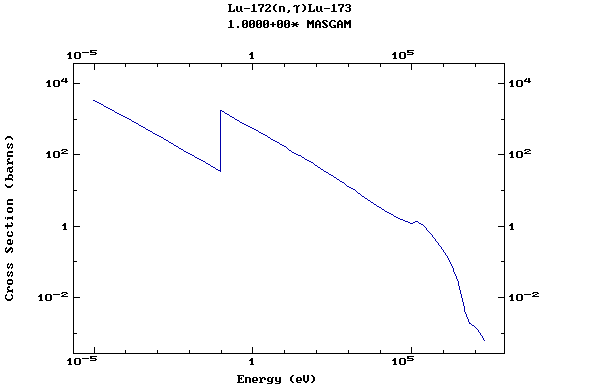
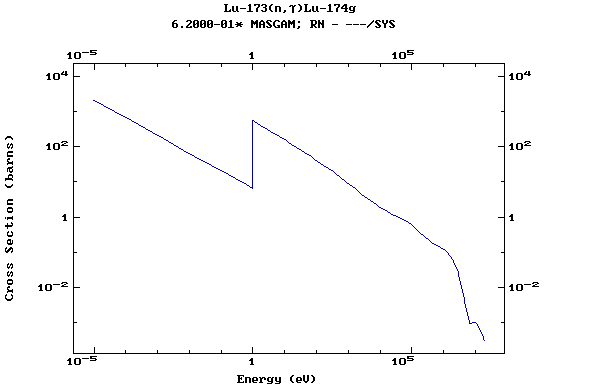
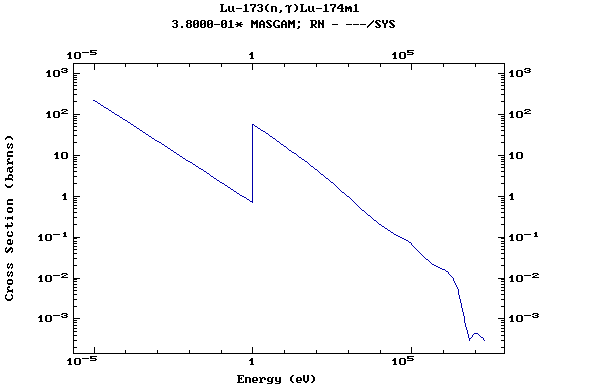
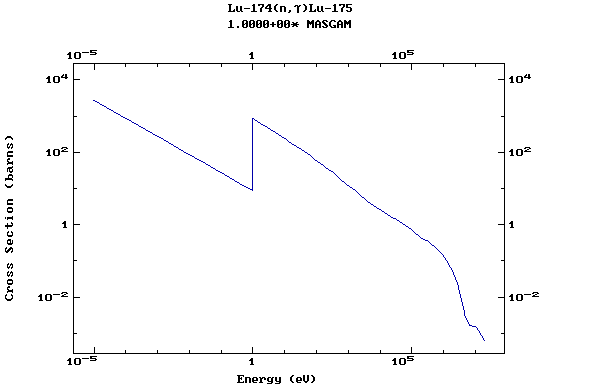
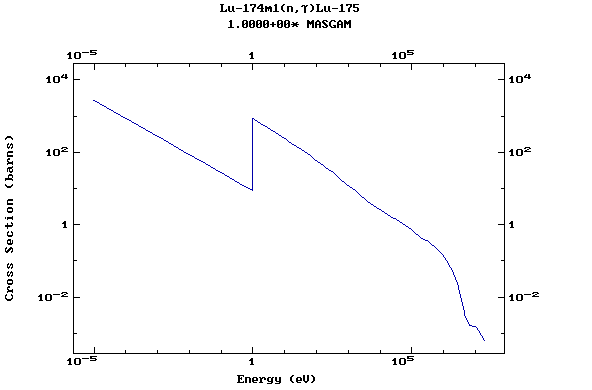
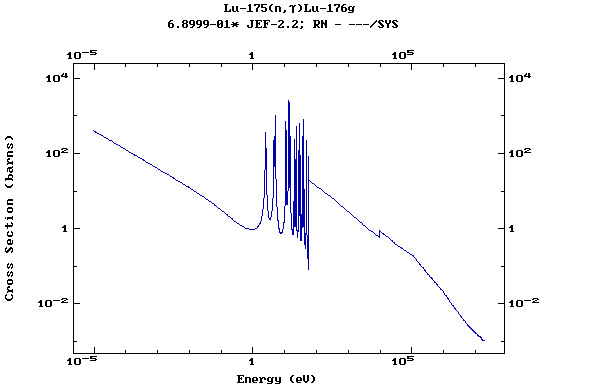
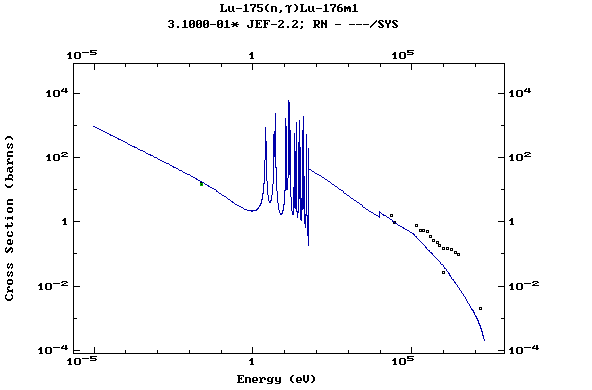
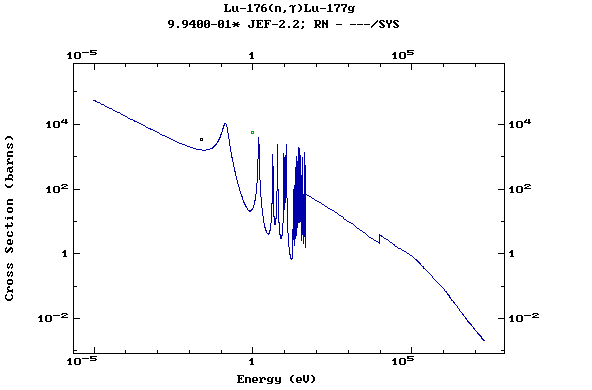
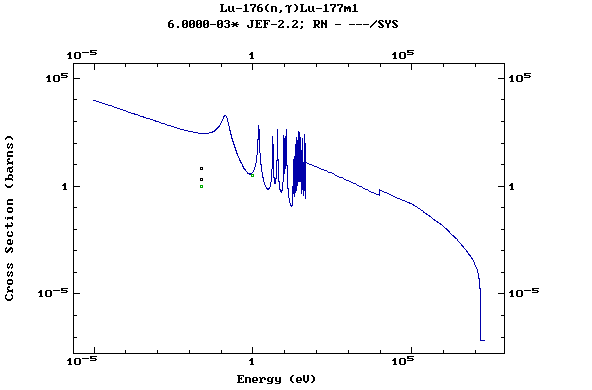
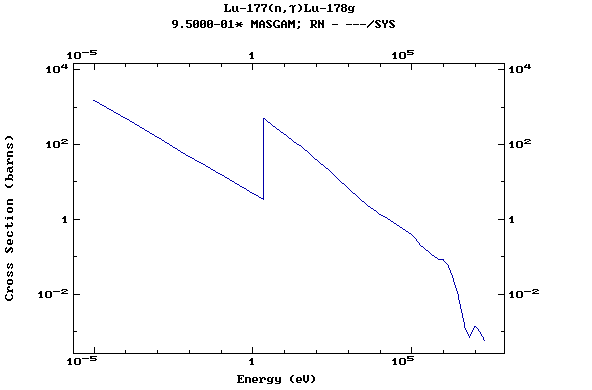
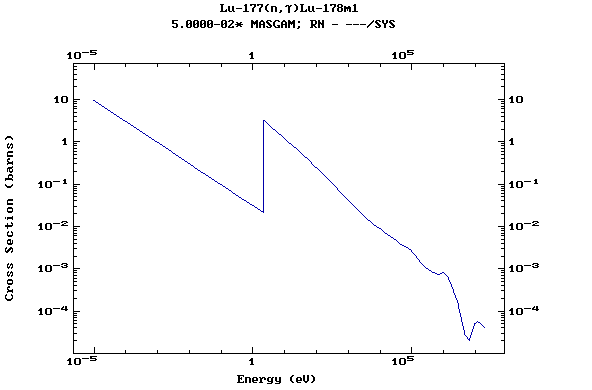
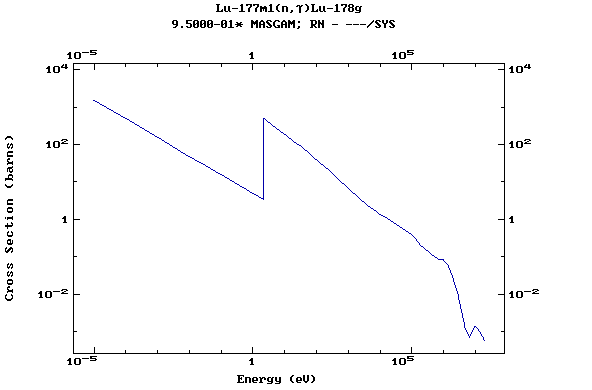
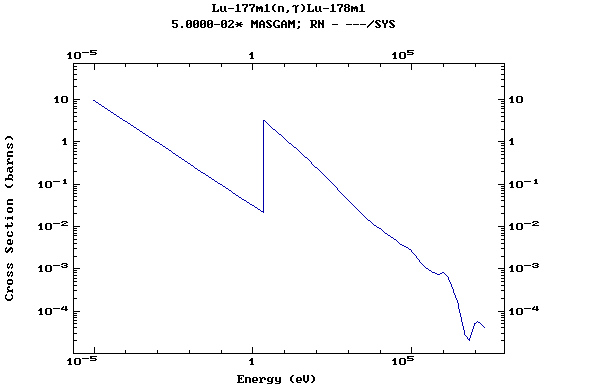
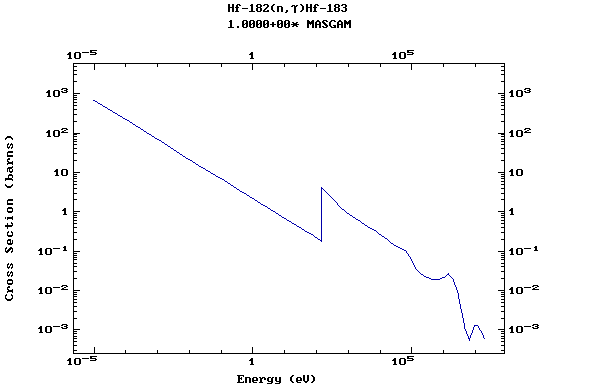
Z=72, Hf
(Hafnium)
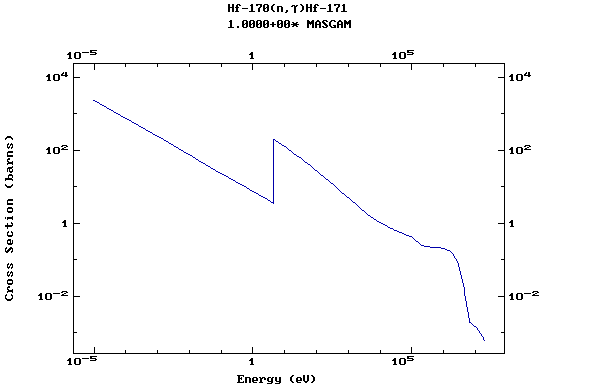
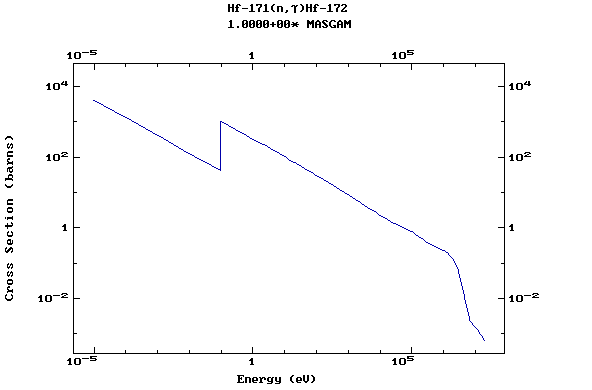
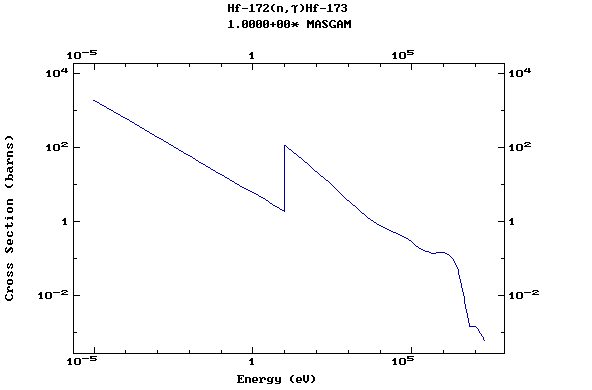
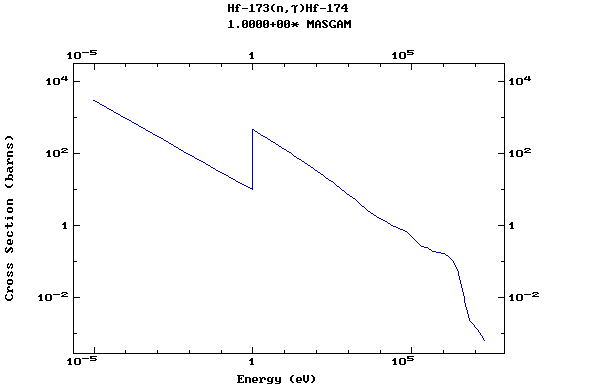
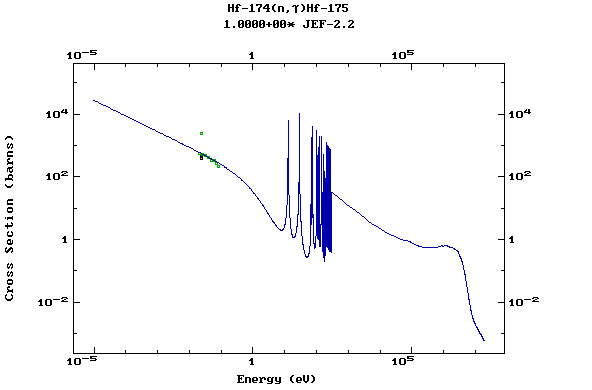
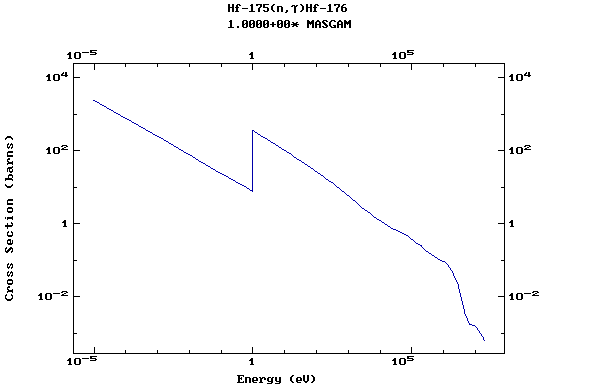
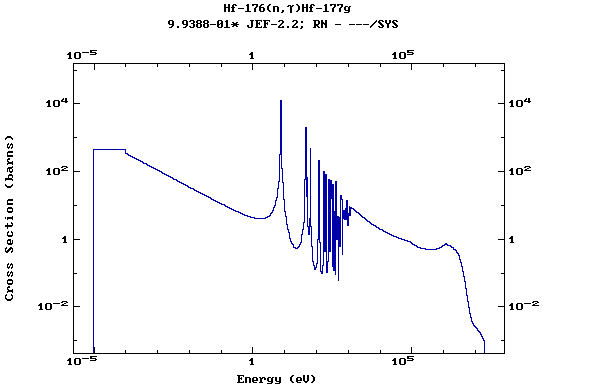
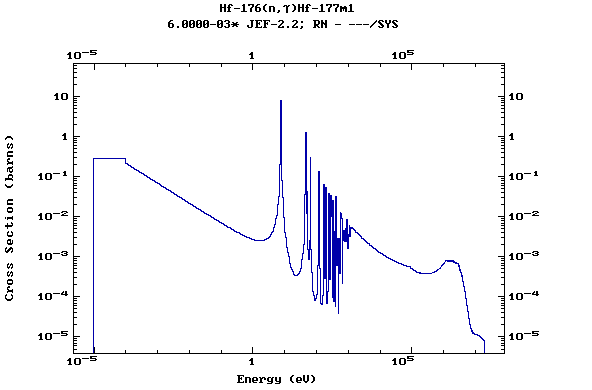
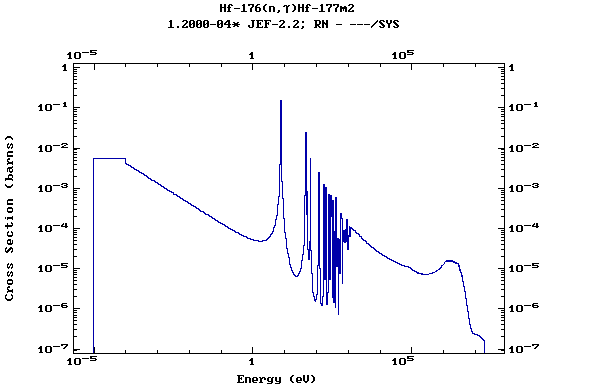
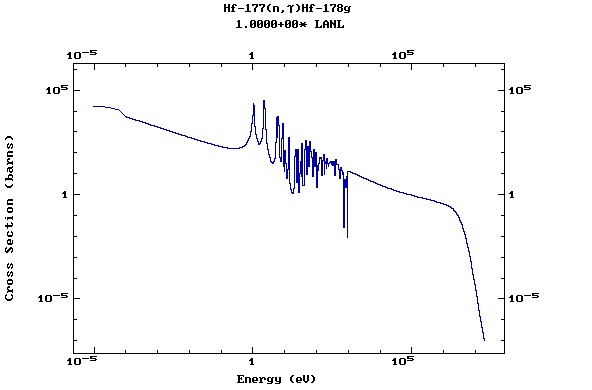
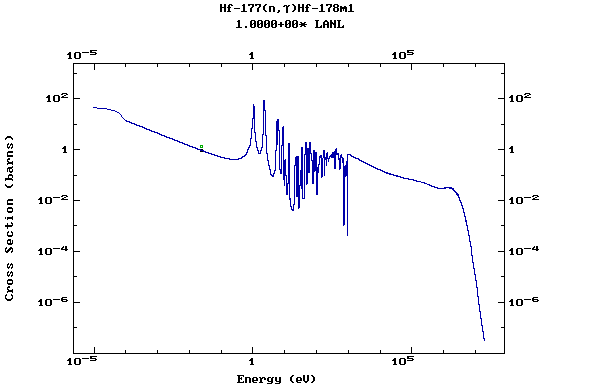
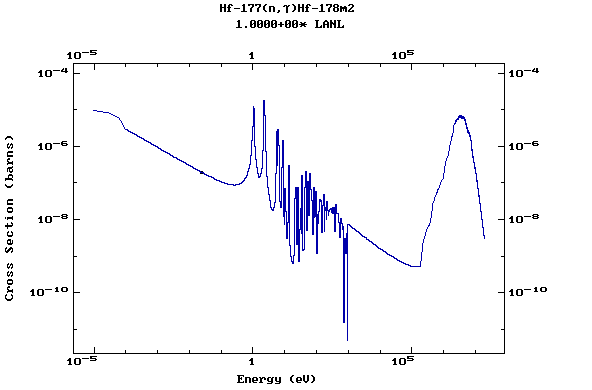
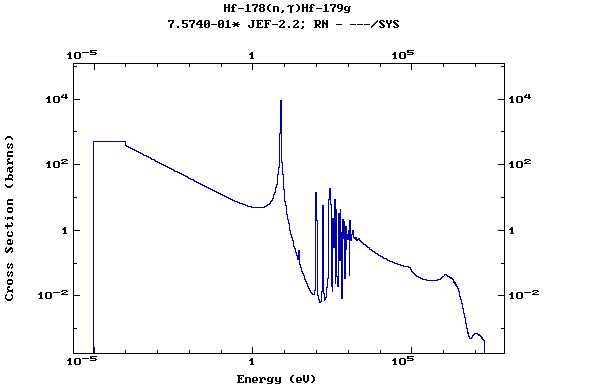
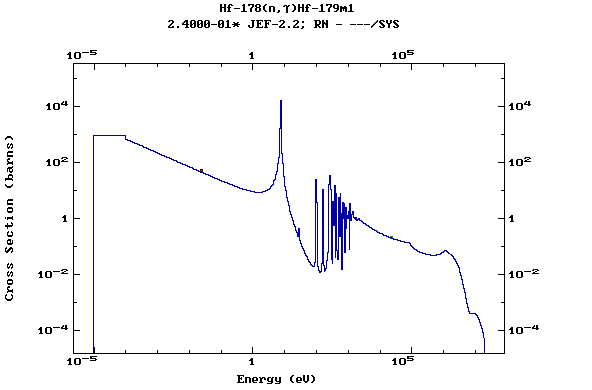
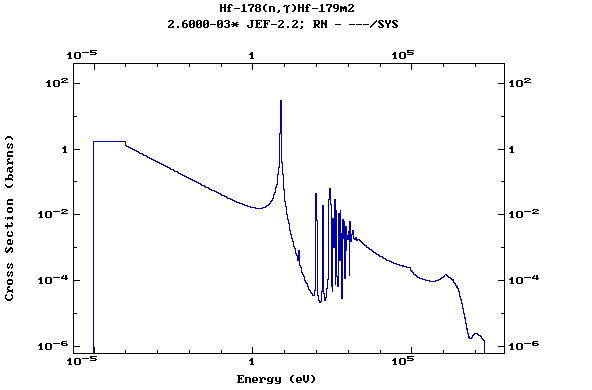
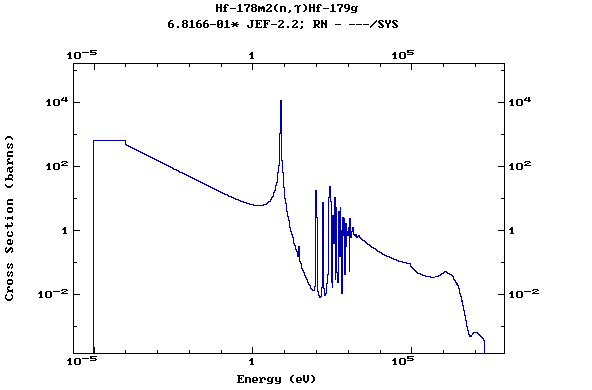
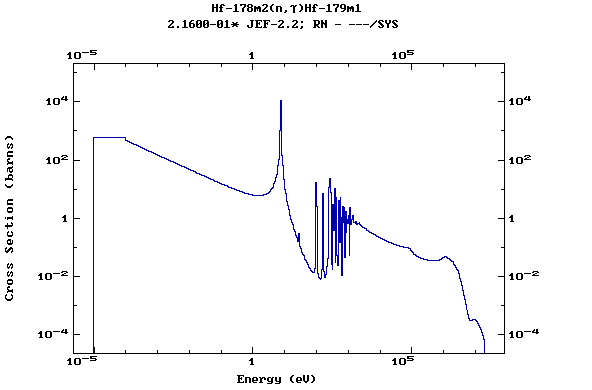
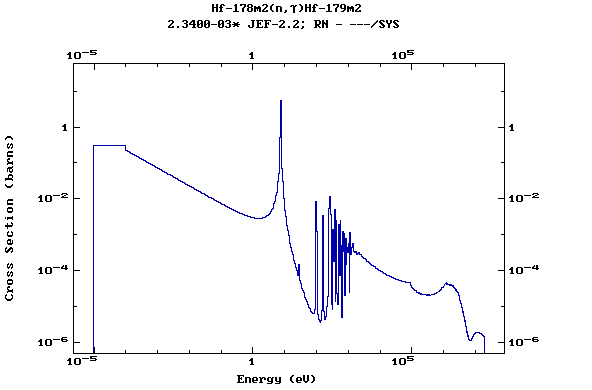
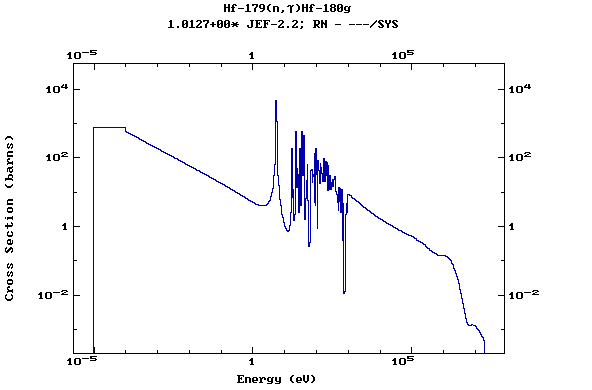
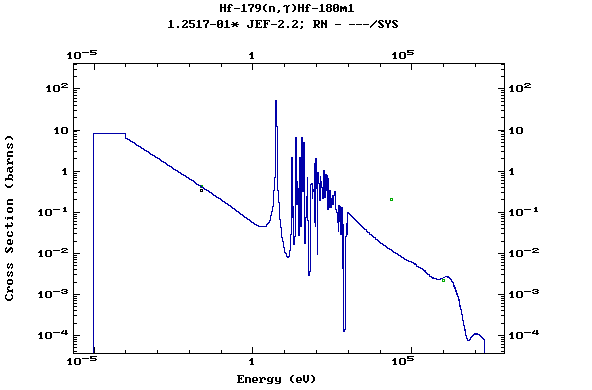
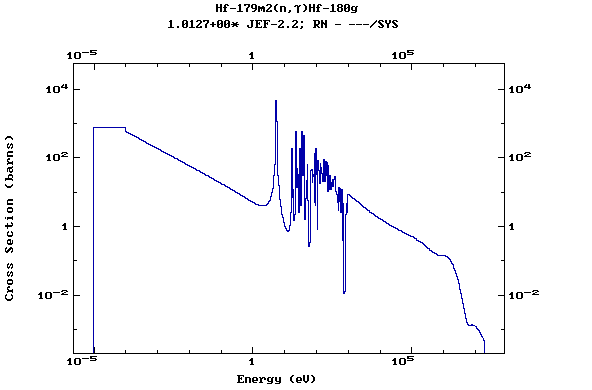
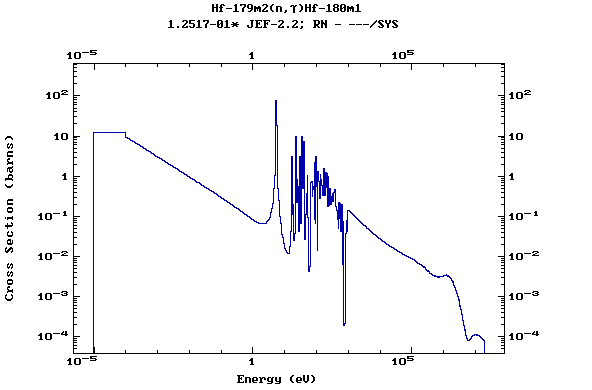
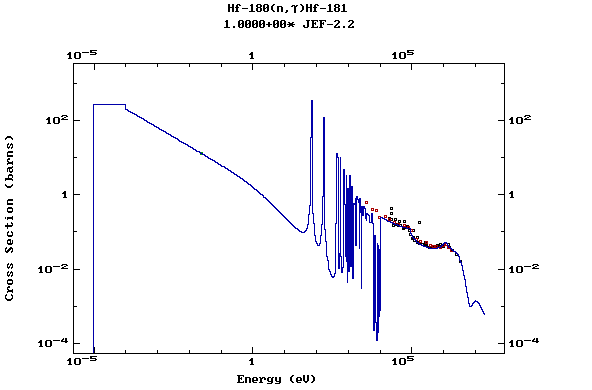
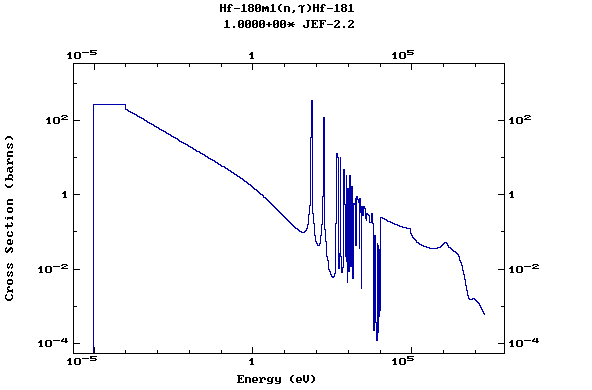
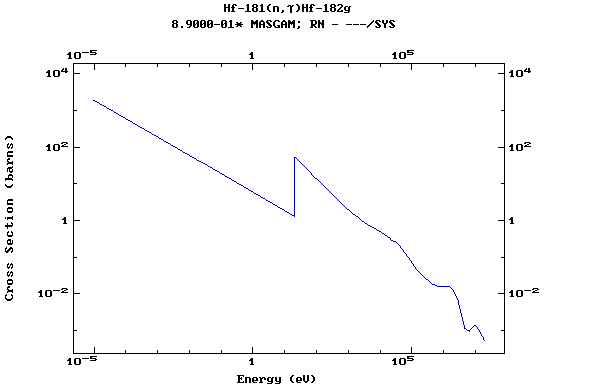
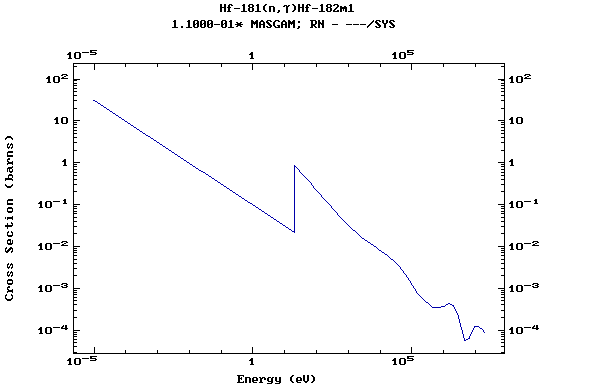
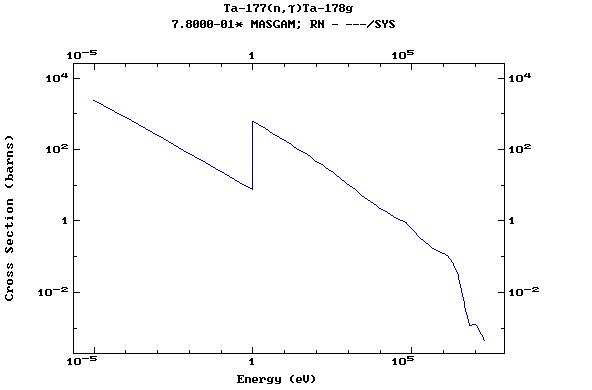
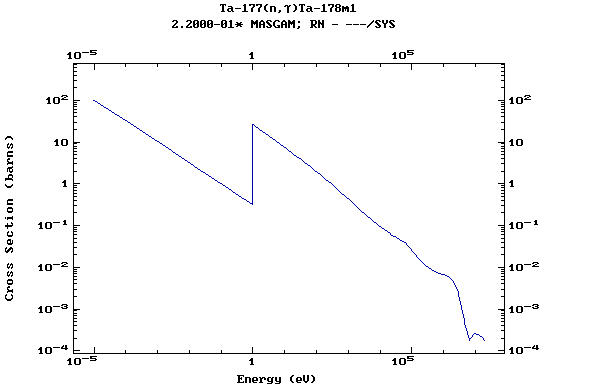
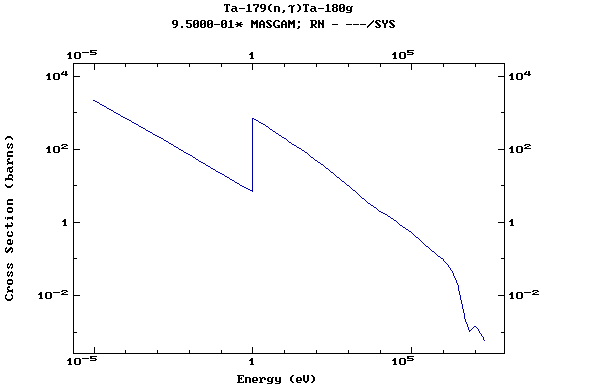
Z=73, Ta
(Tantalum)
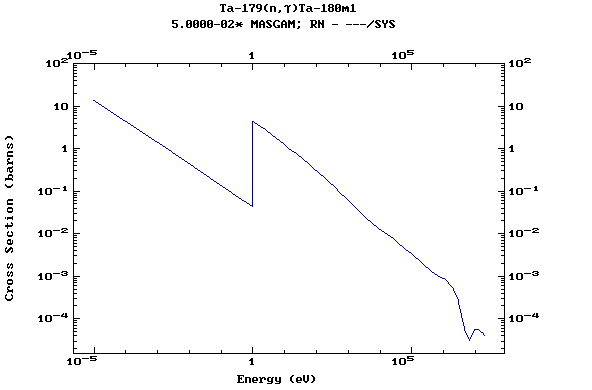
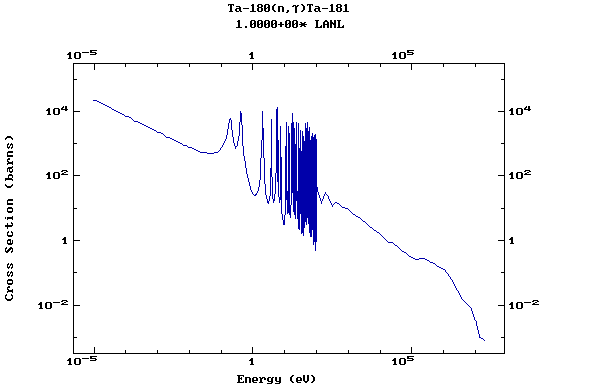
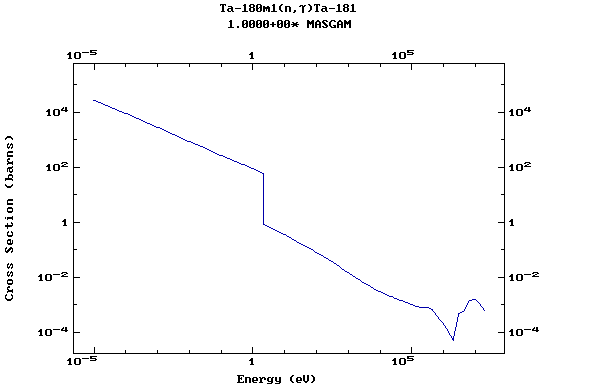
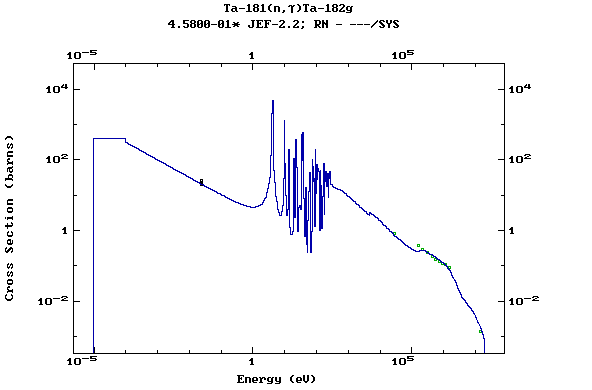
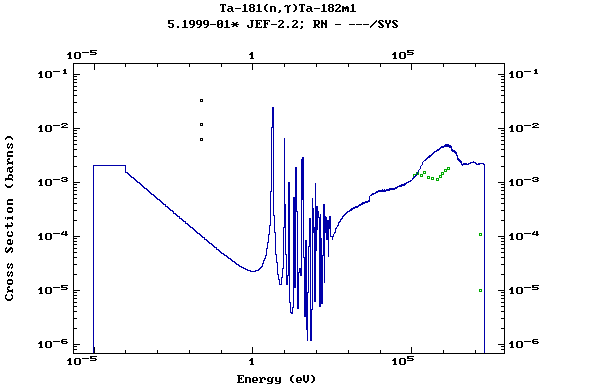
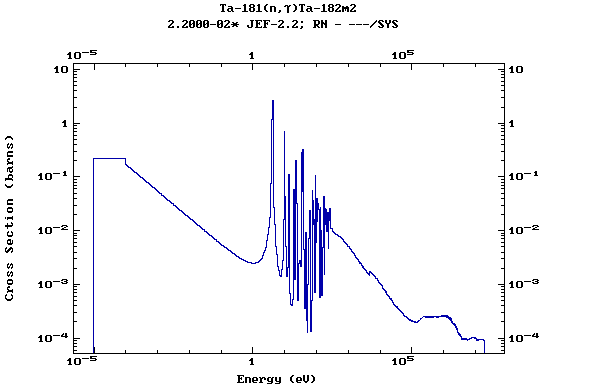
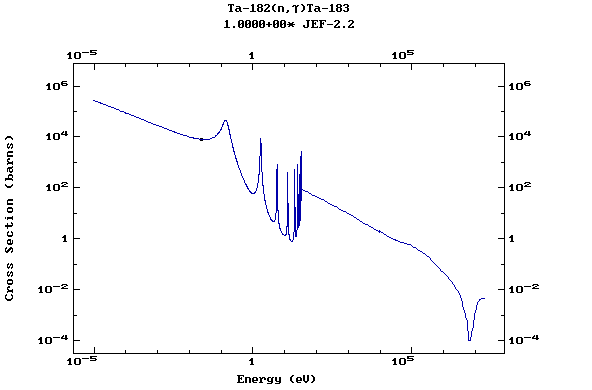
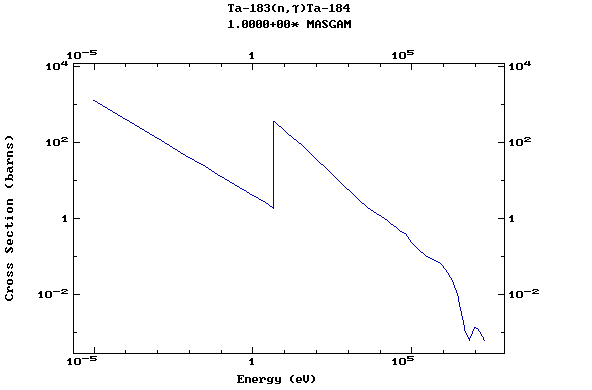
Z=74, W
(Tungsten)
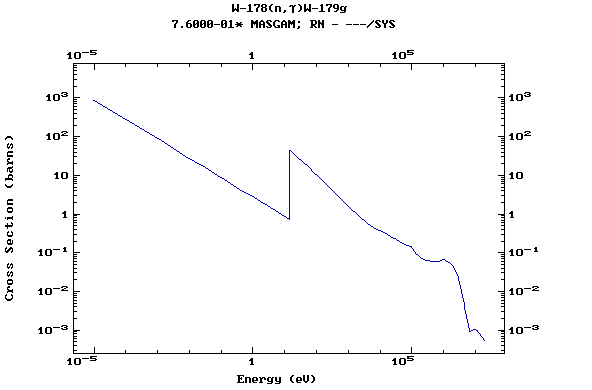
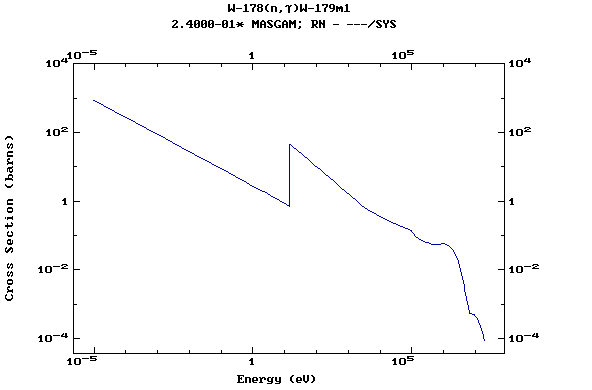
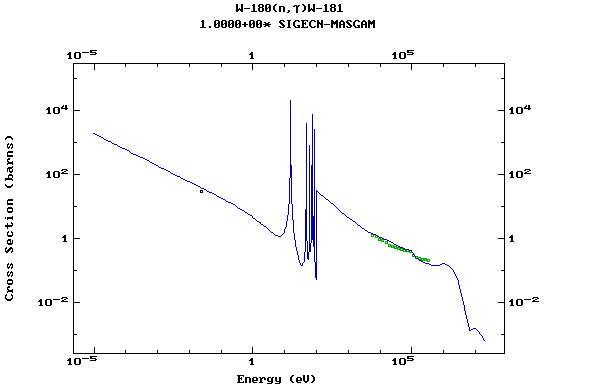
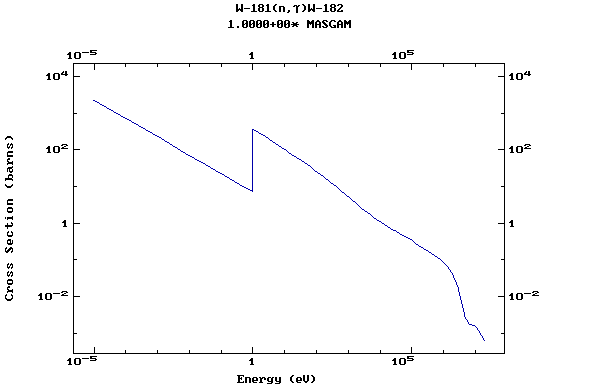
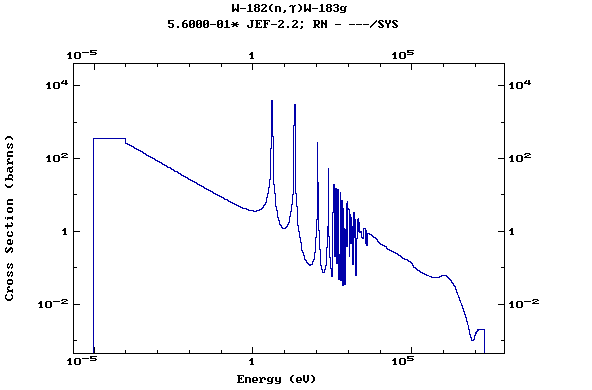
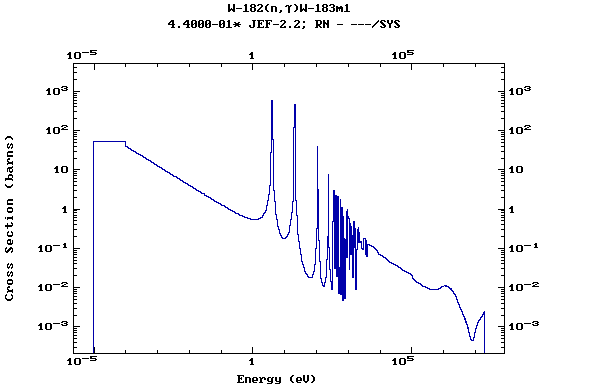
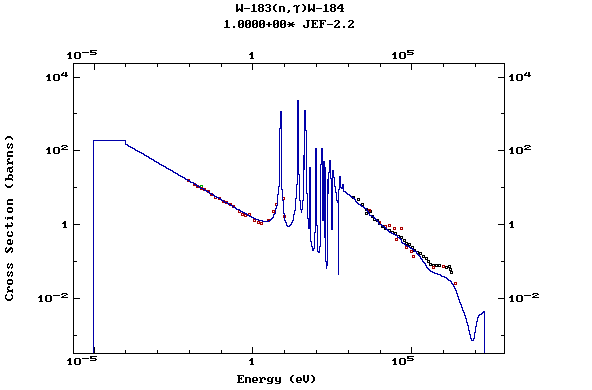
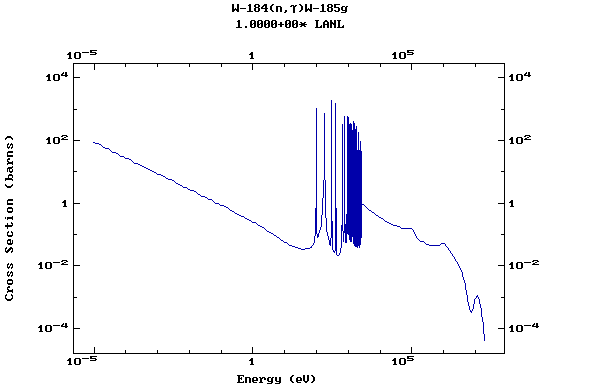
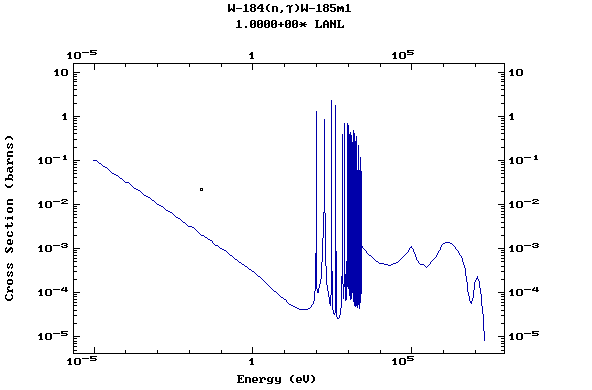
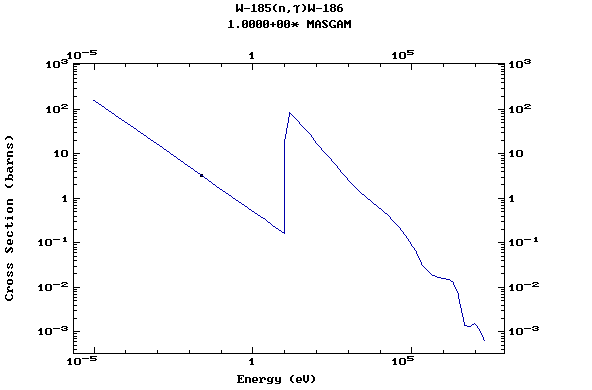
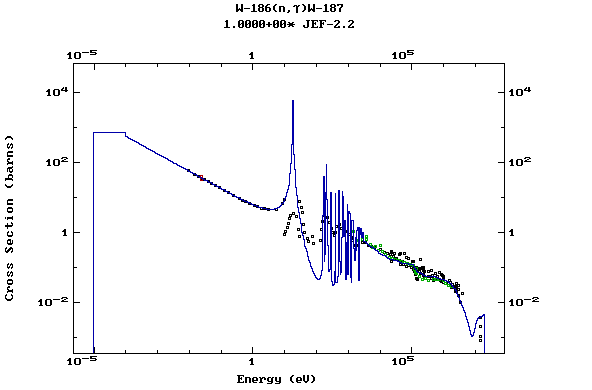
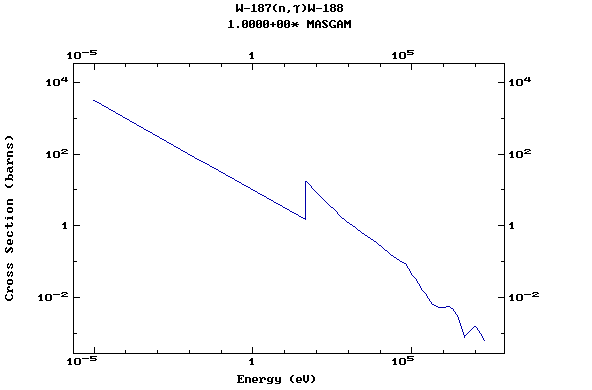
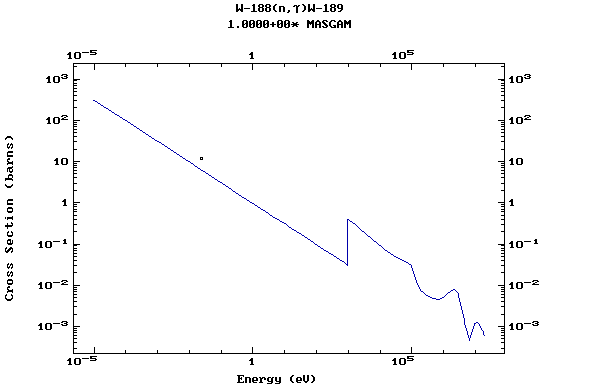
Z=75, Re
(Rhenium)
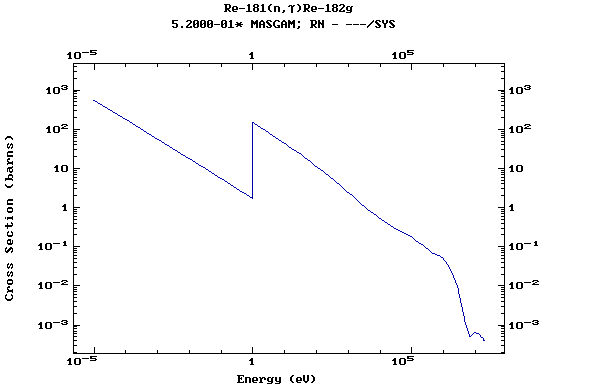
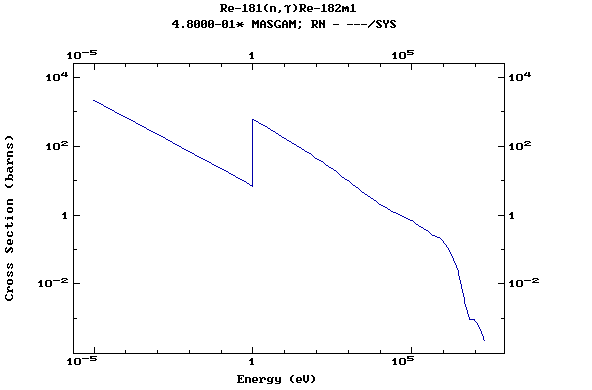
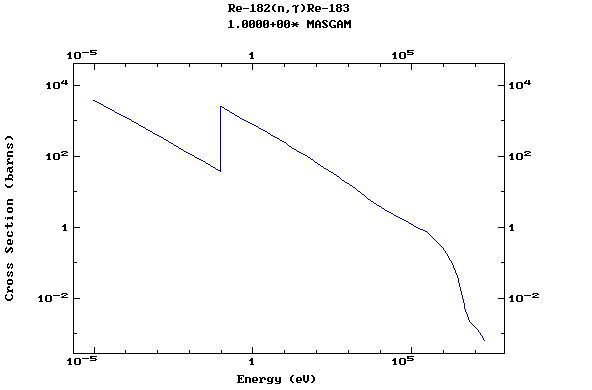
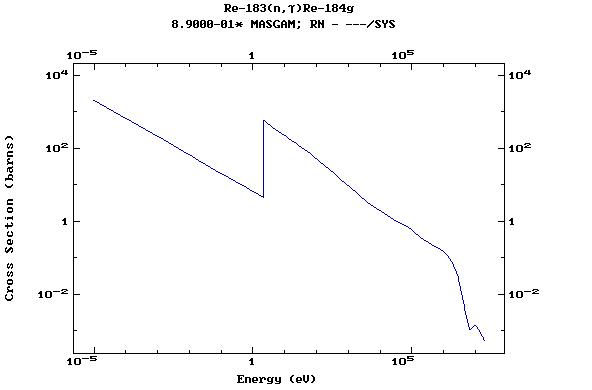
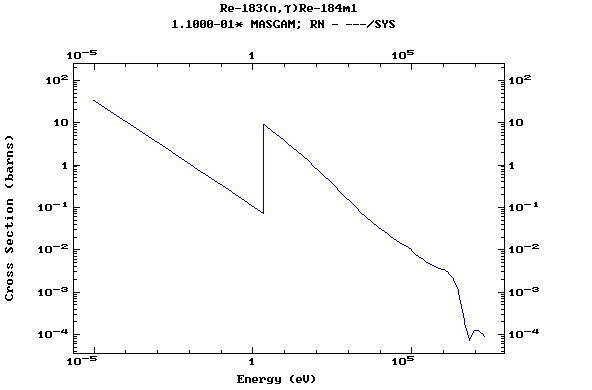
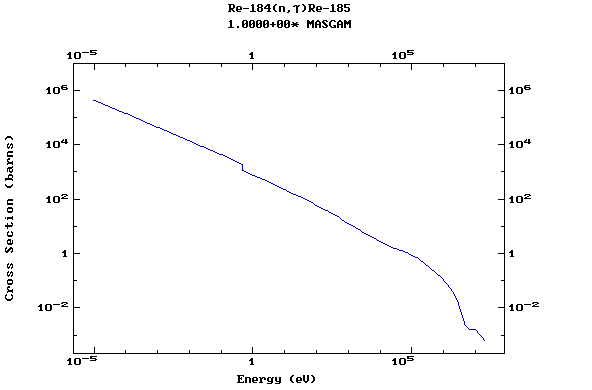
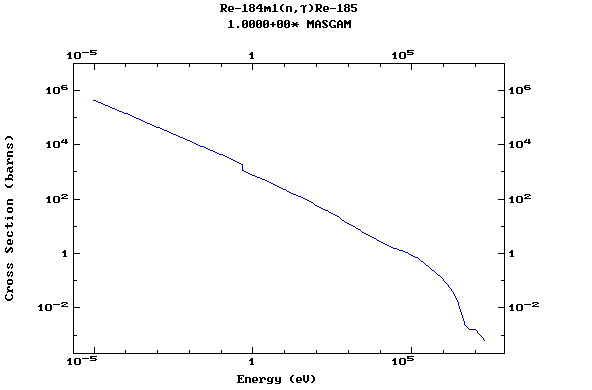
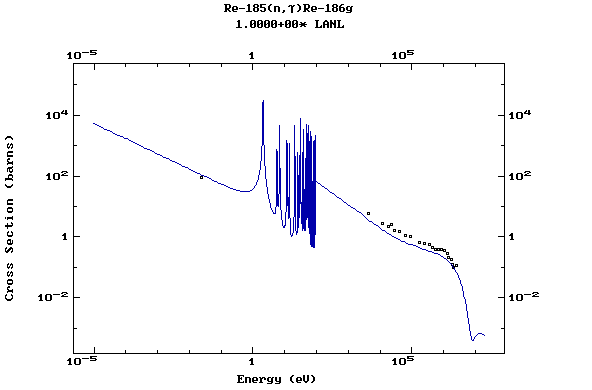
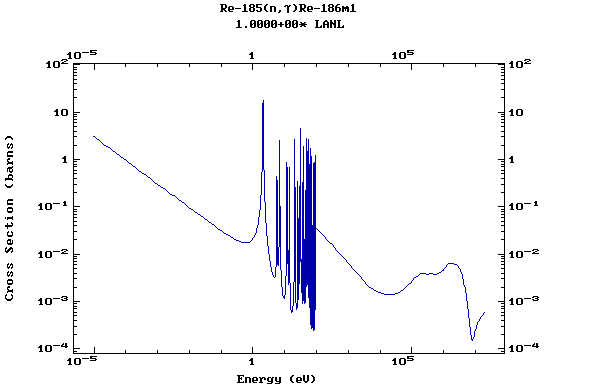
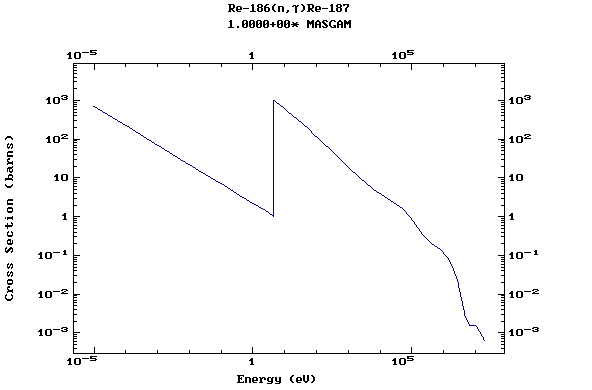
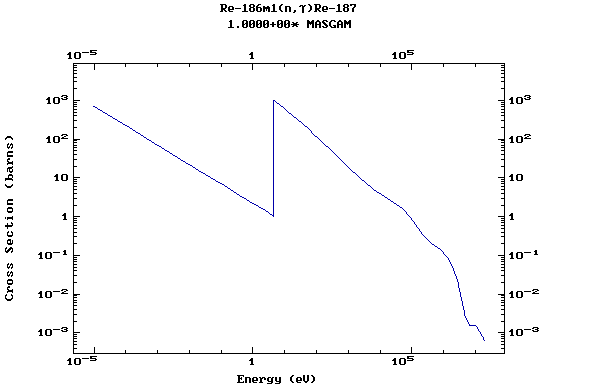
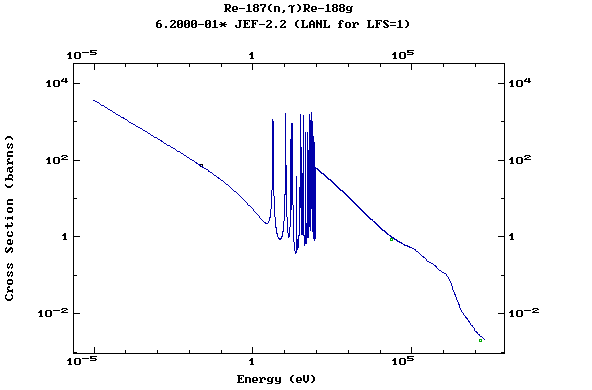
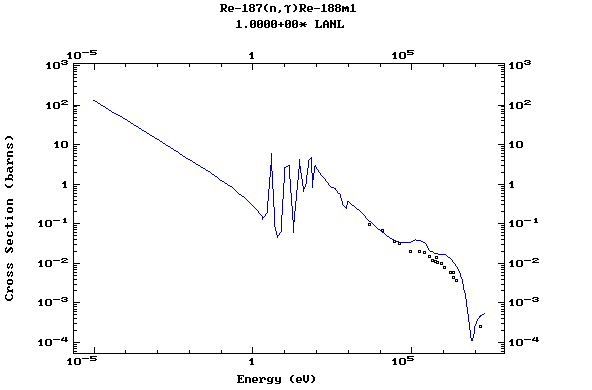
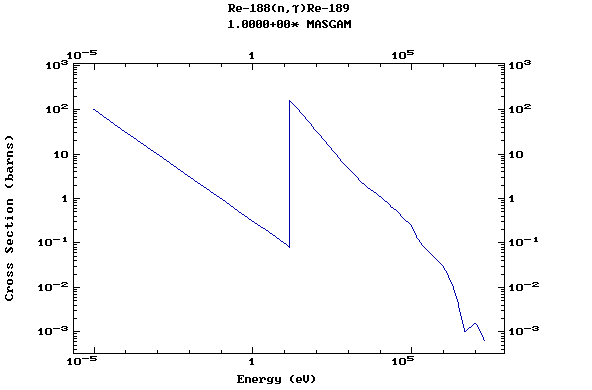
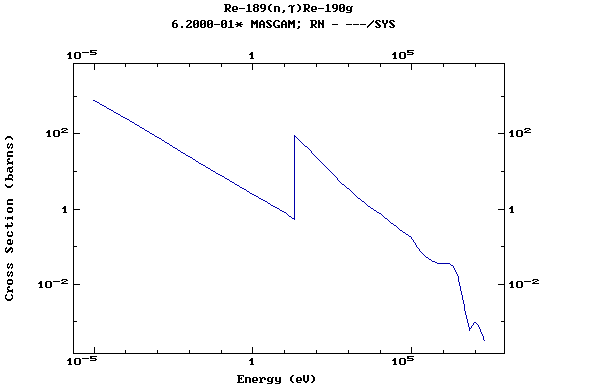
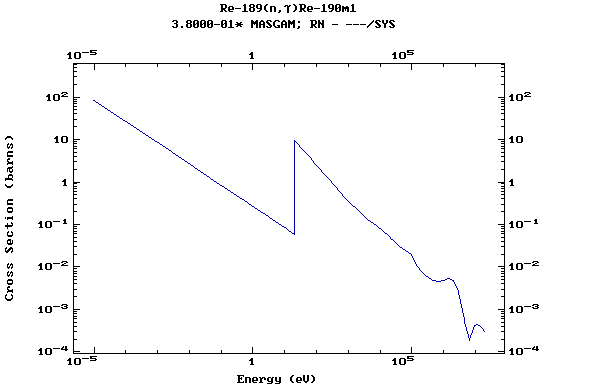
Z=76, Os
(Osmium)
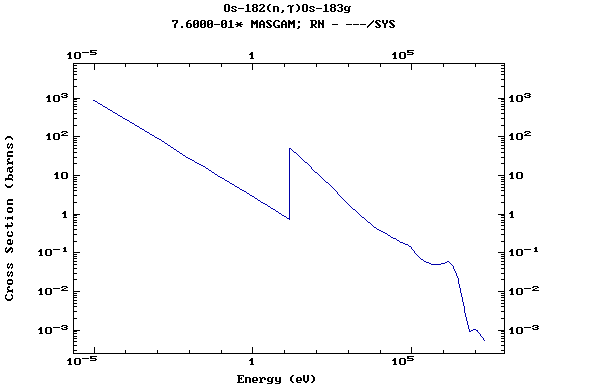
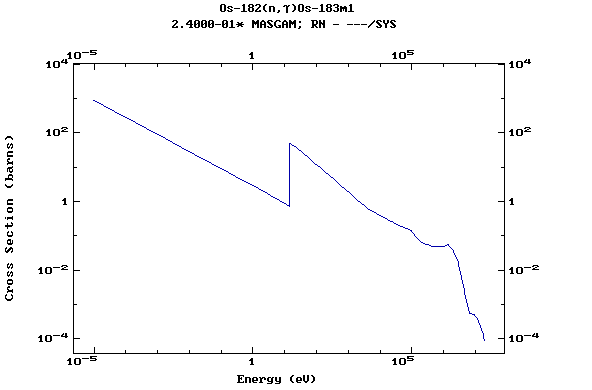
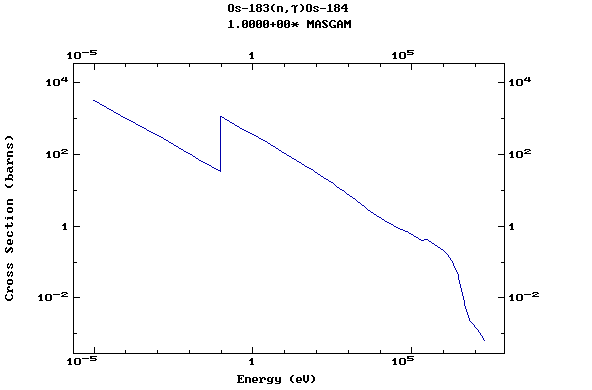
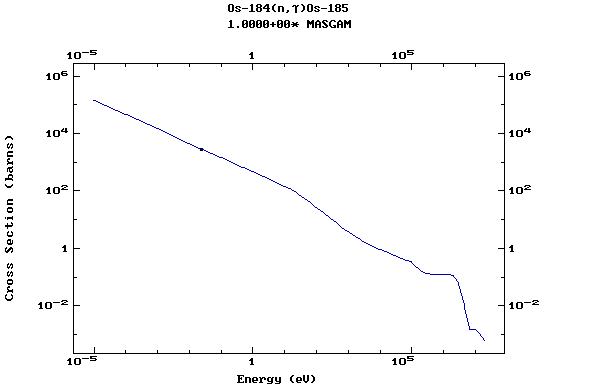
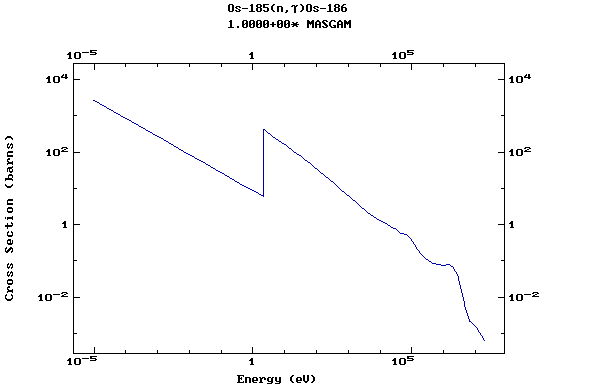
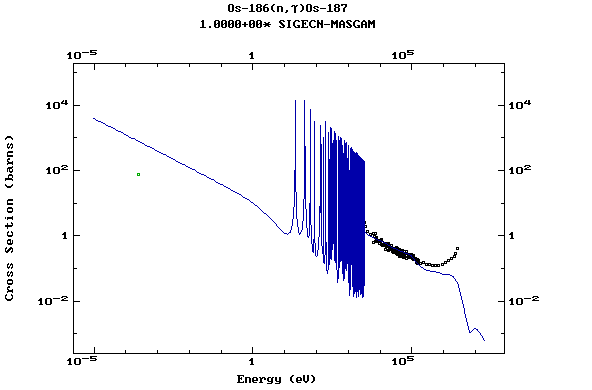
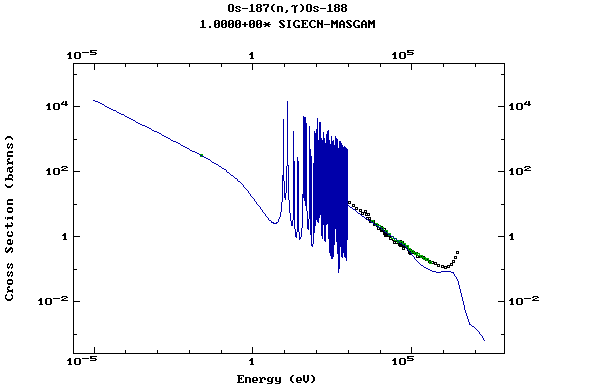
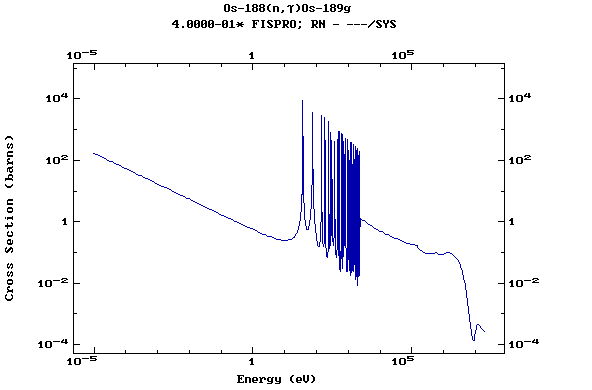
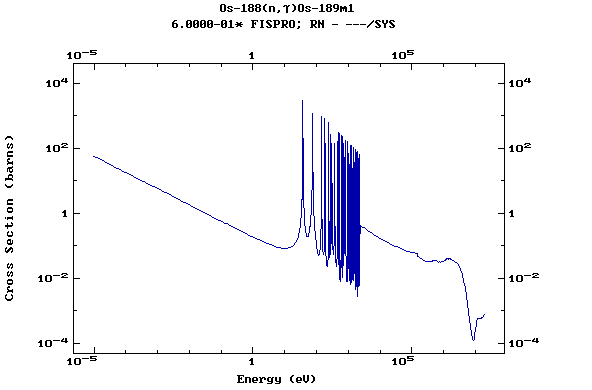
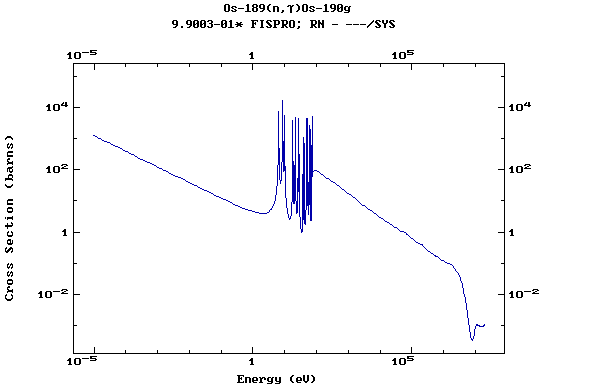
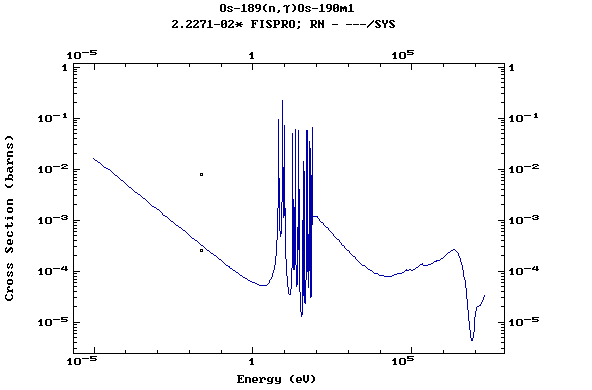
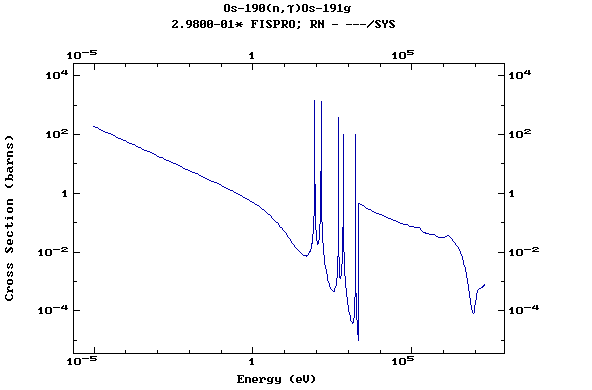
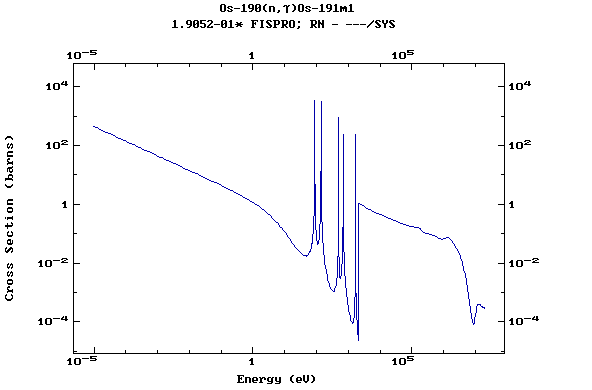
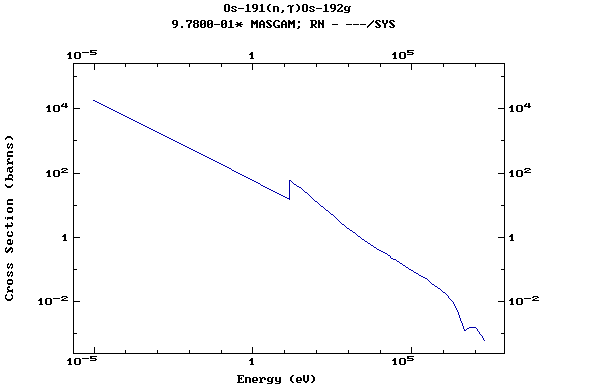
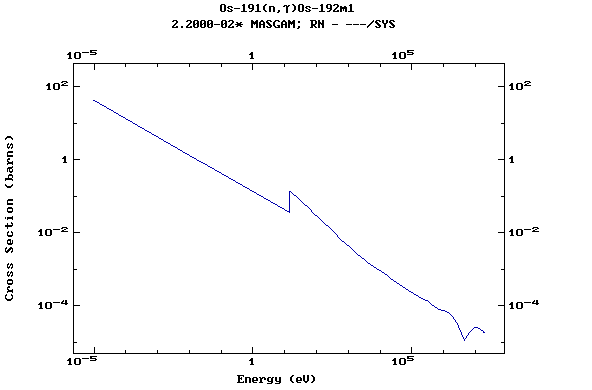
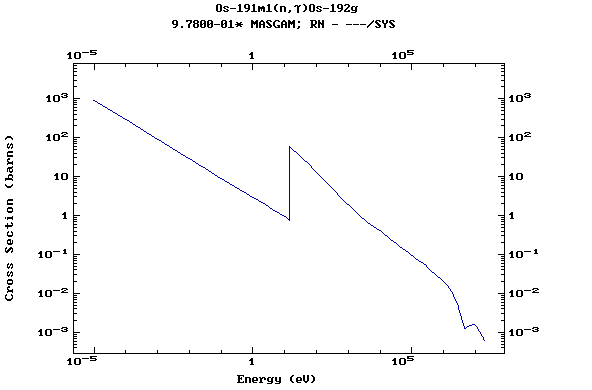
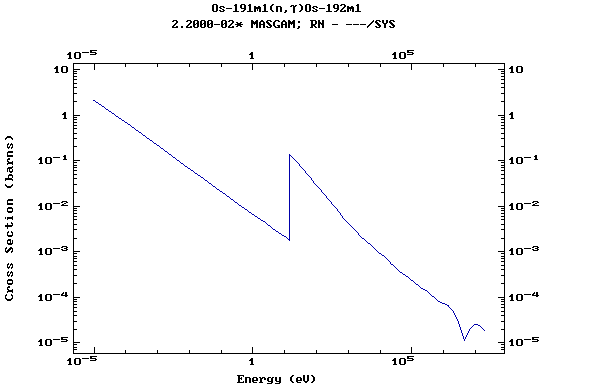
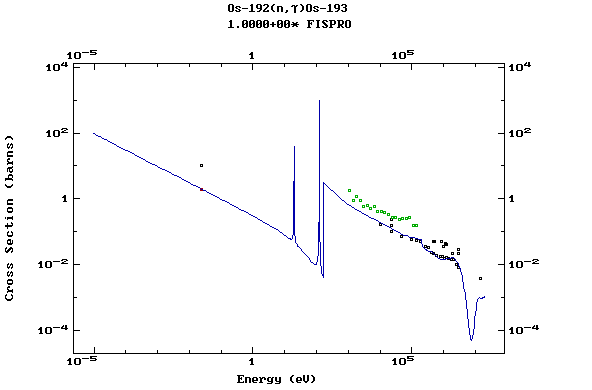
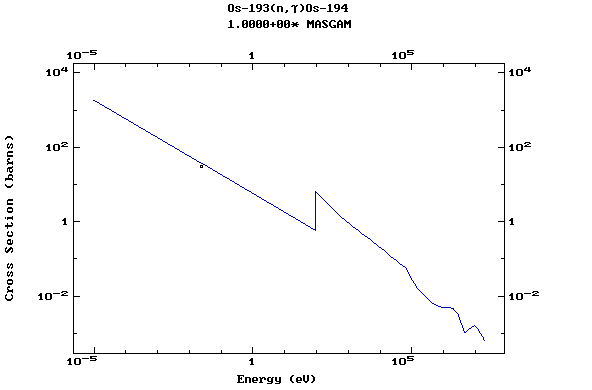
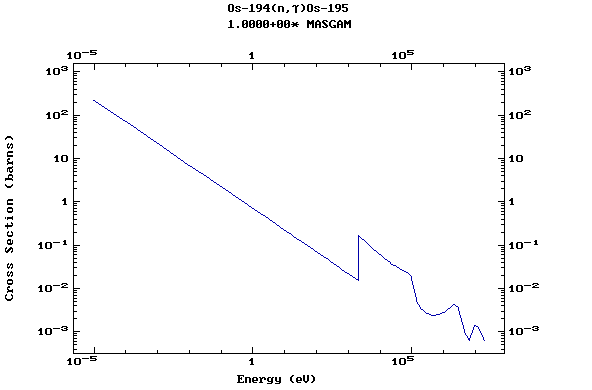
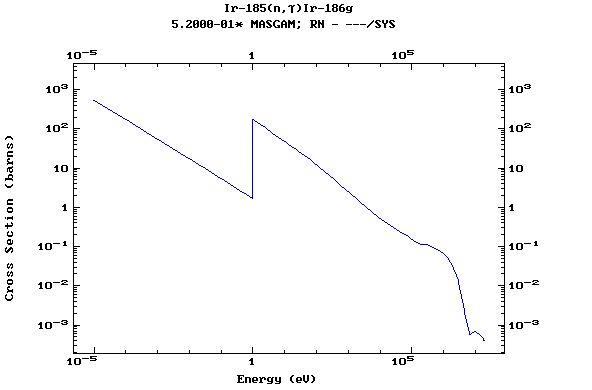
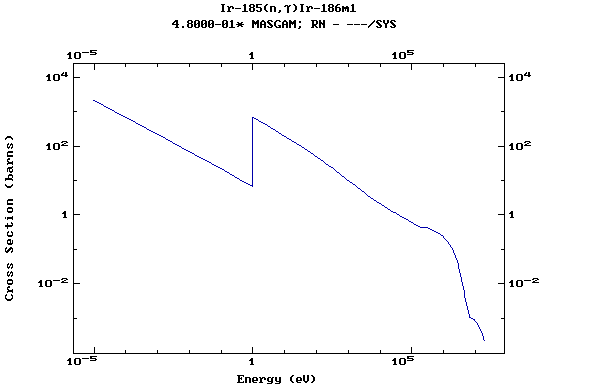
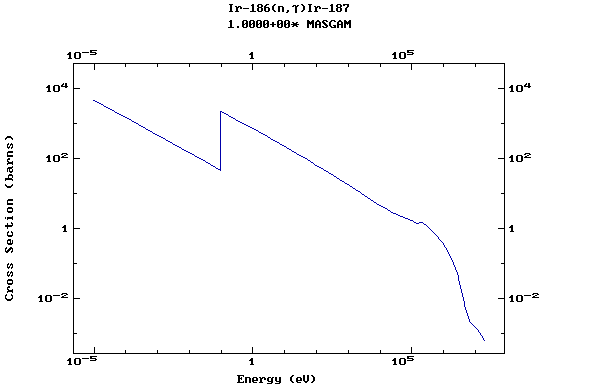
Z=77, Ir
(Irirdium)
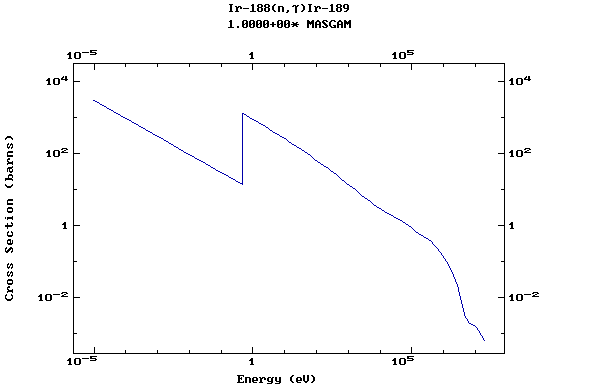
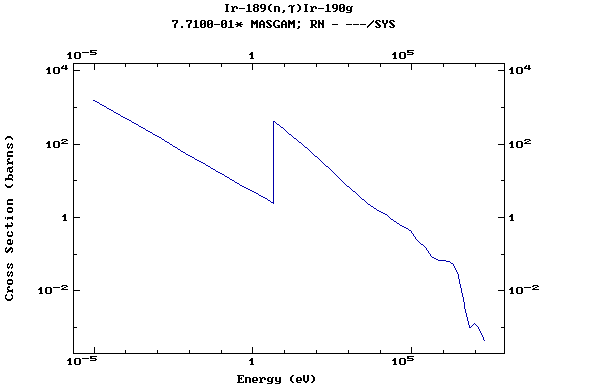
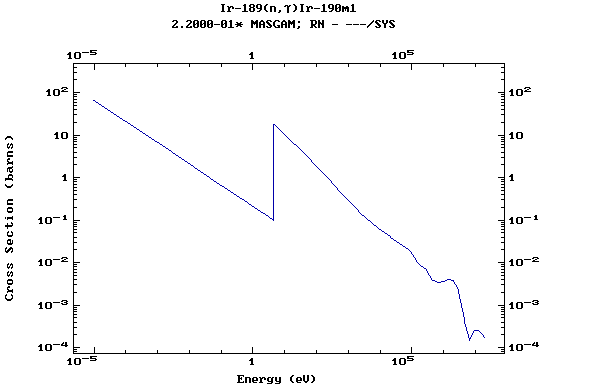
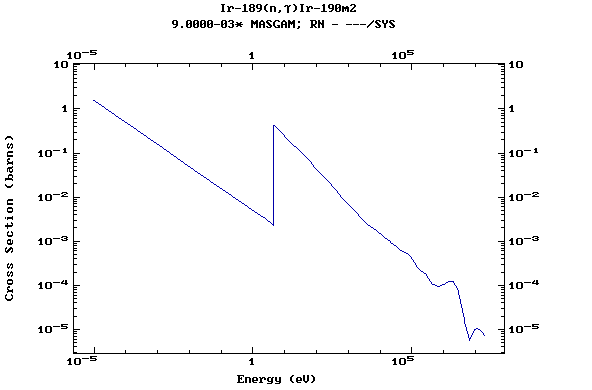
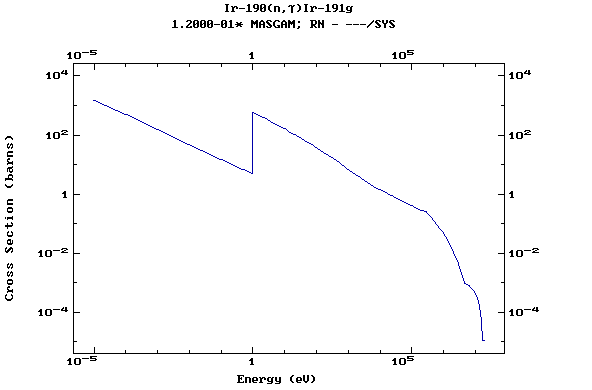
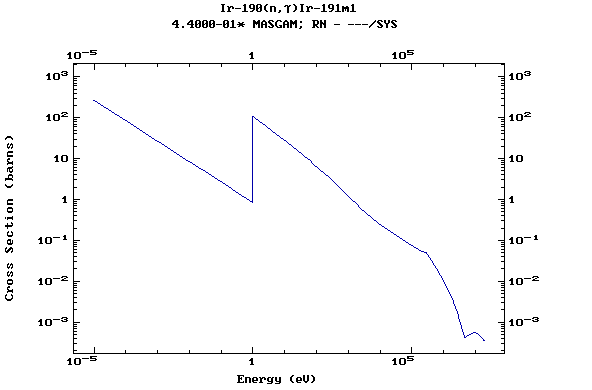
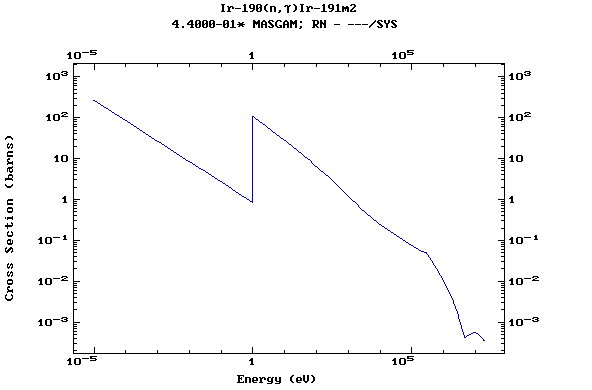
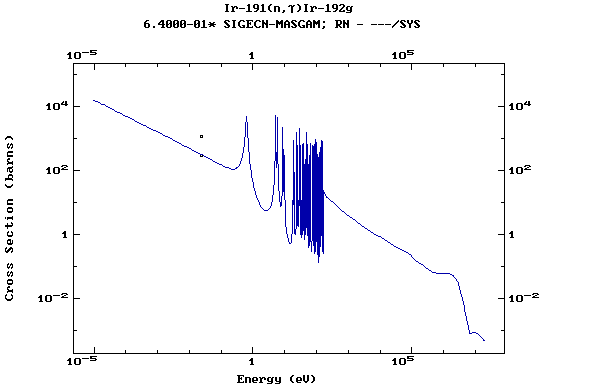
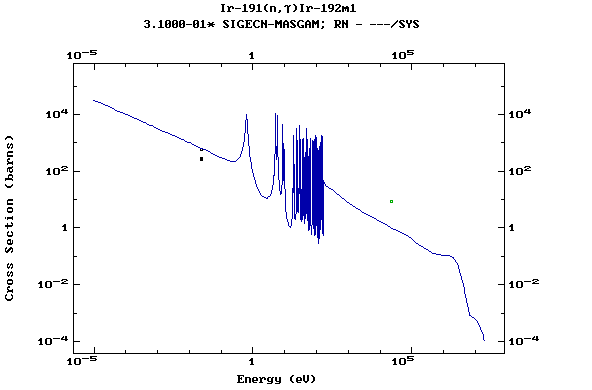
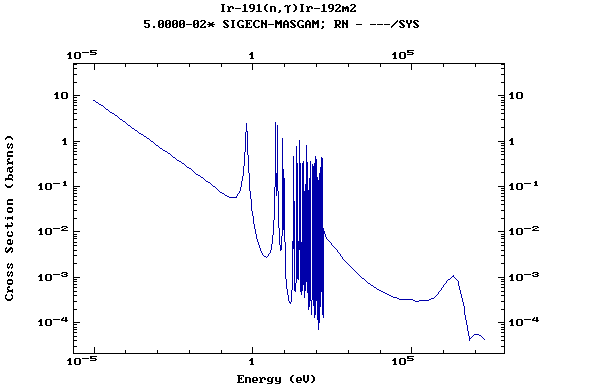
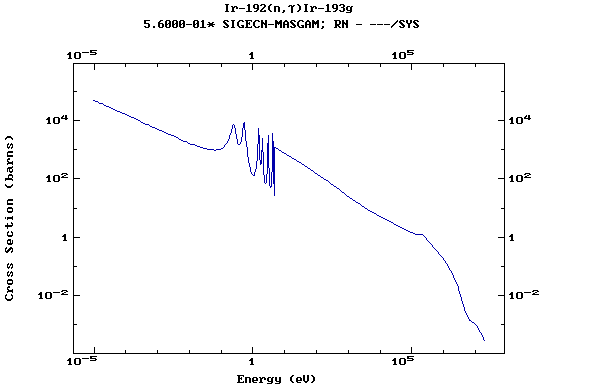
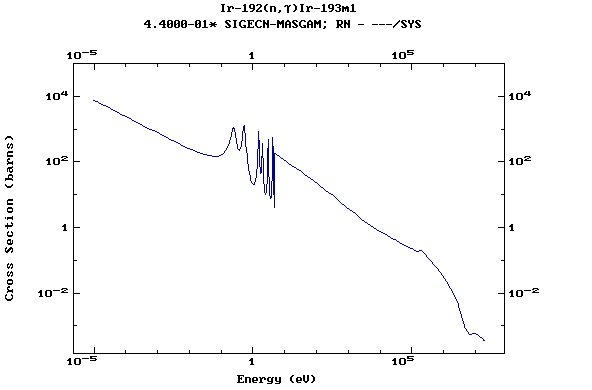
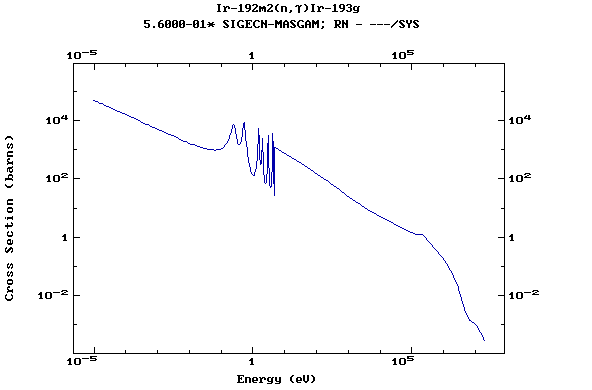
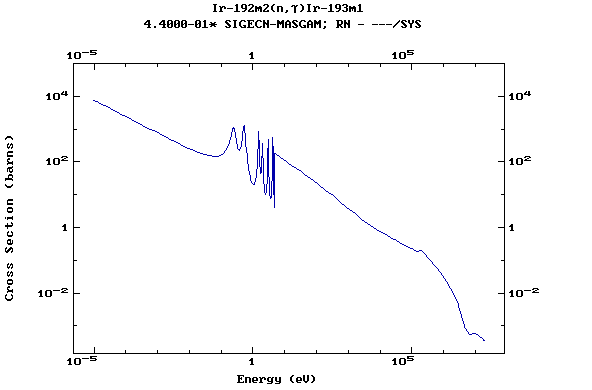
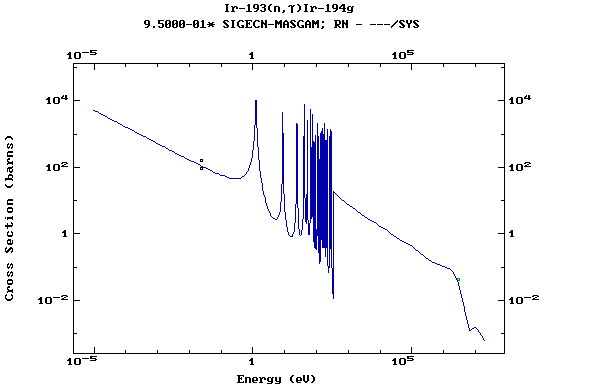
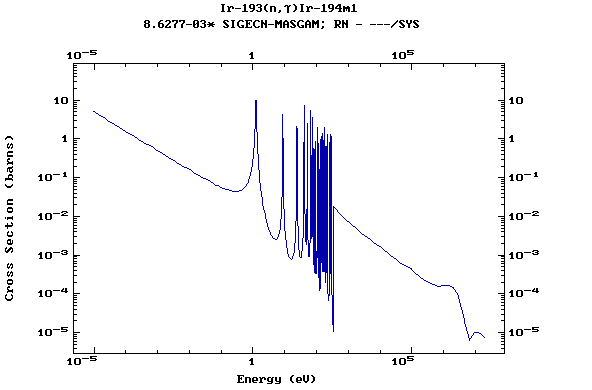
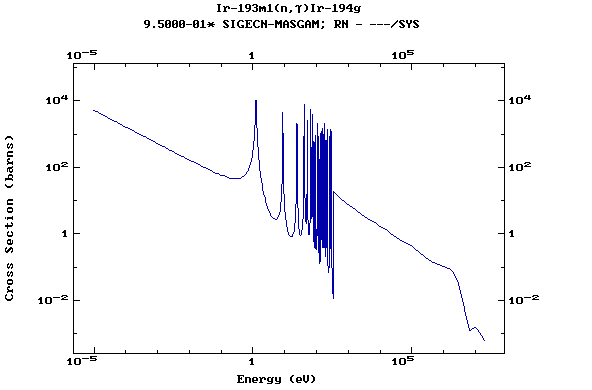
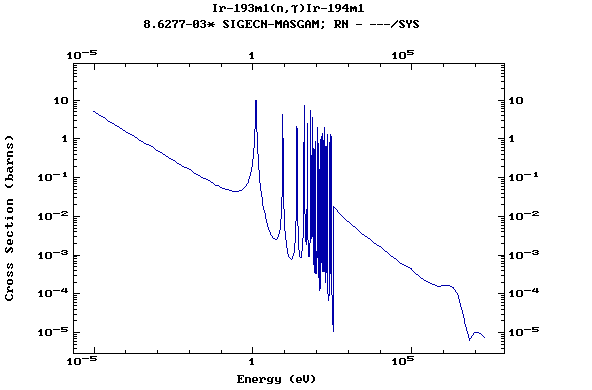
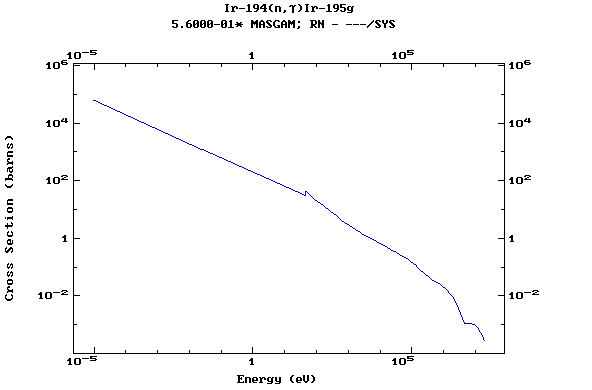
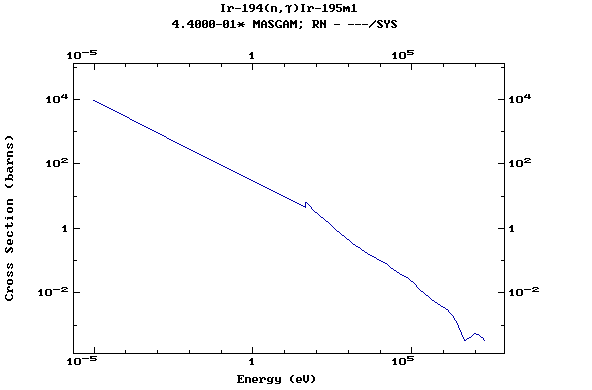
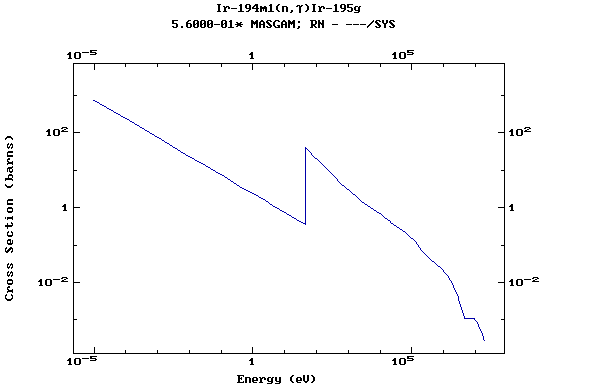
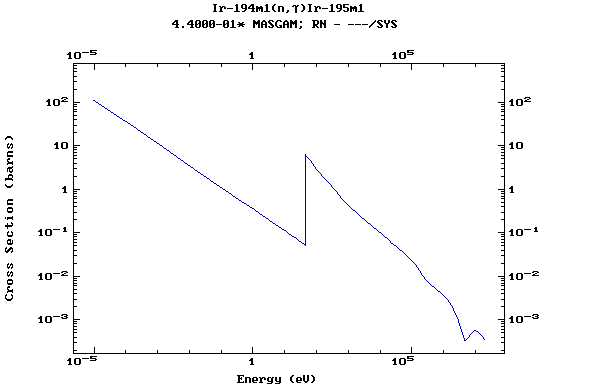
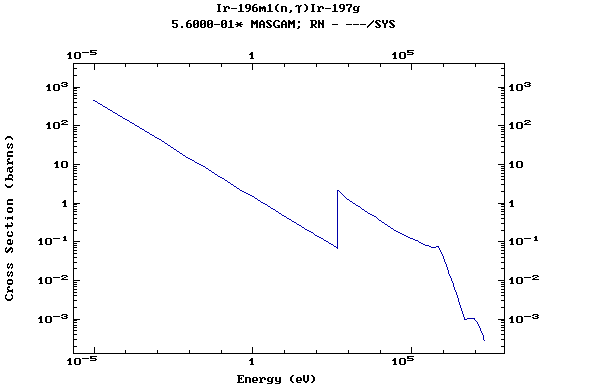
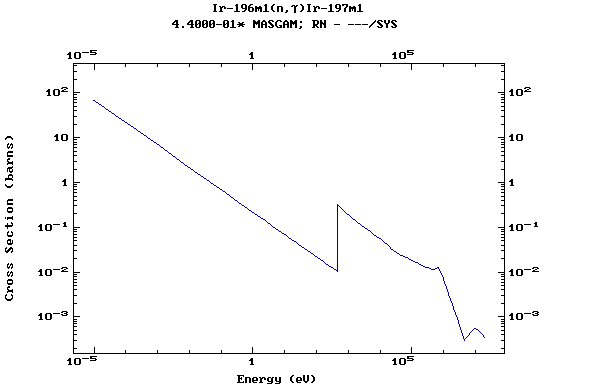
Z=78, Pt
(Platinum)
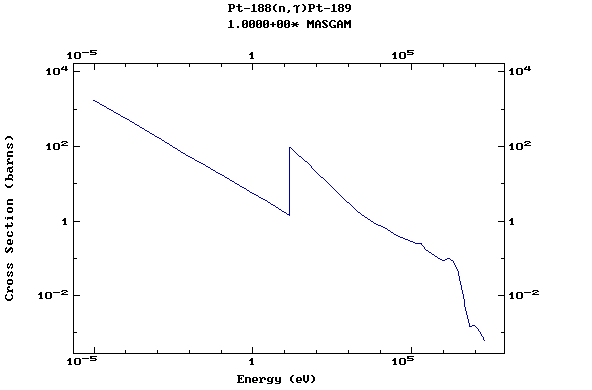
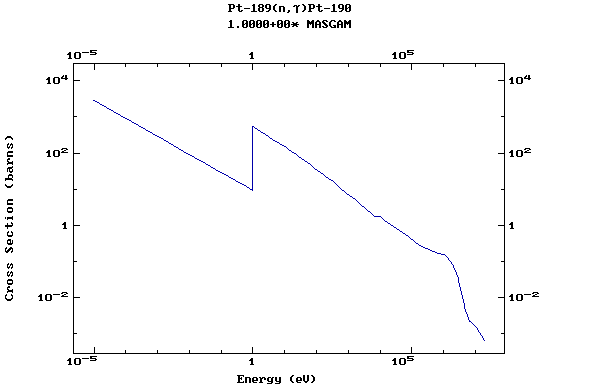
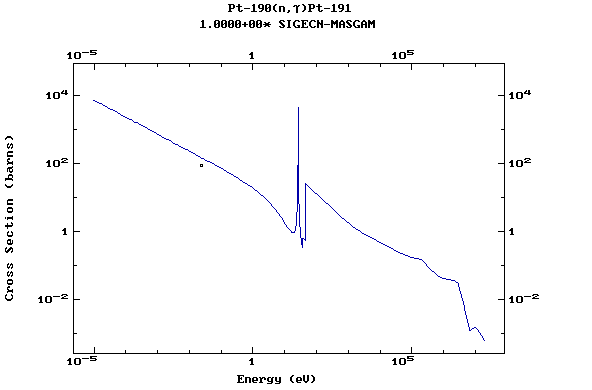
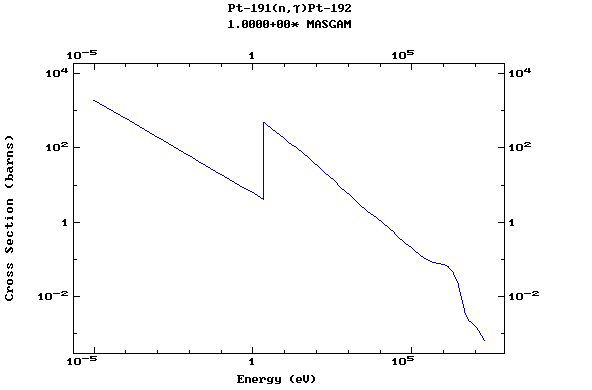
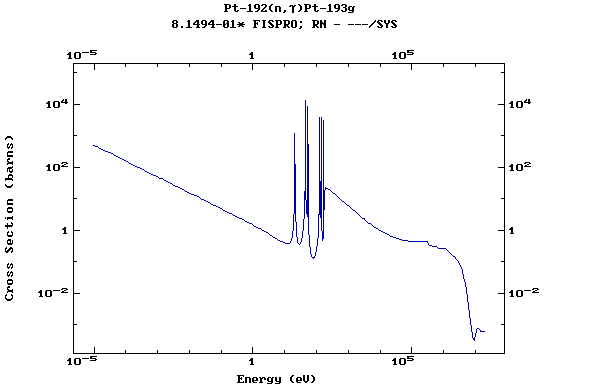
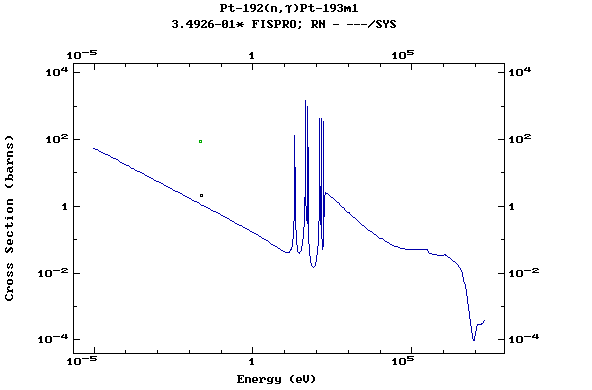
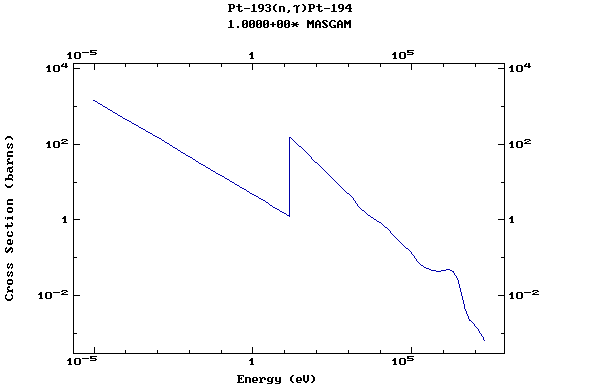
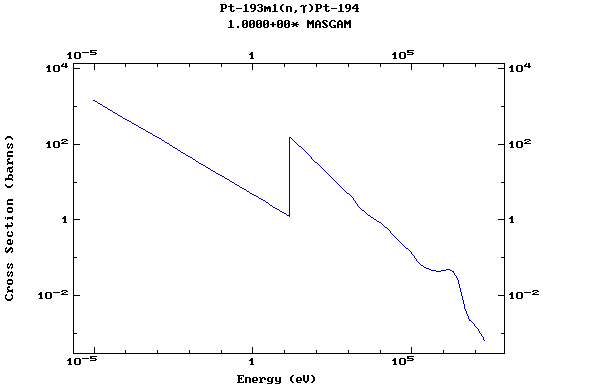
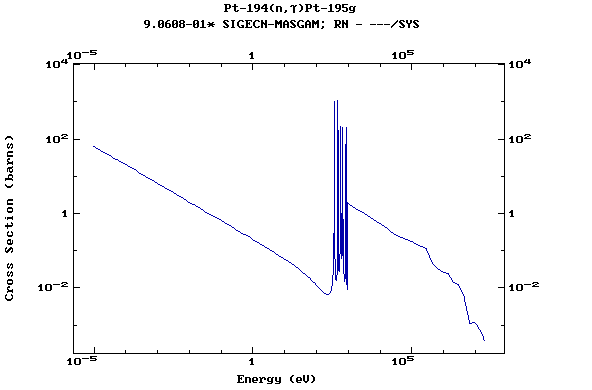
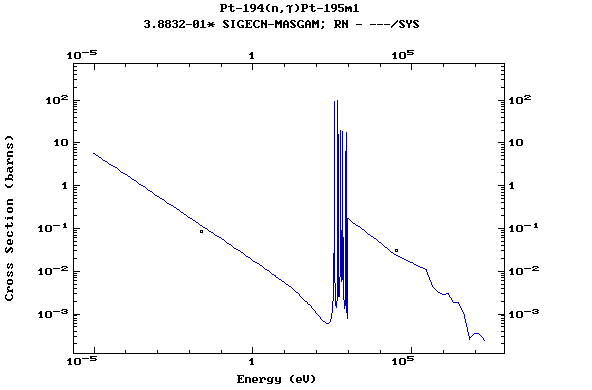
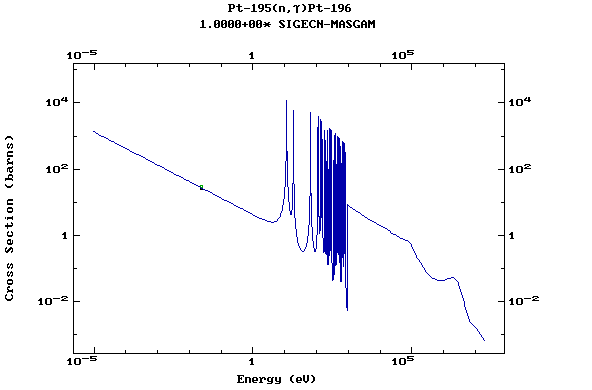
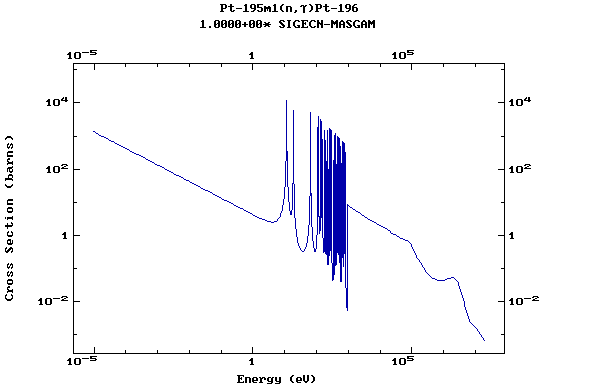
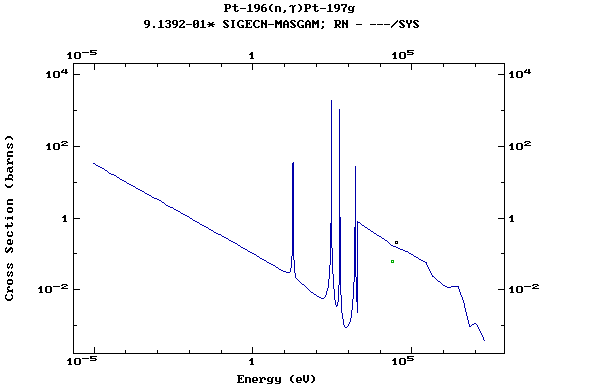
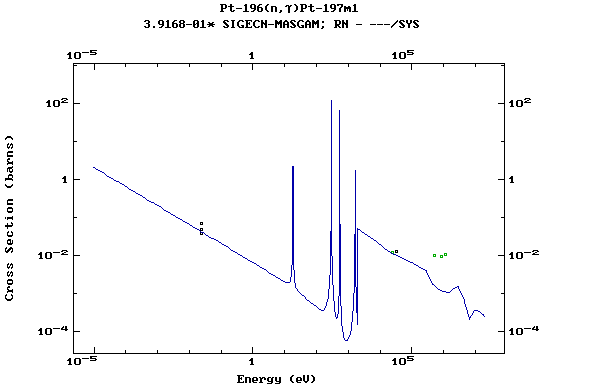
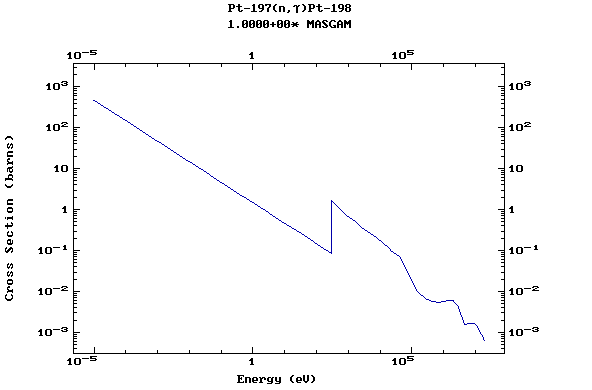
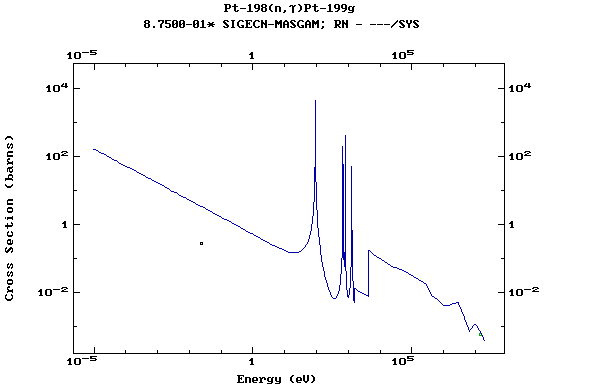
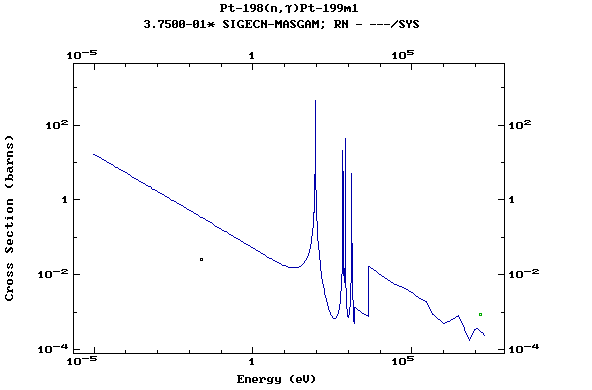
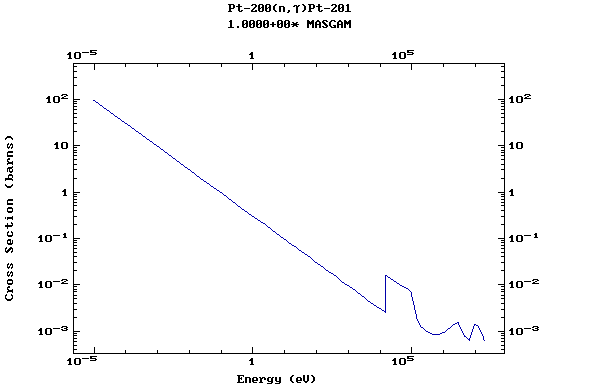
Z=79, Au
(Gold)
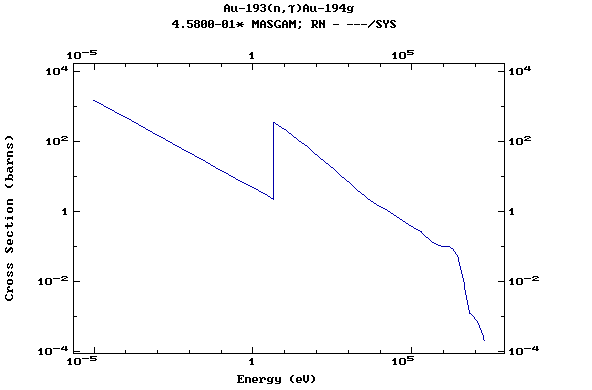
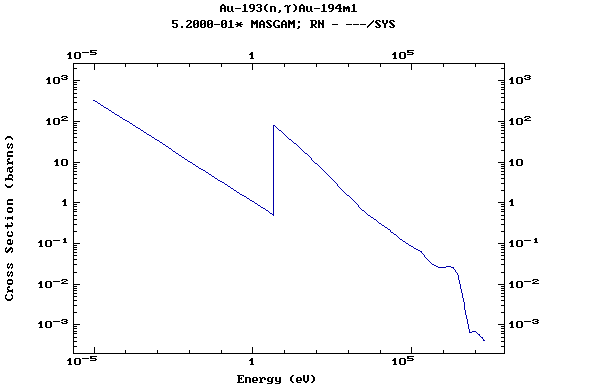
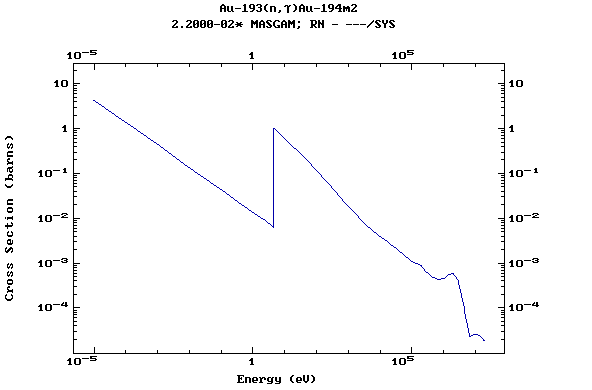
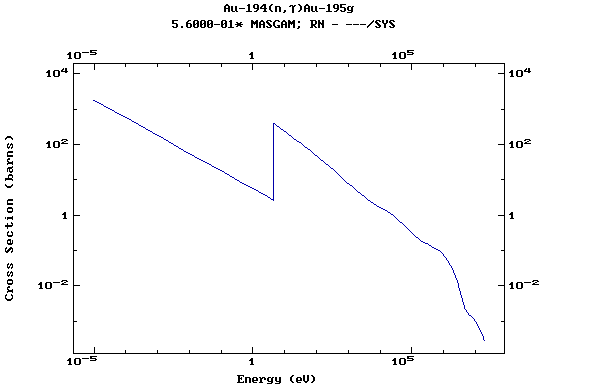
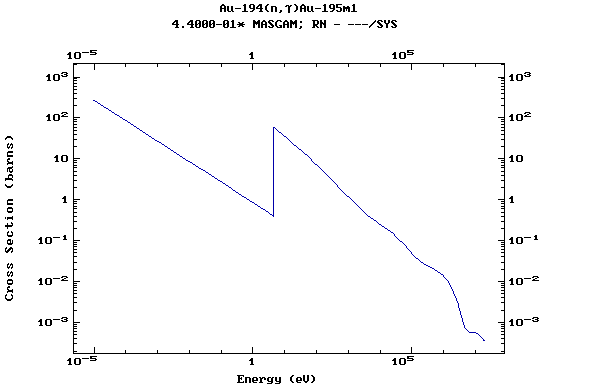
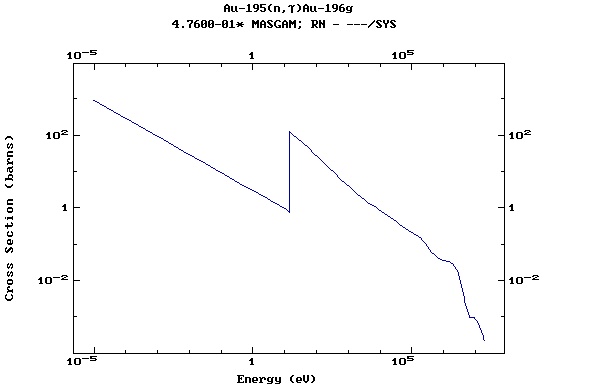
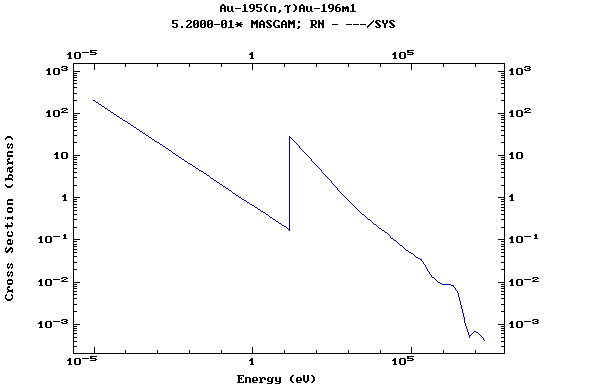
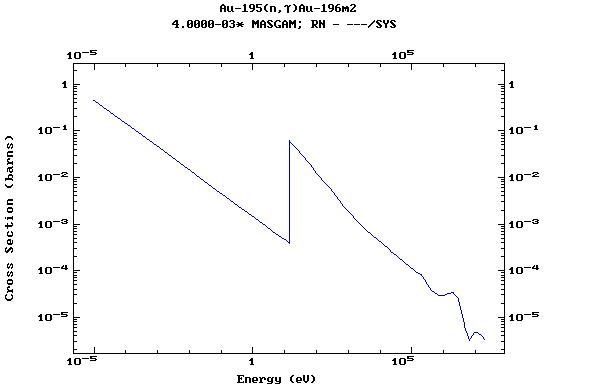
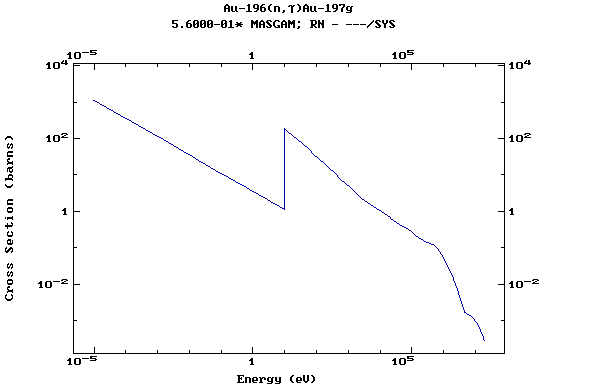
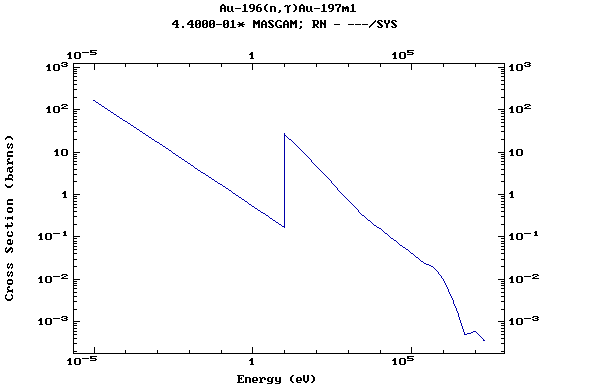
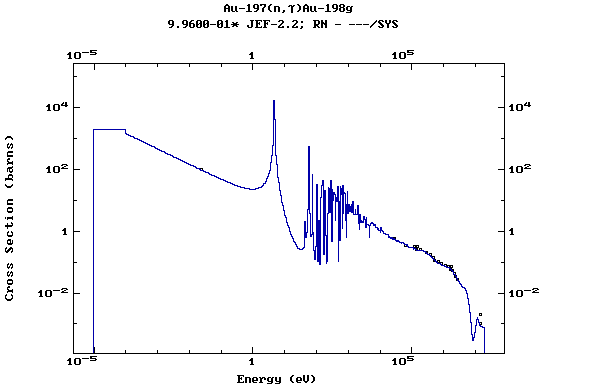
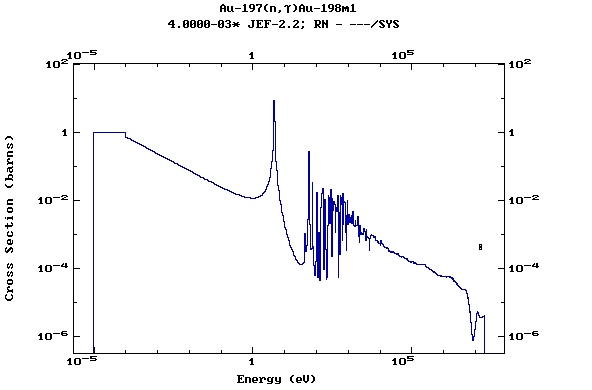
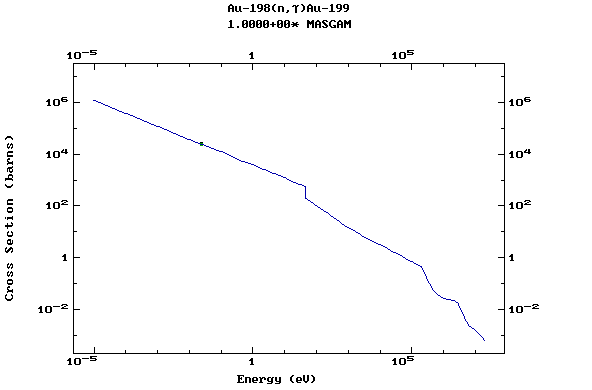
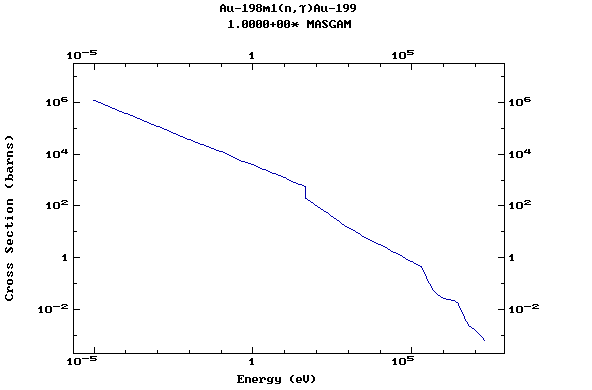
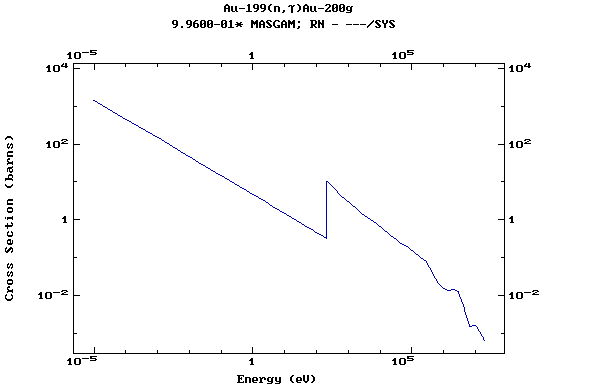
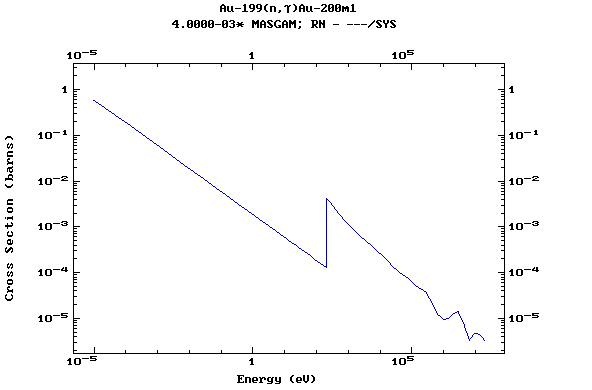
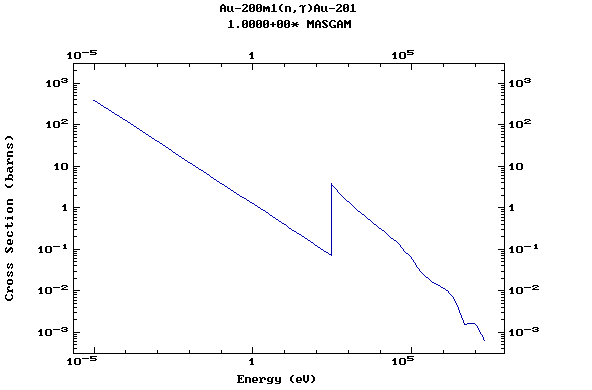
Z=80, Hg
(Mercury)
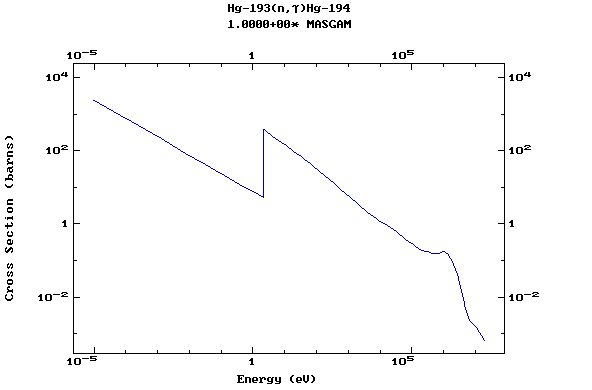
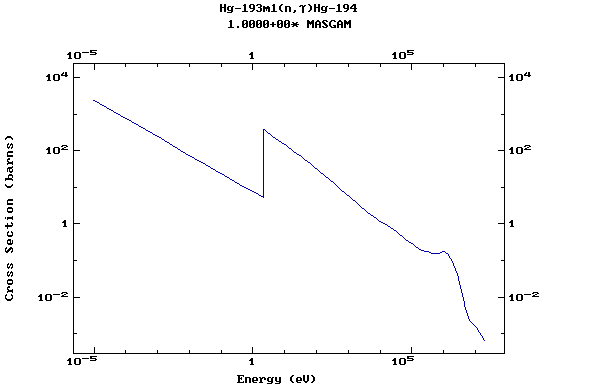
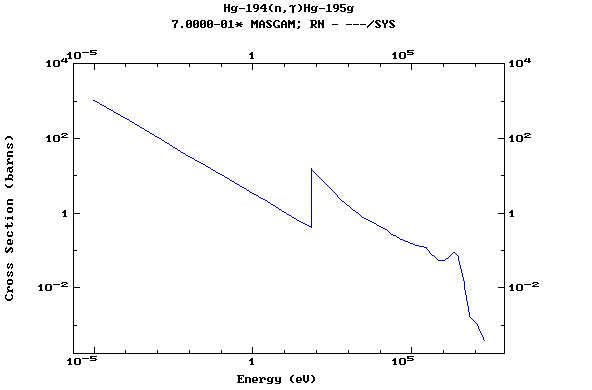
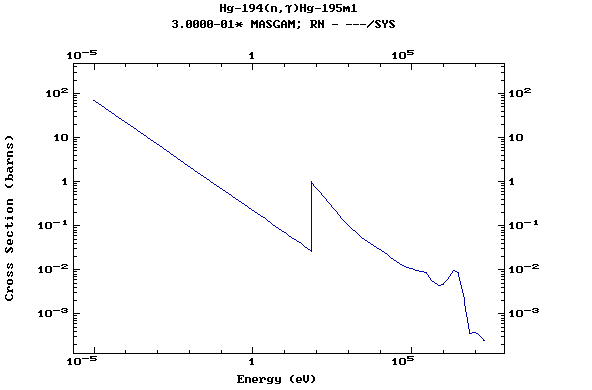
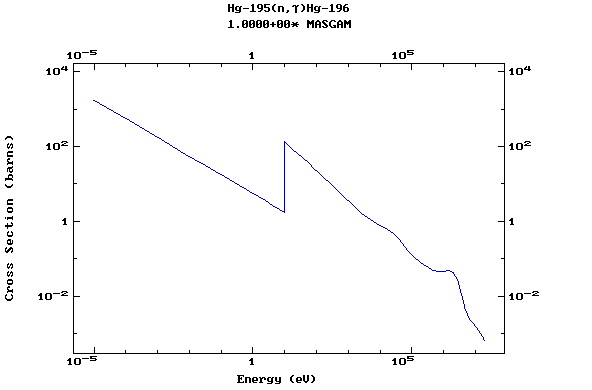
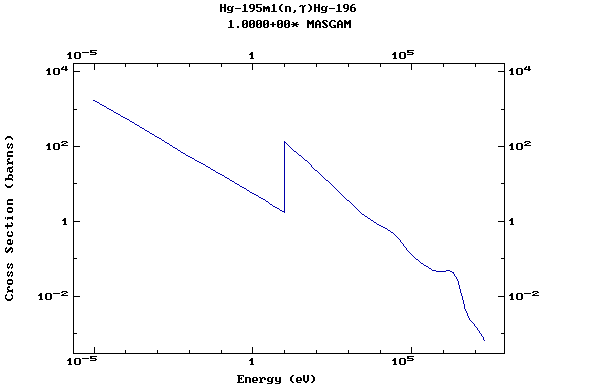
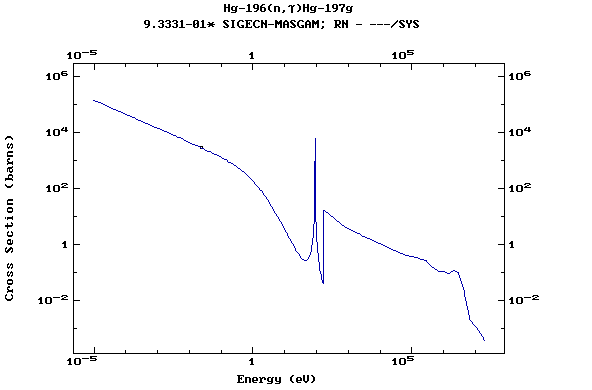
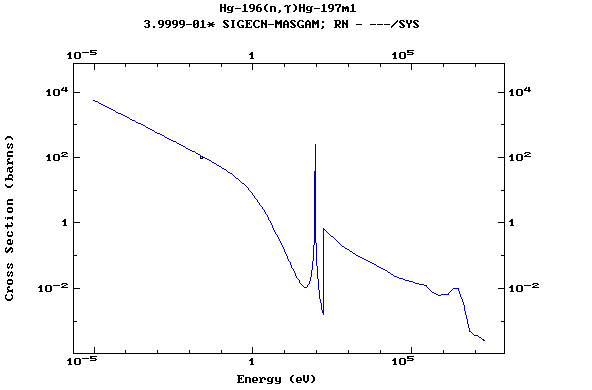
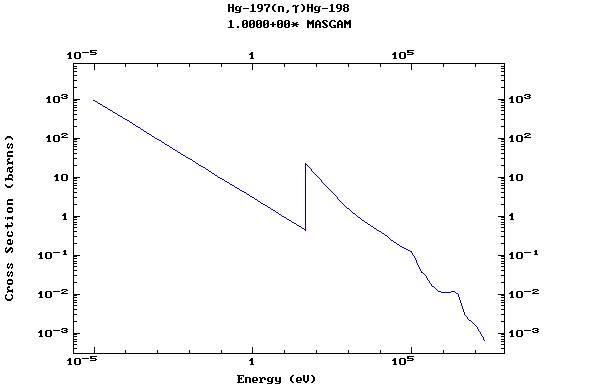
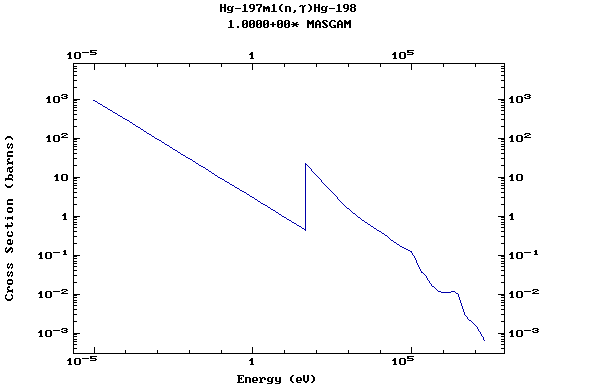
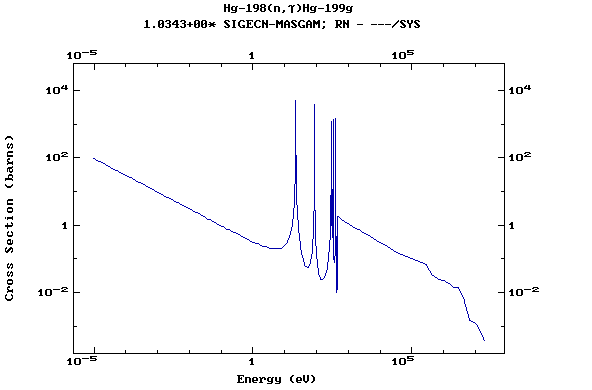
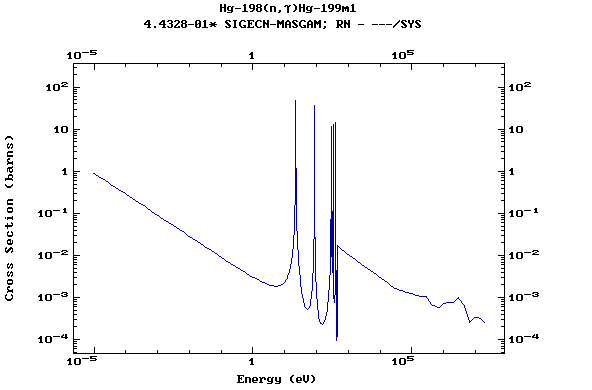
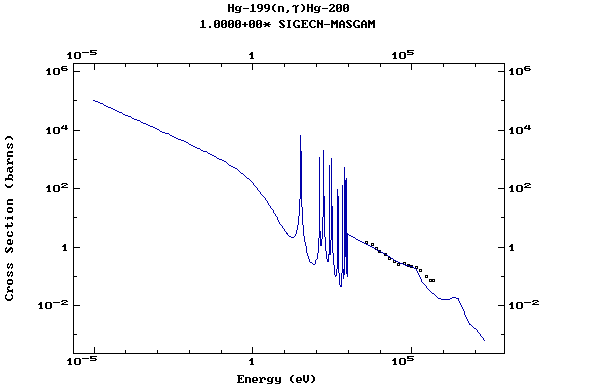
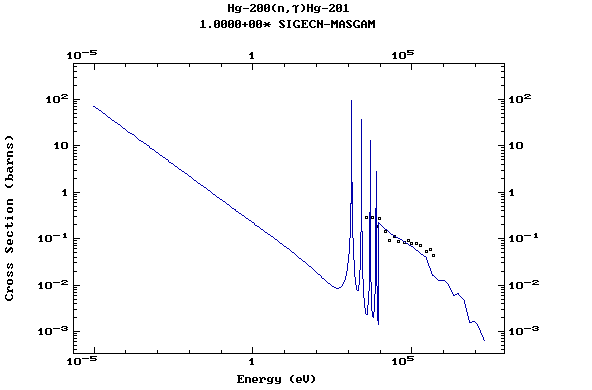
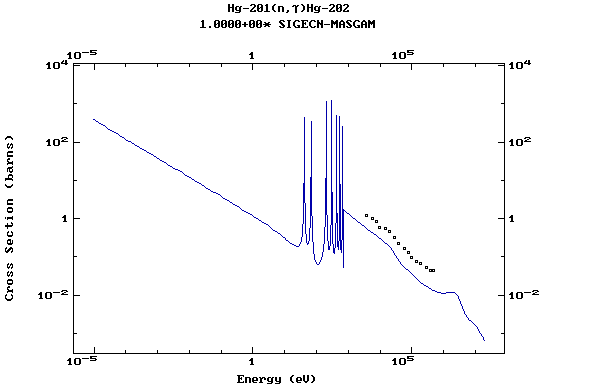
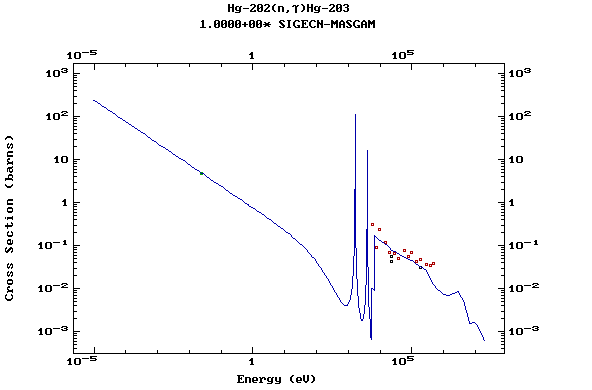
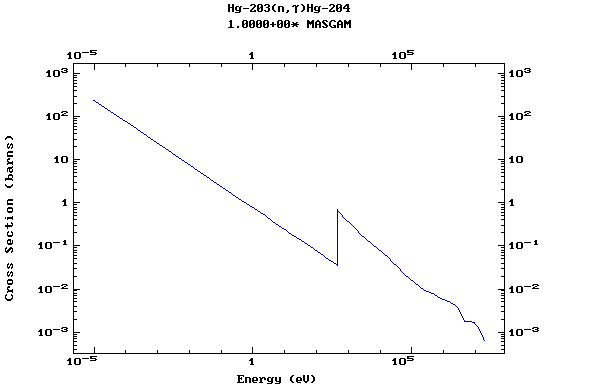
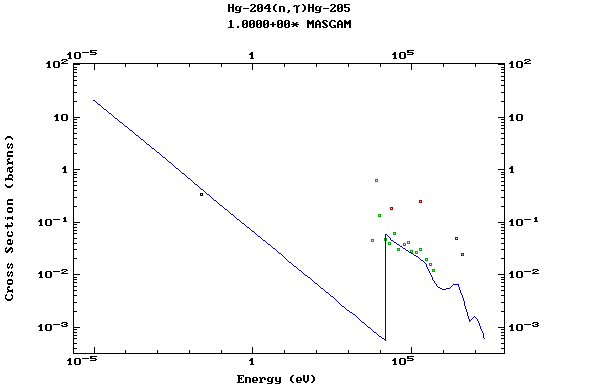
Z=81, Tl
(Thallium)
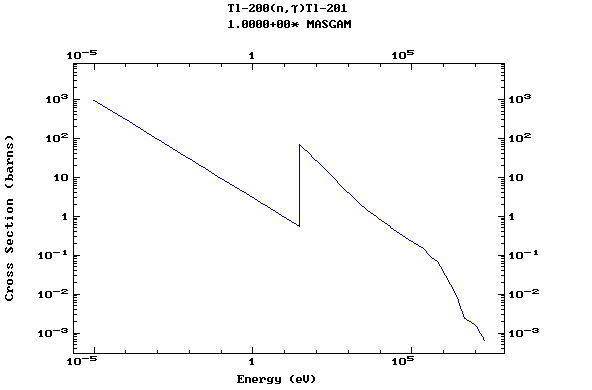
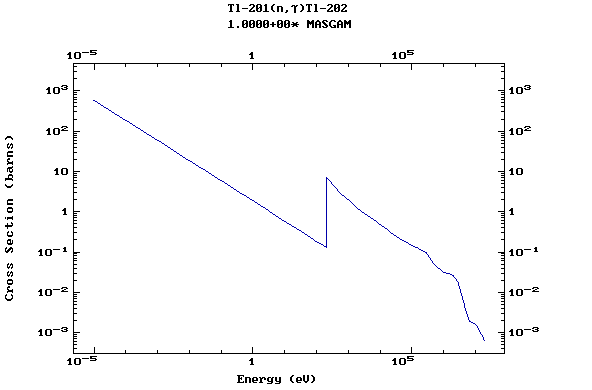
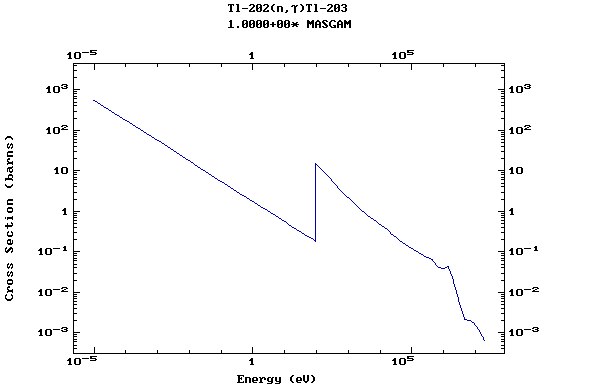
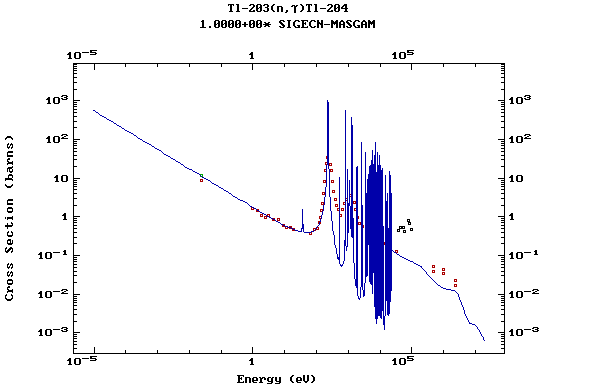
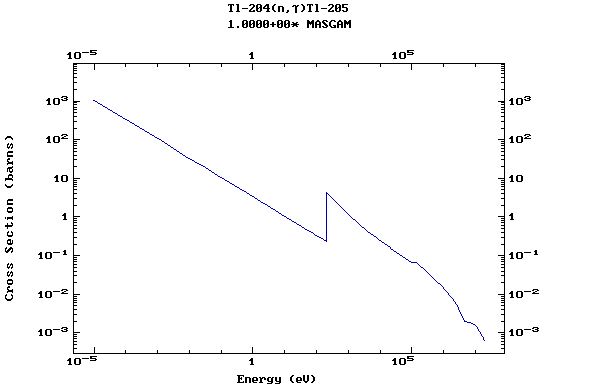
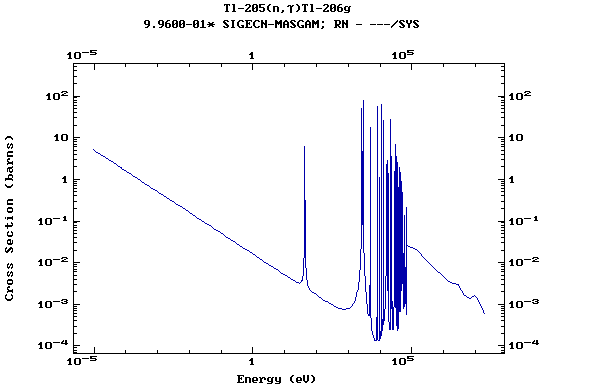
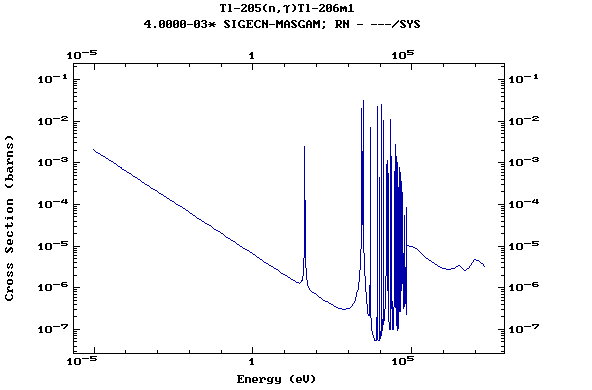
Z=82, Pb
(Lead)
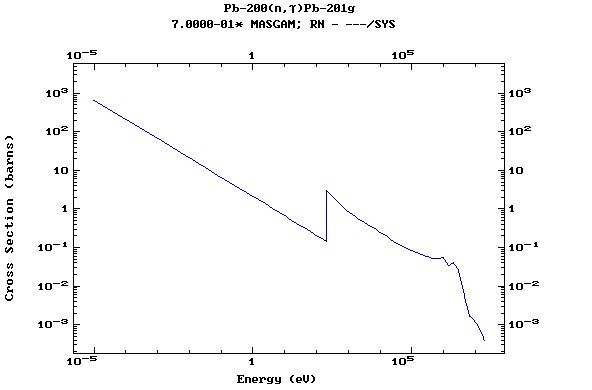
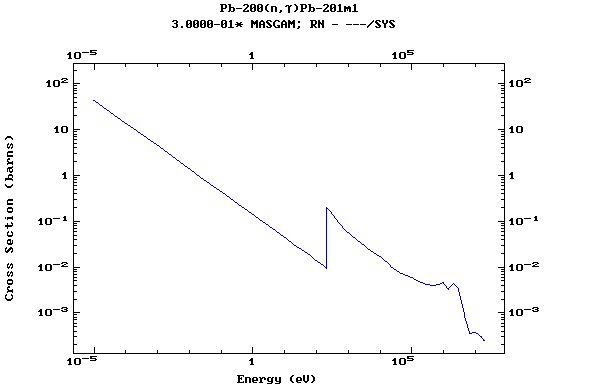
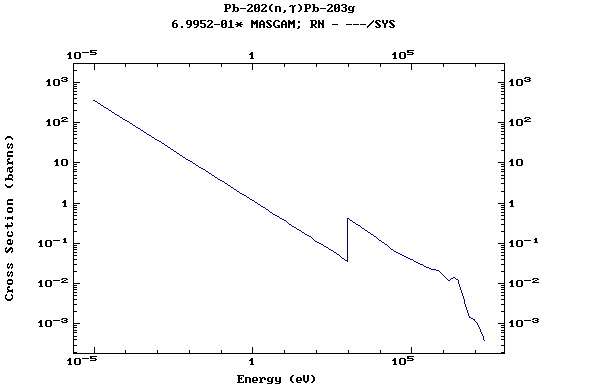
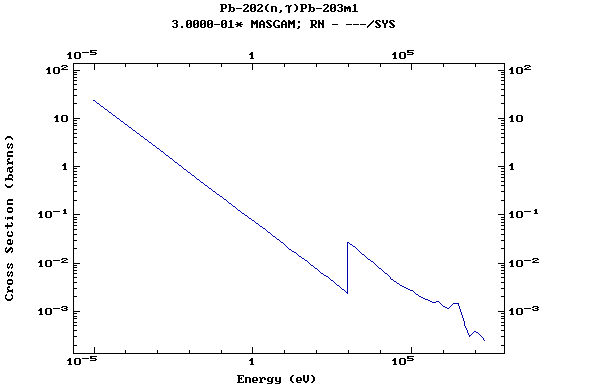
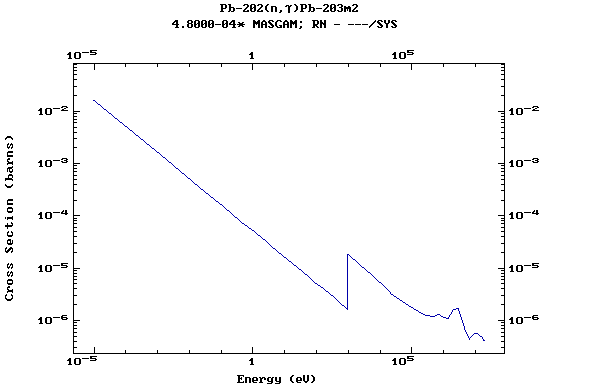
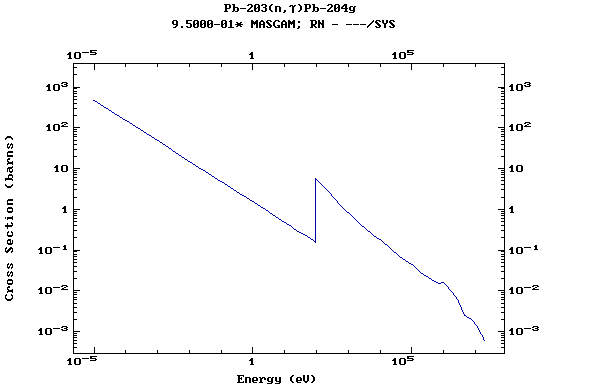
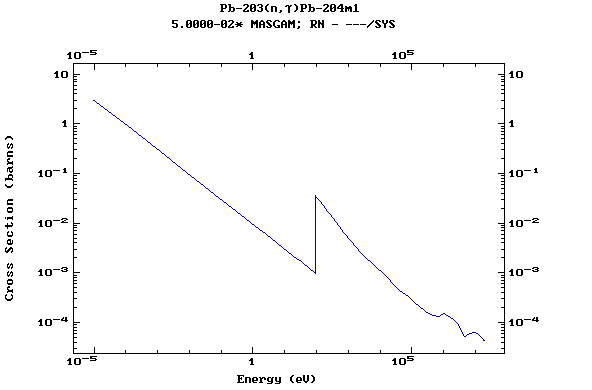
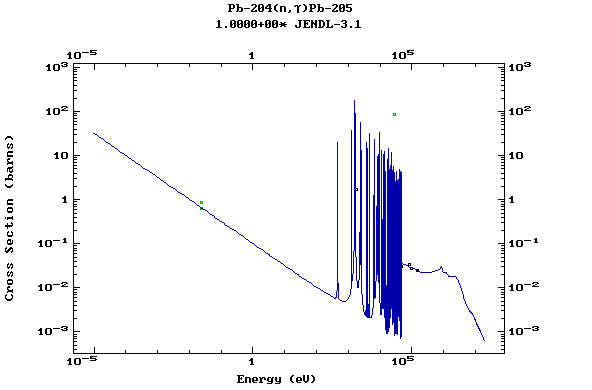
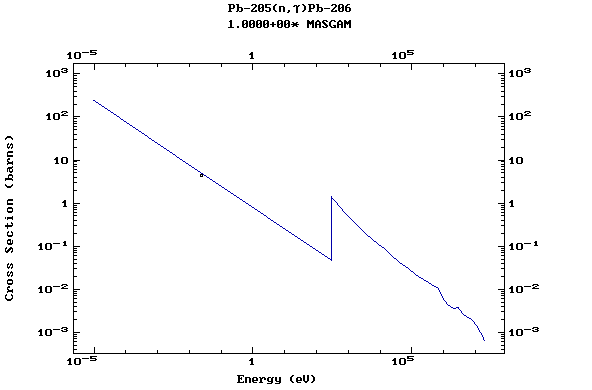
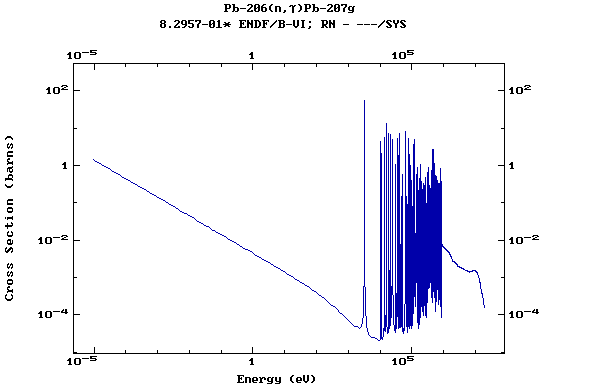
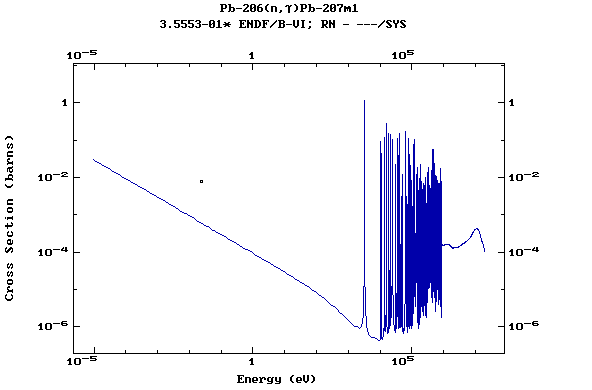
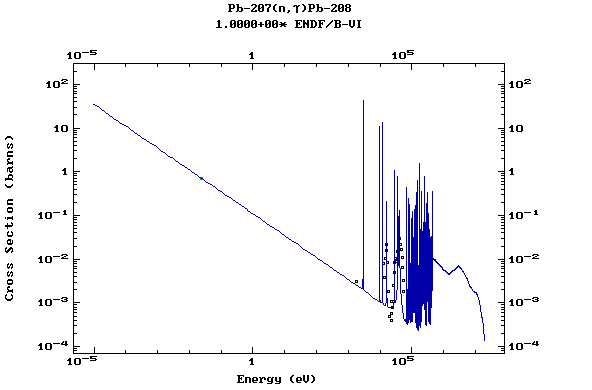
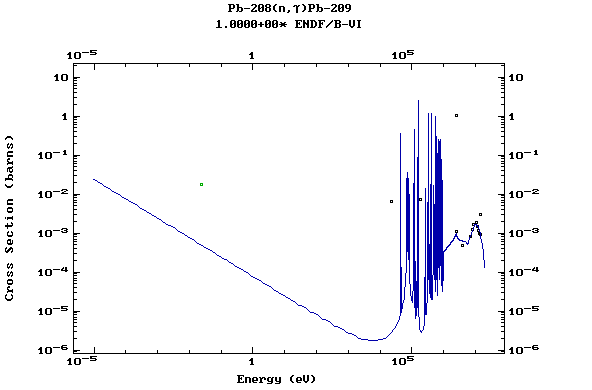
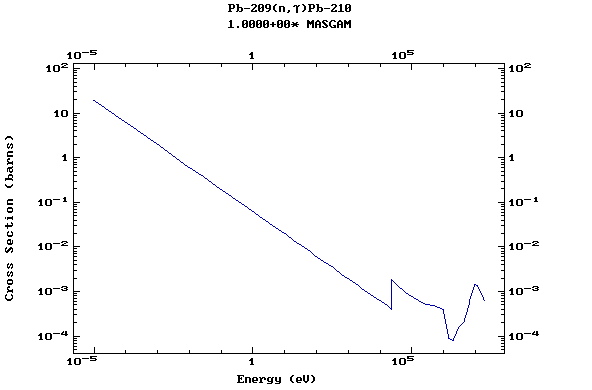
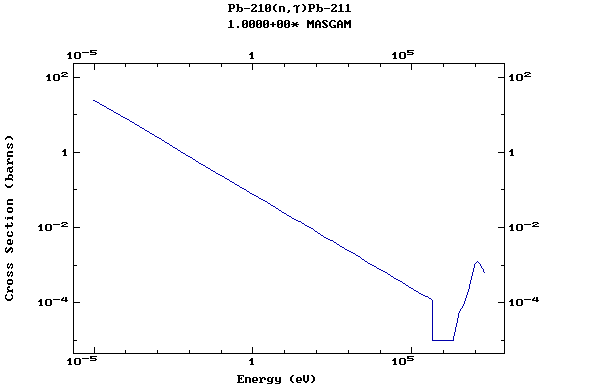
Z=83, Bi
(Bismuth)
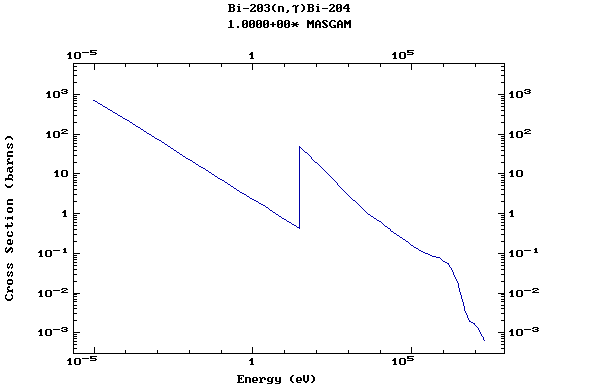
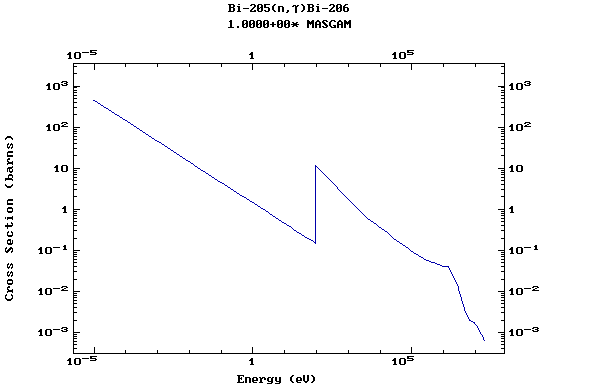
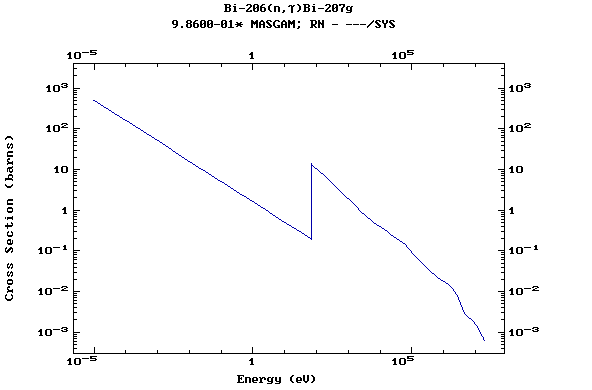
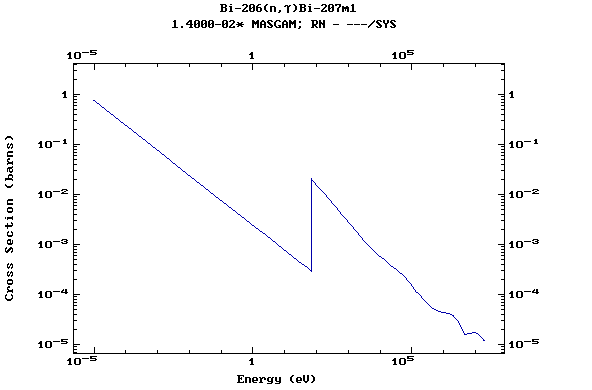
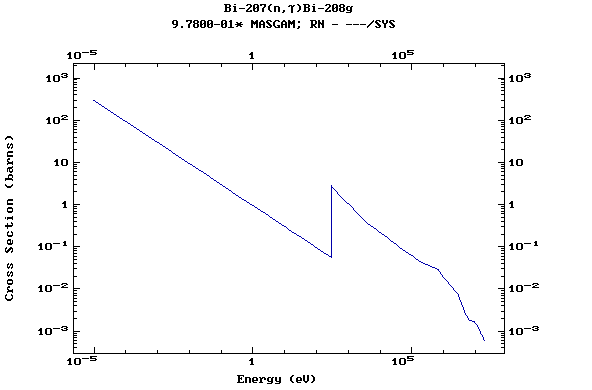
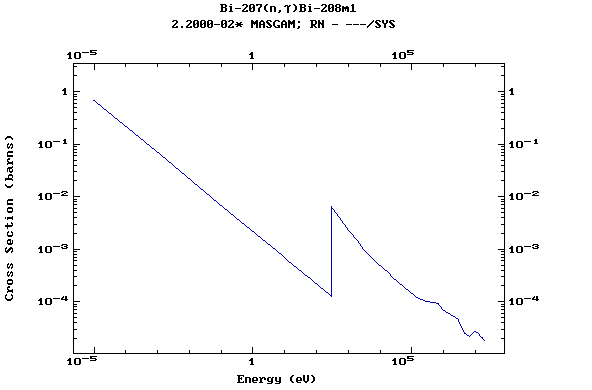
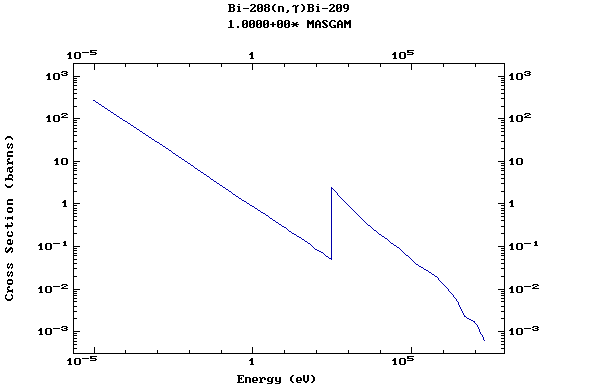
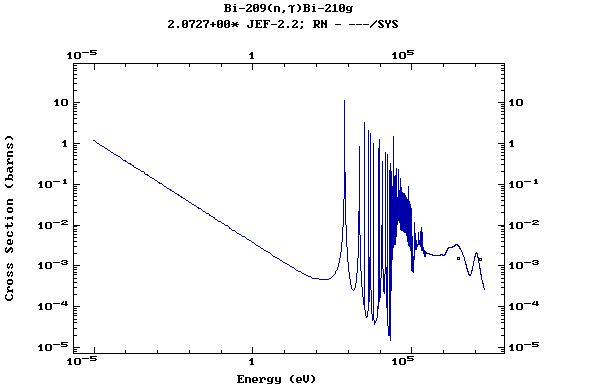
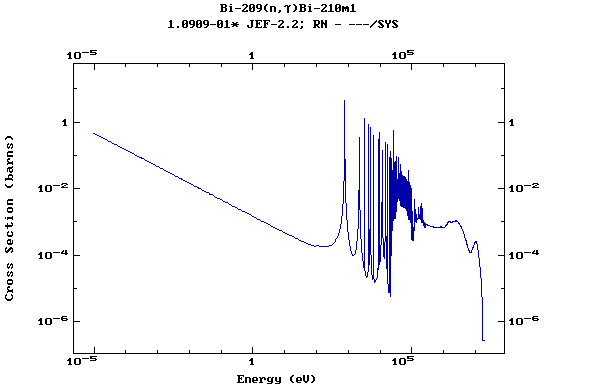
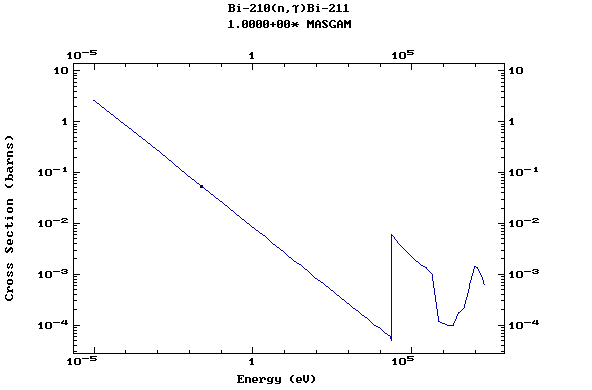
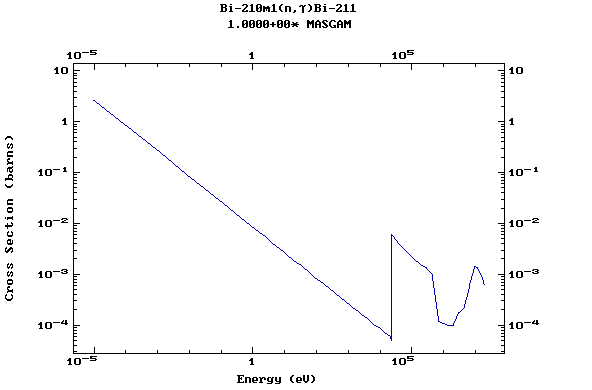
Z=84, Po
(Polonium)
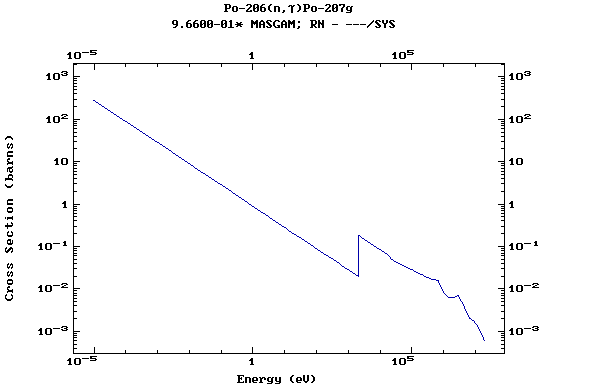
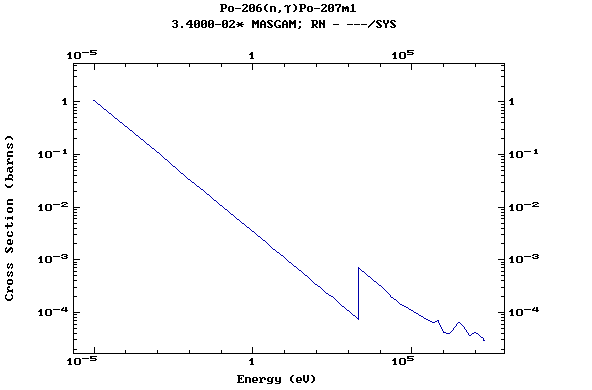
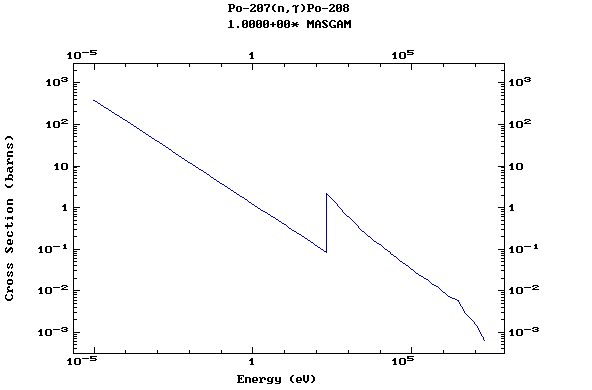
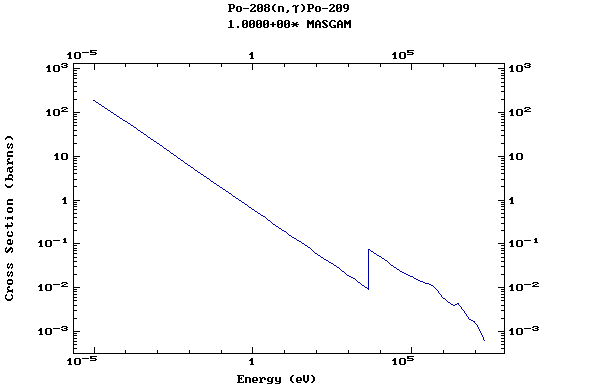
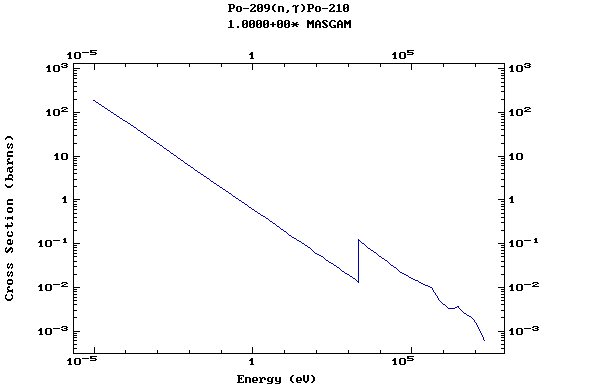
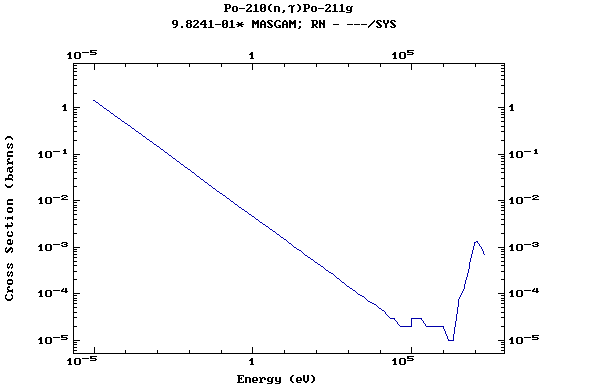
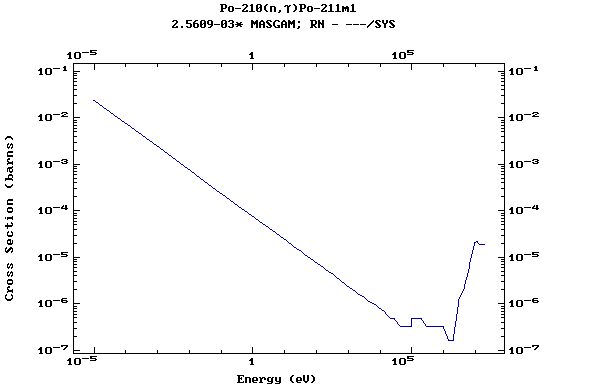
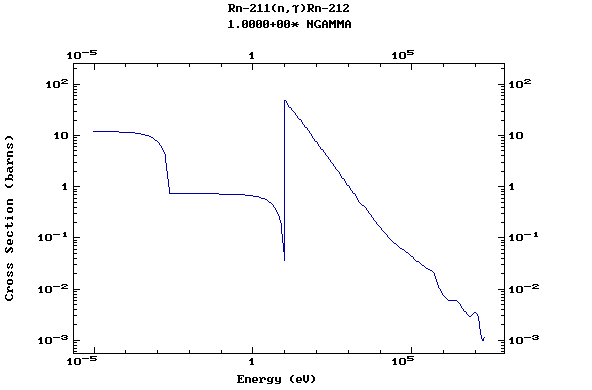
Z=86, Rn
(Radon)
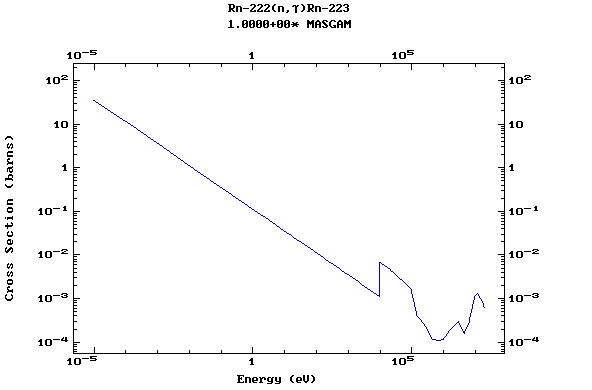
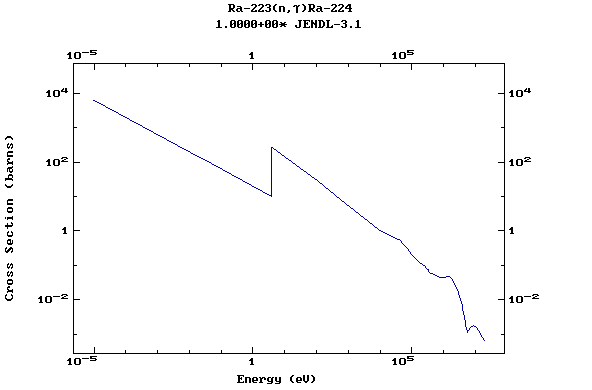
Z=88, Ra
(Radium)
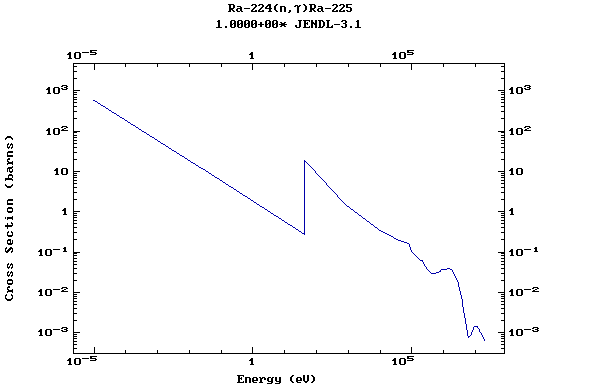
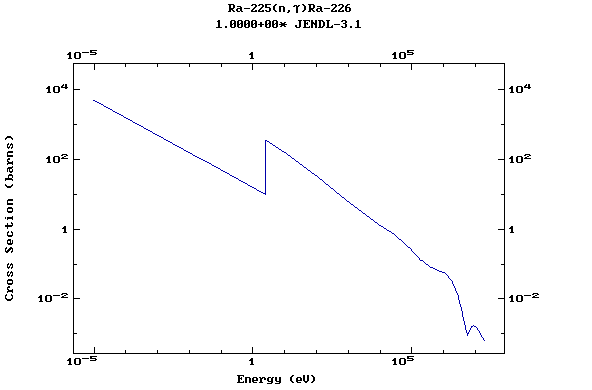
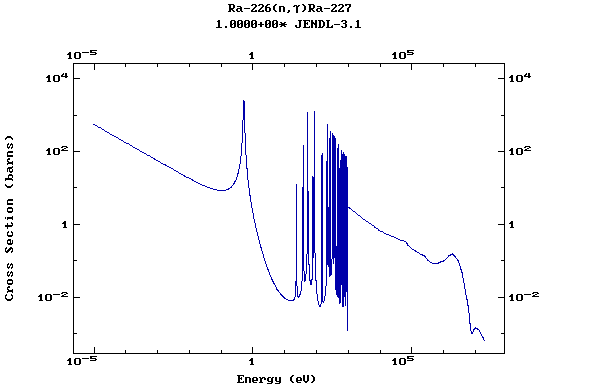
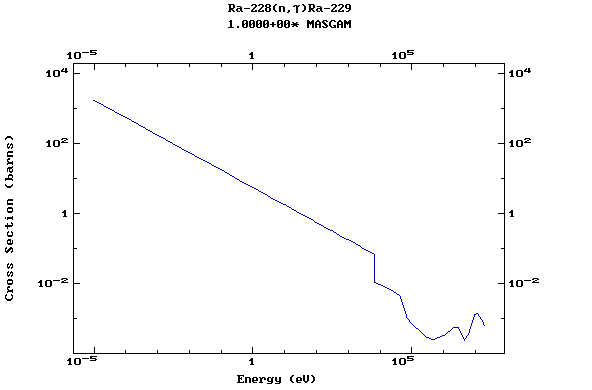
Z=89, Ac
(Actinium)
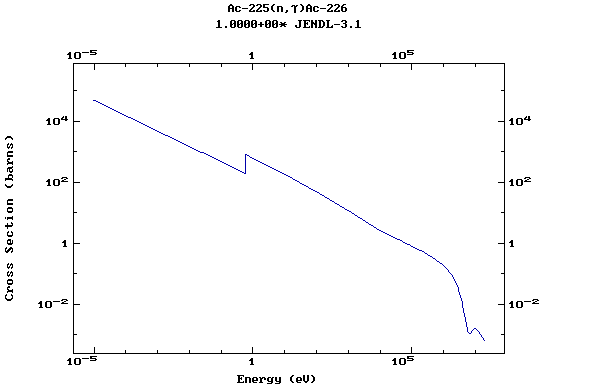
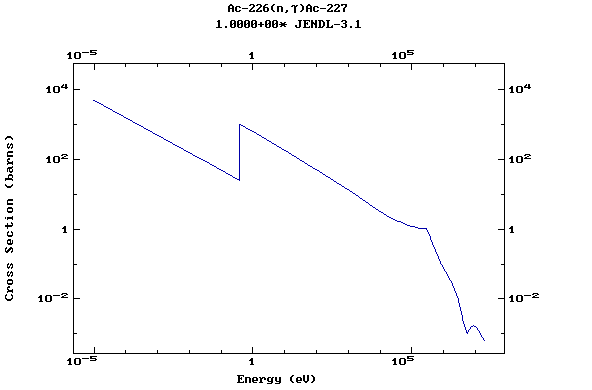
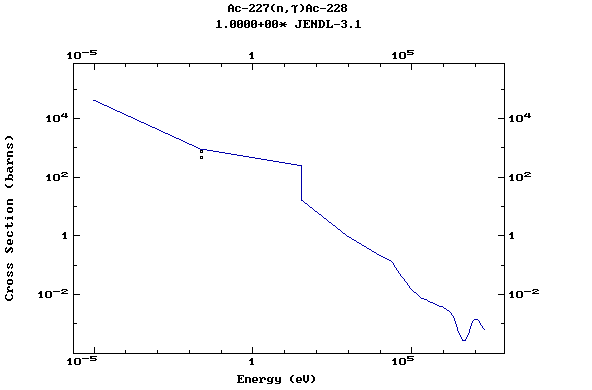
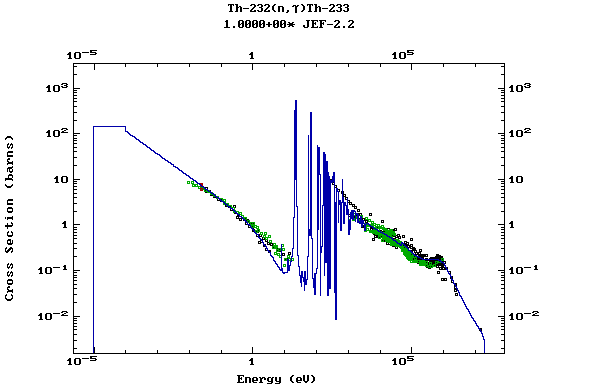
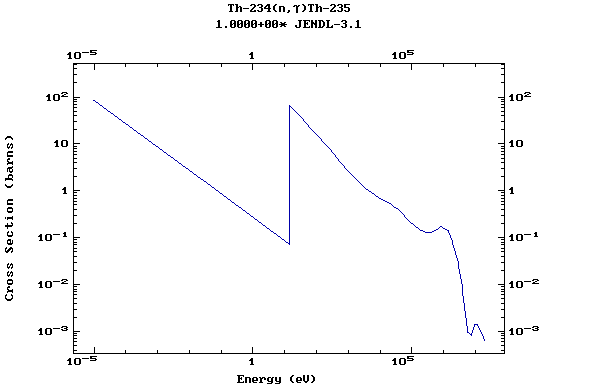
Z=90, Th
(Thorium)
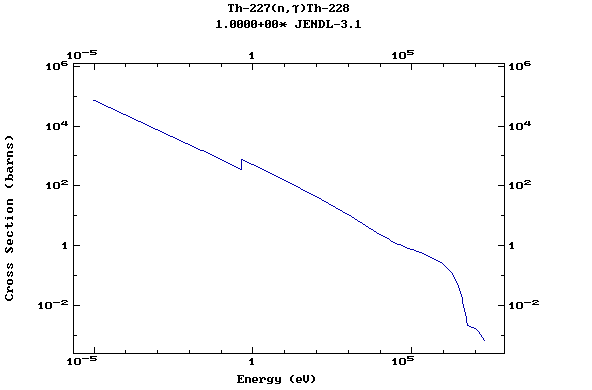
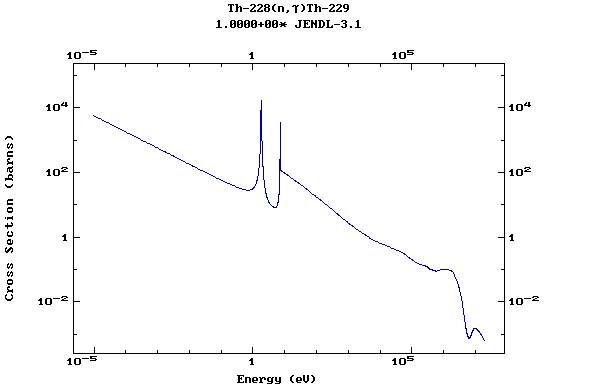
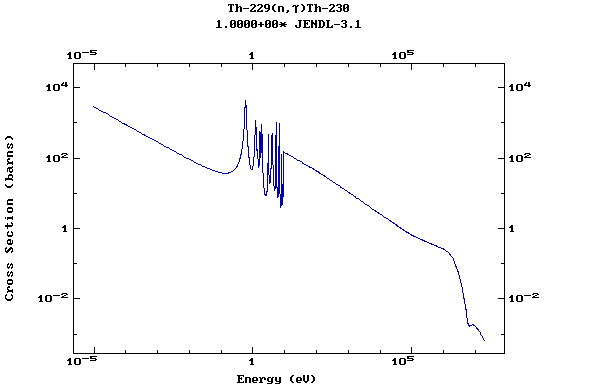
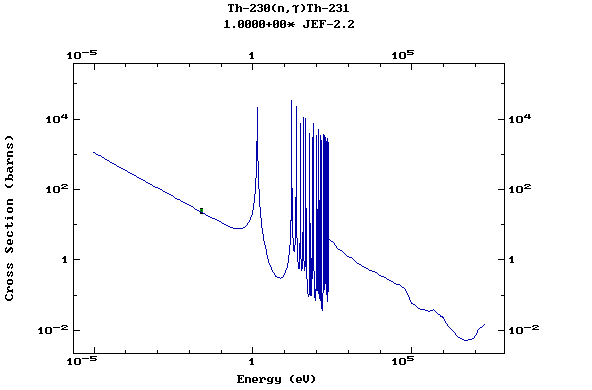
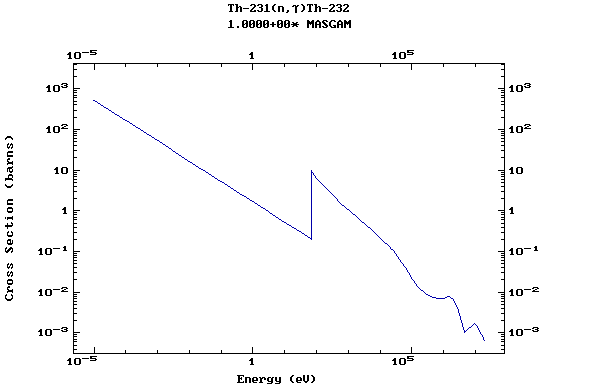
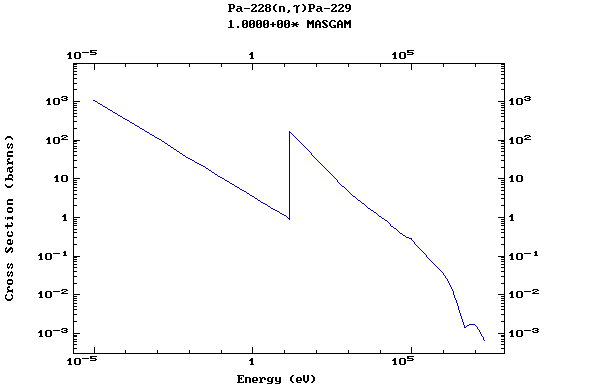
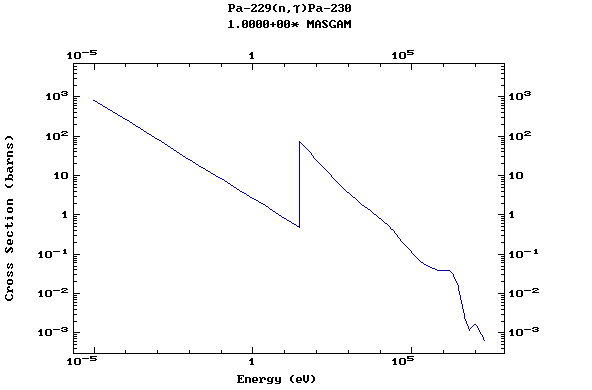
Z=91, Pa
(Protactinium)
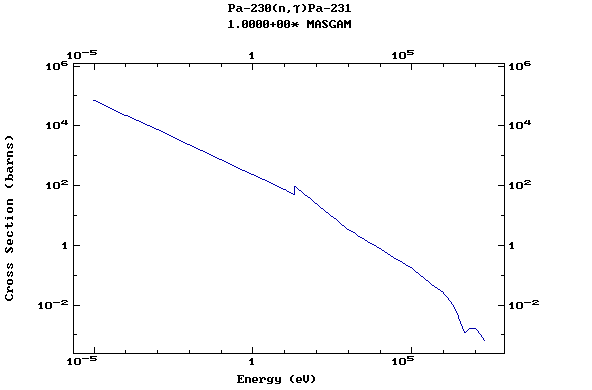
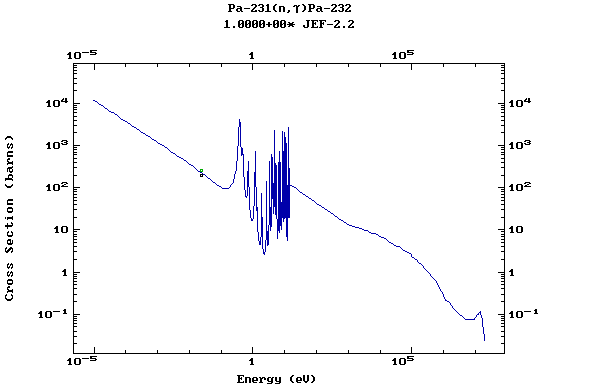
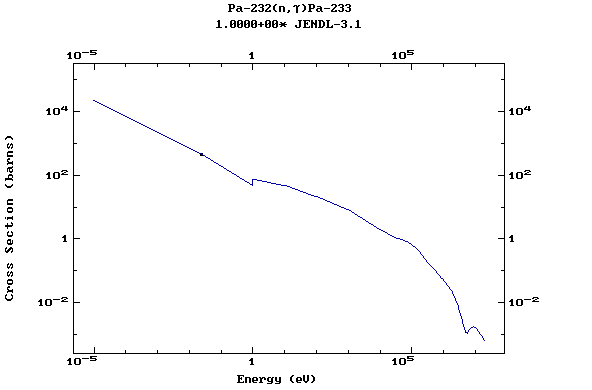
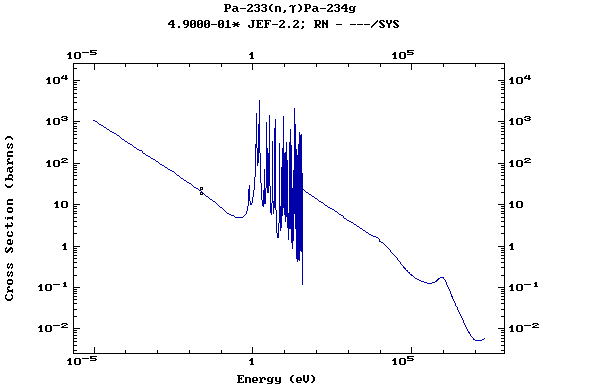
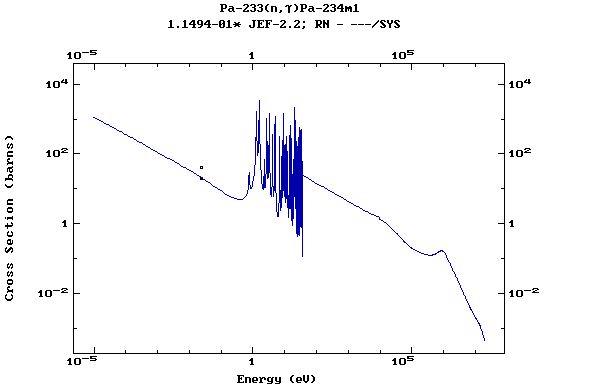
Z=92, U
(Uranium)
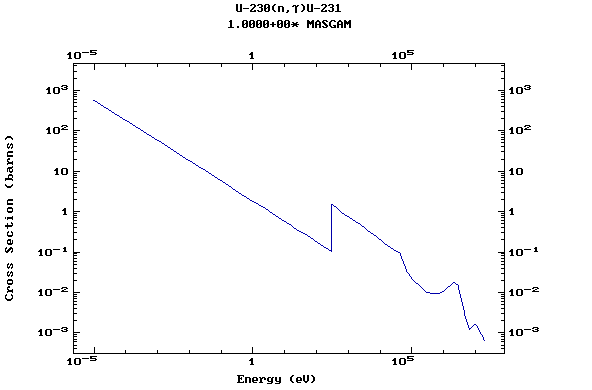
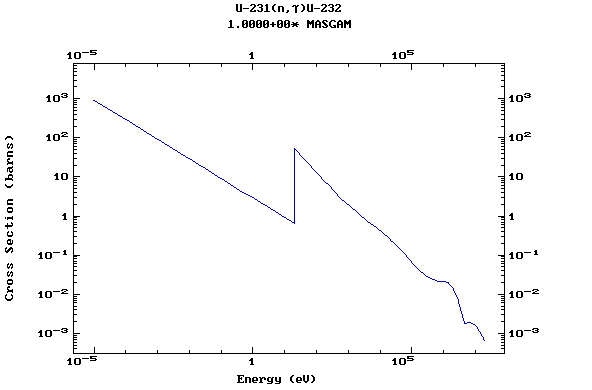
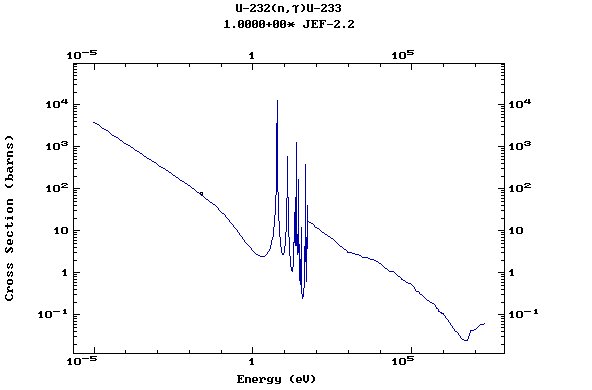
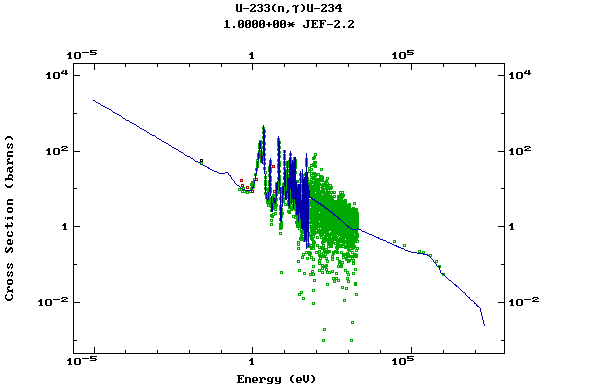
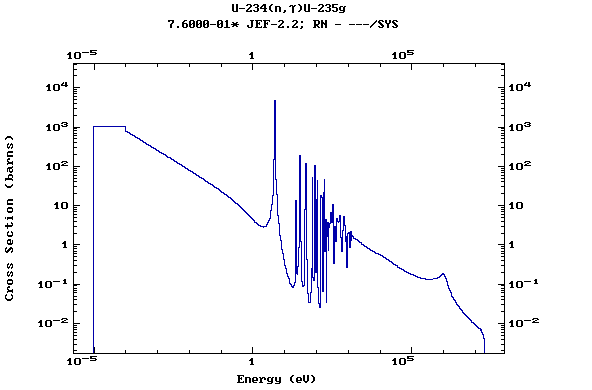
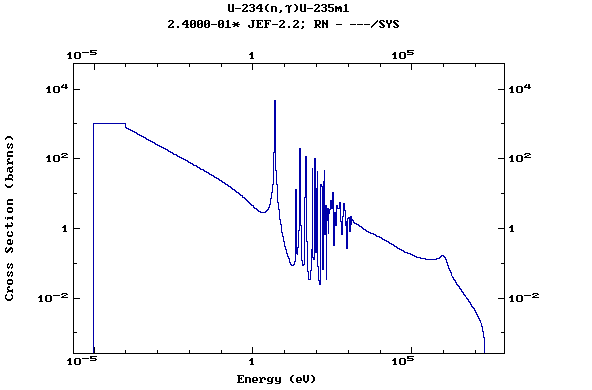
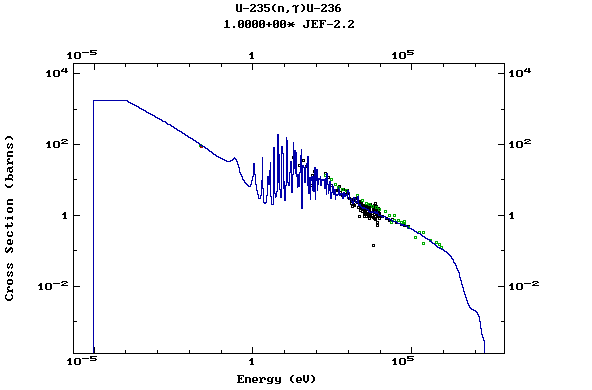
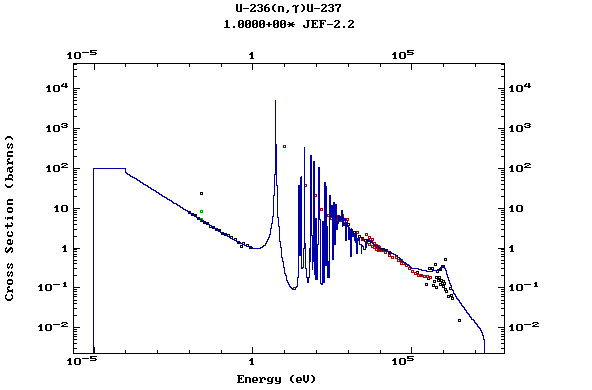
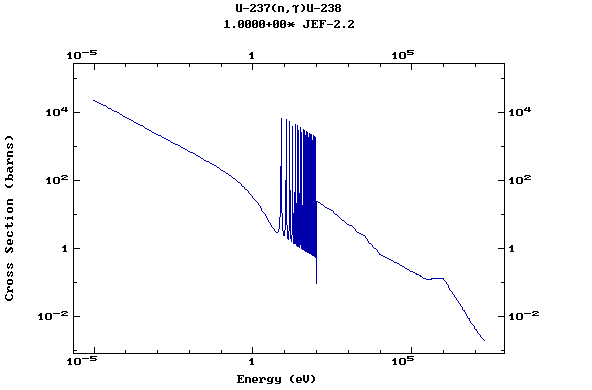
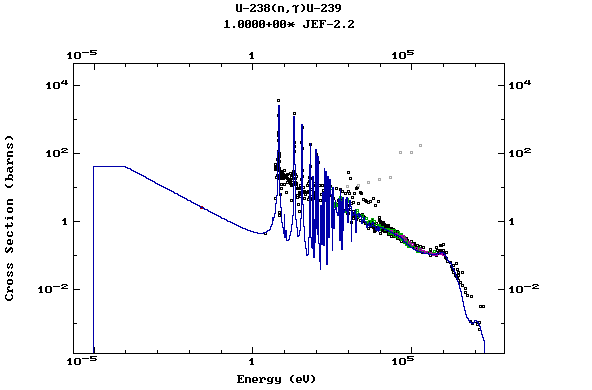
Z=93, Np
(Neptunium)
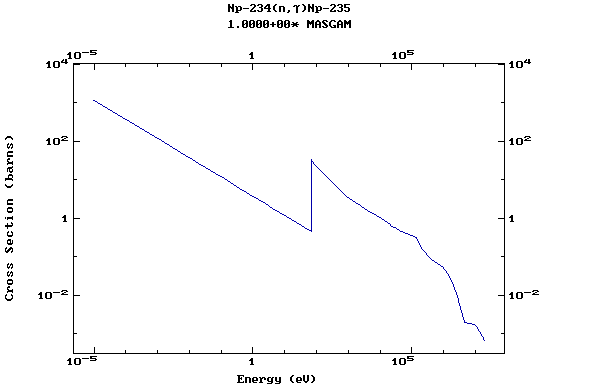
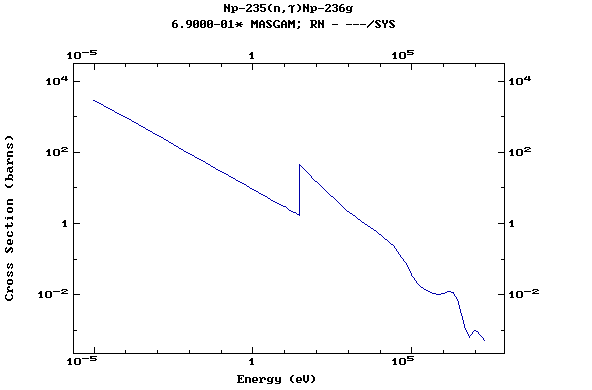
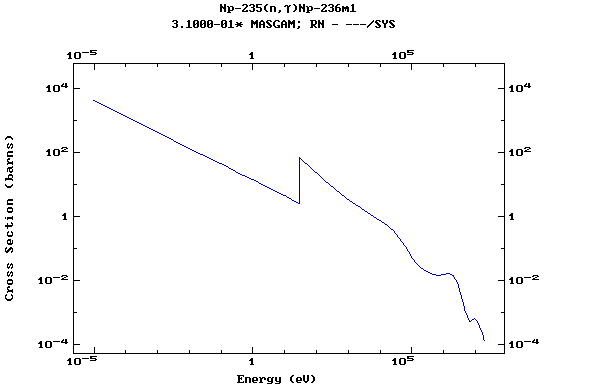
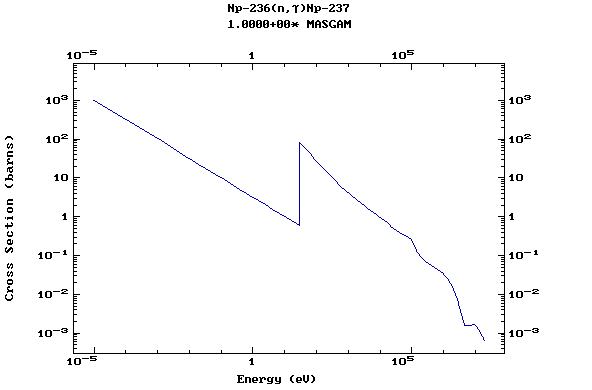
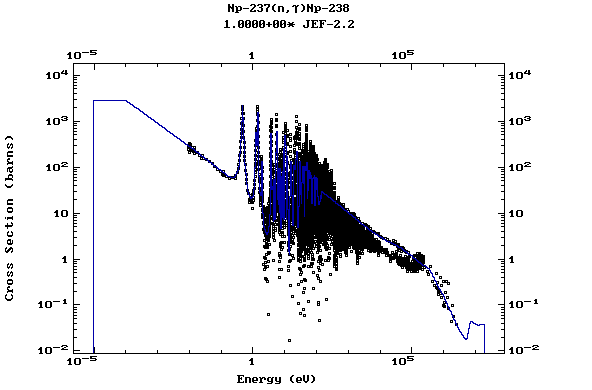
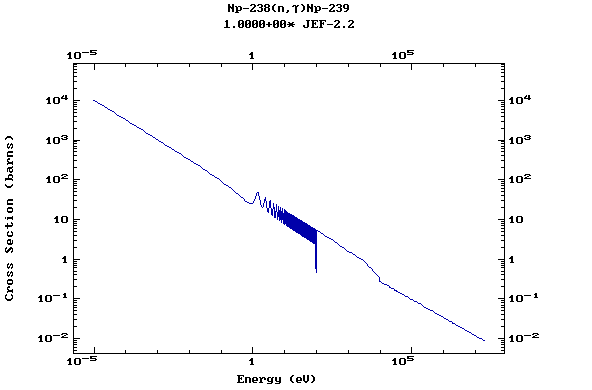
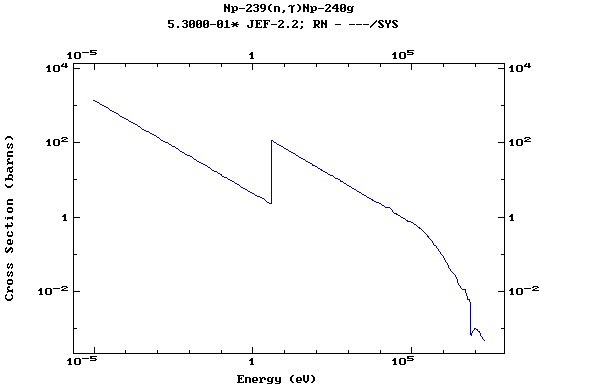
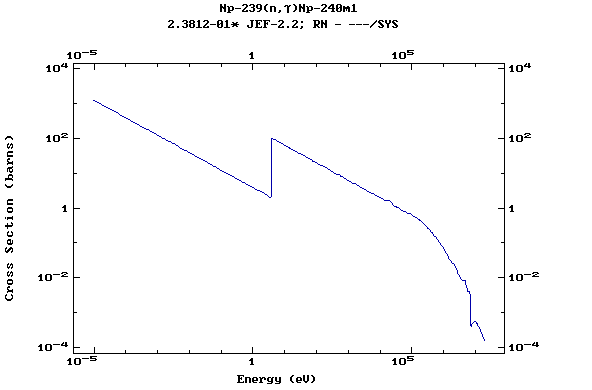
Z=94, Pu
(Plutonium)
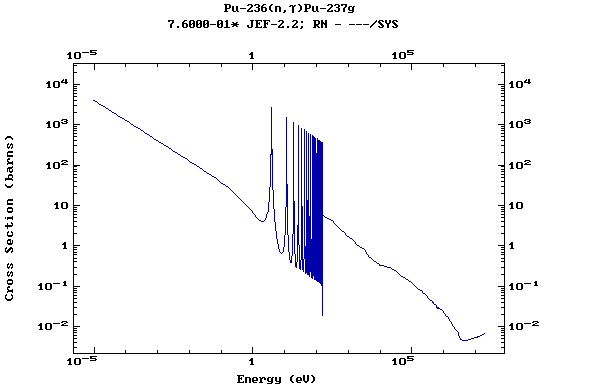
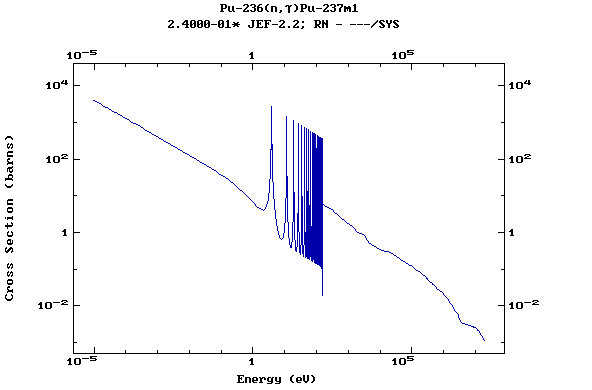
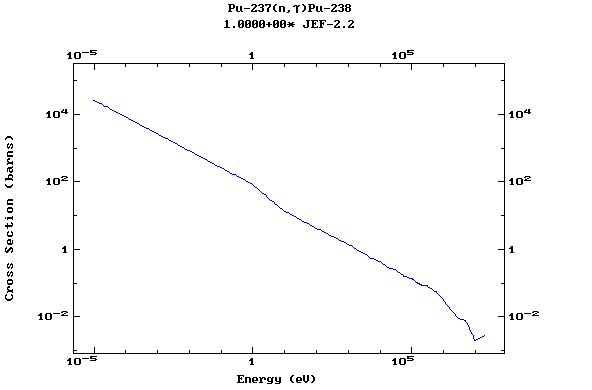
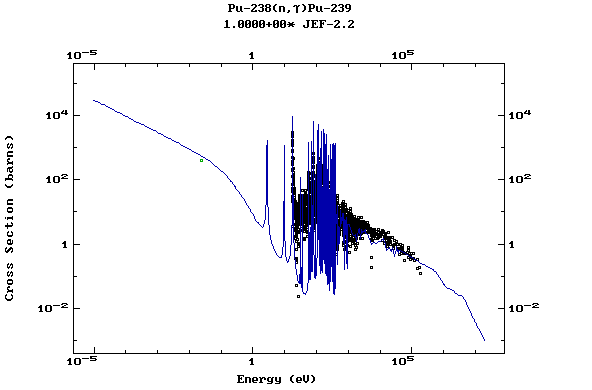
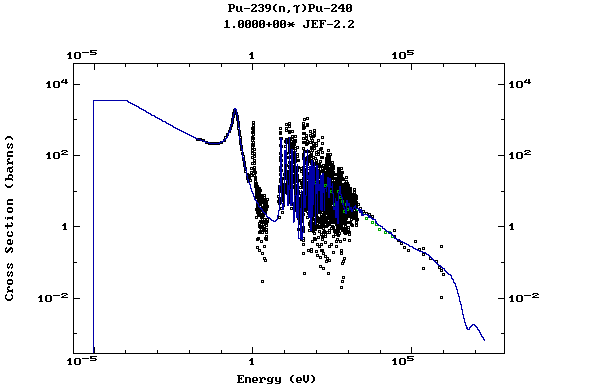
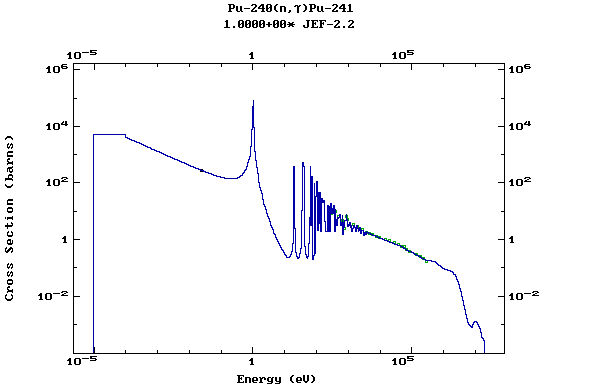
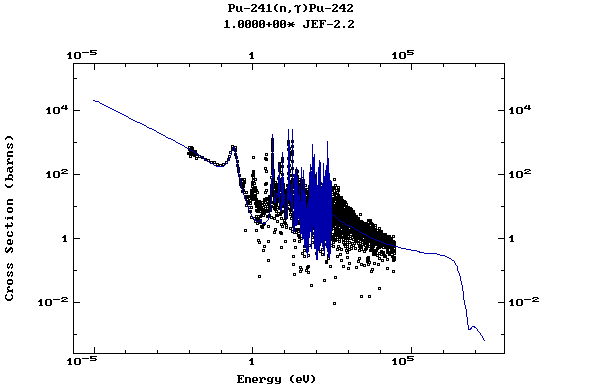
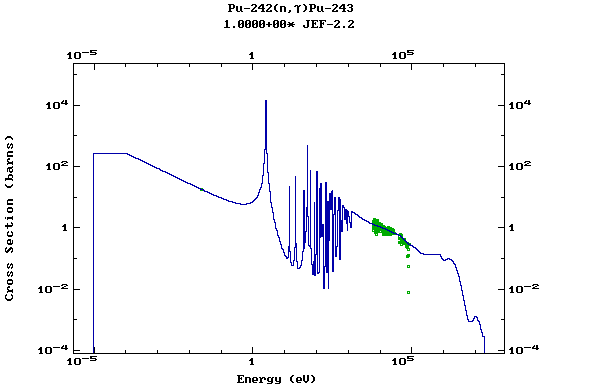
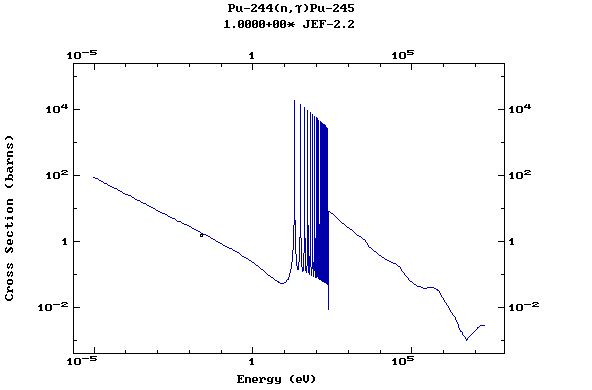
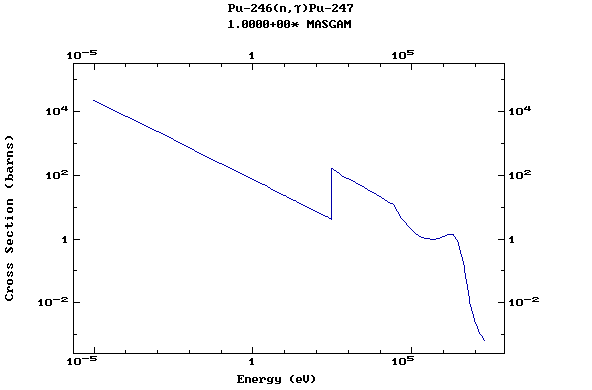
Z=95, Am
(Americium)
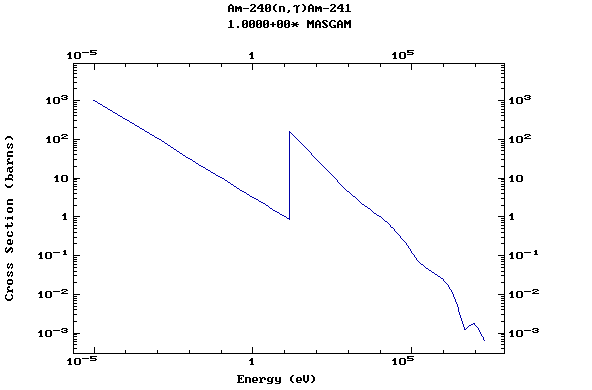
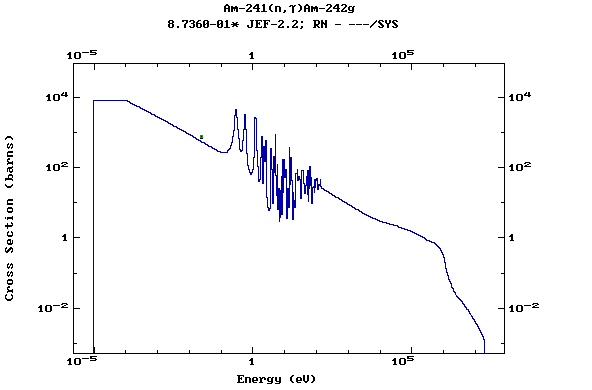
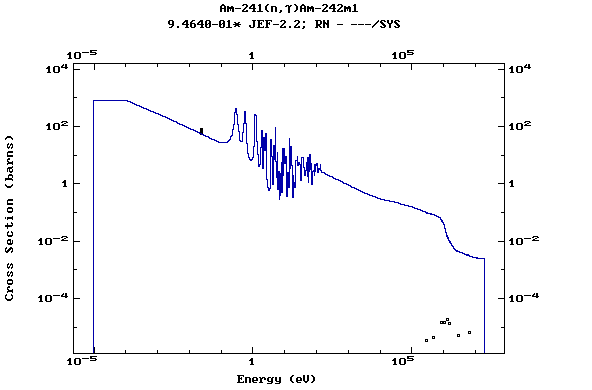
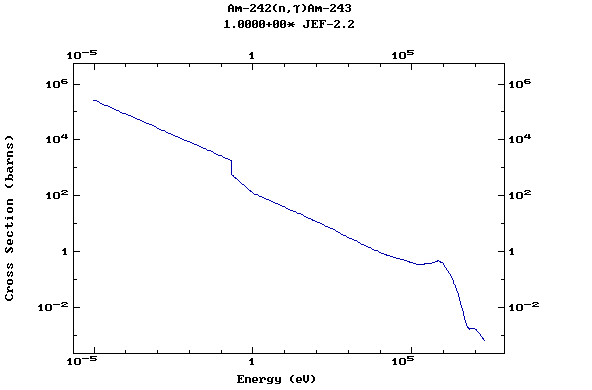
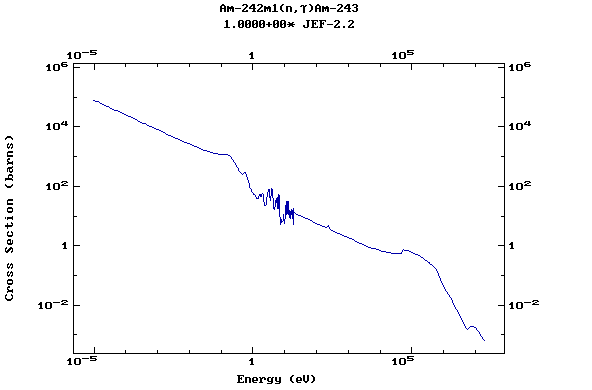
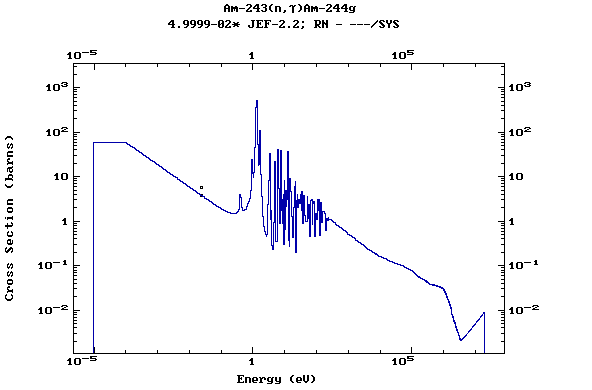
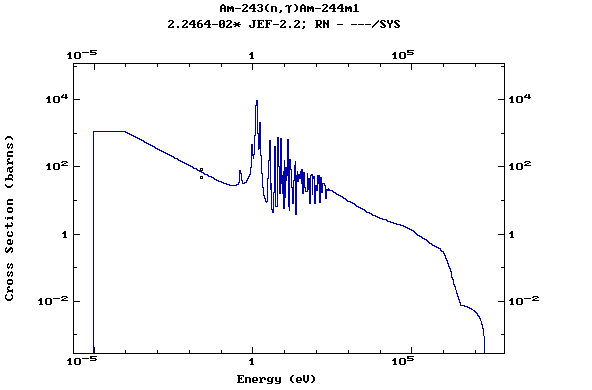
Z=96, Cm
(Curium)
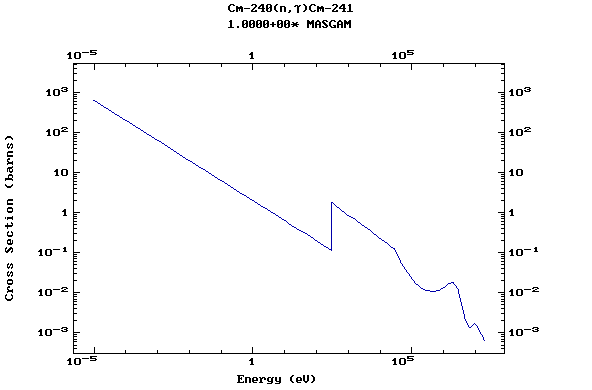
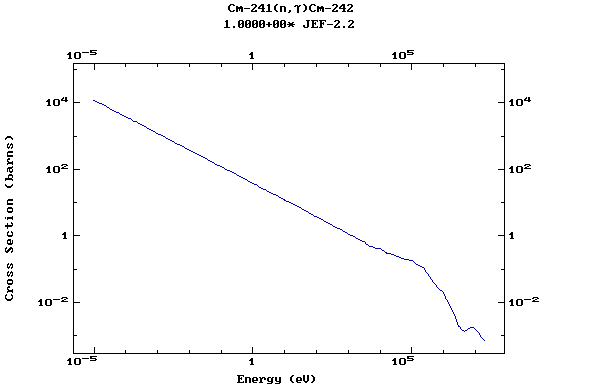
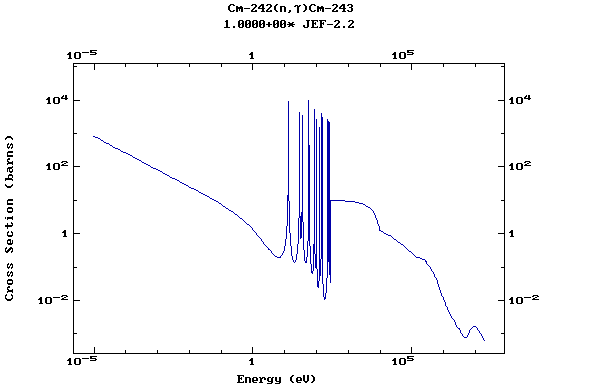
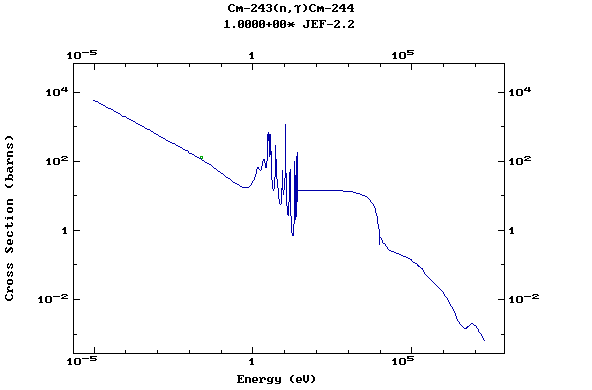
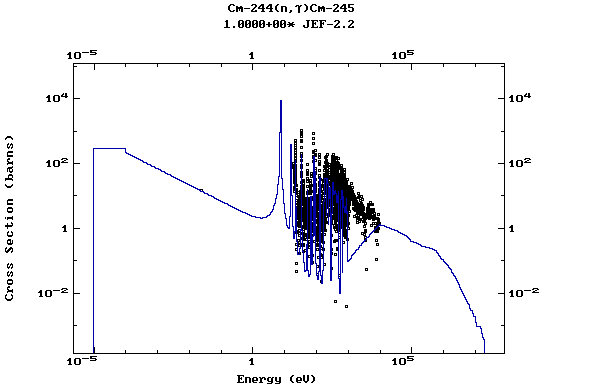
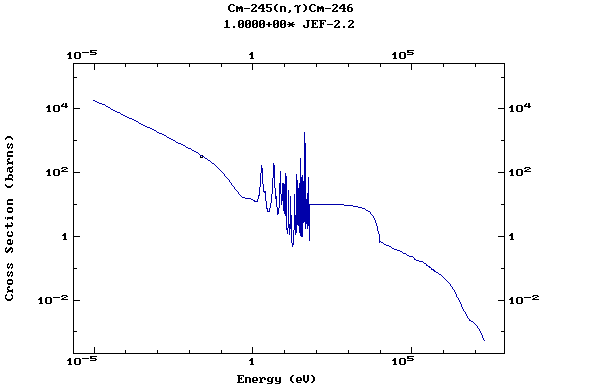
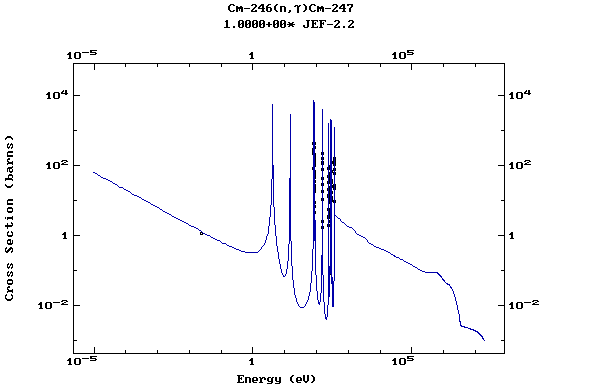
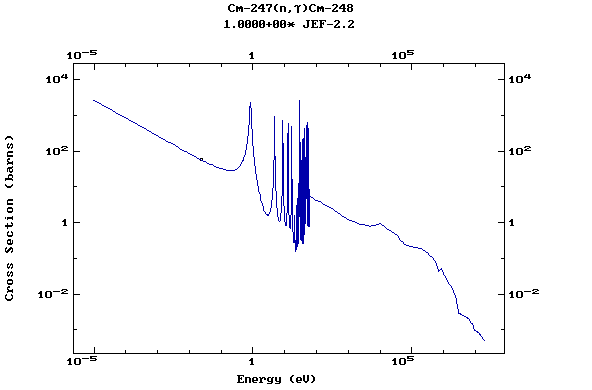
Web design: V.Zerkin, IAEA, September-2001
Last updated: 05/22/2012 09:29:56












































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































